Caution: Failure to adhere to the following precautions before tire balancing
can result in personal injury or damage to components:
• Clean away any dirt or deposits from the inside of the wheels. • Remove any stones from the tread. • Wear eye protection. • Use coated weights on aluminum wheels.
Important: On-vehicle balancing is not recommended on the Catera due to the silicone injected front control arm bushings. Only off-vehicle balancing is recommended.
Tire and wheel balancers can drift out of calibration without warning, or can become inaccurate as a result of abuse. The balancer calibration should be inspected according to the manufacturer's requirements.
Tire Balancer Calibration Test
- Spin the balancer without a wheel or any of the adapters on the shaft.
- Inspect the balancer readings.
- Balance a tire and wheel assembly that is within radial and lateral tolerances to ZERO.
- Add an 85 g (3 oz) test weight to the wheel at any location.
- Spin the tire and wheel assembly again. Observe the readings.
- With the assembly unbalanced to 85 g (3 oz), cycle the balancer 5 times.
- Take the balancer readings:
- Index the tire and wheel assembly at 4 separate locations on the balancer shaft, 90 degrees apart.
- Cycle the balancer with the assembly at each location.
- Take the balancer readings:

Important: Calibrate the tire balancer according to the manufacturer's recommendations, or use the following procedure.
Specification
0-7 g (0.00-0.25 oz)
| • | In the static and dynamic modes, the balancer should call for 85 g (3 oz) of weight, 180 degrees opposite the test weight. |
| • | In the dynamic mode only, the weight should be called for on the flange of the wheel opposite the last weight. |
Specification
Variation: 7 g (0.25 oz) or less
Specification
Variation: 7 g (0.25 oz) or less
Tire Balancing Guidelines
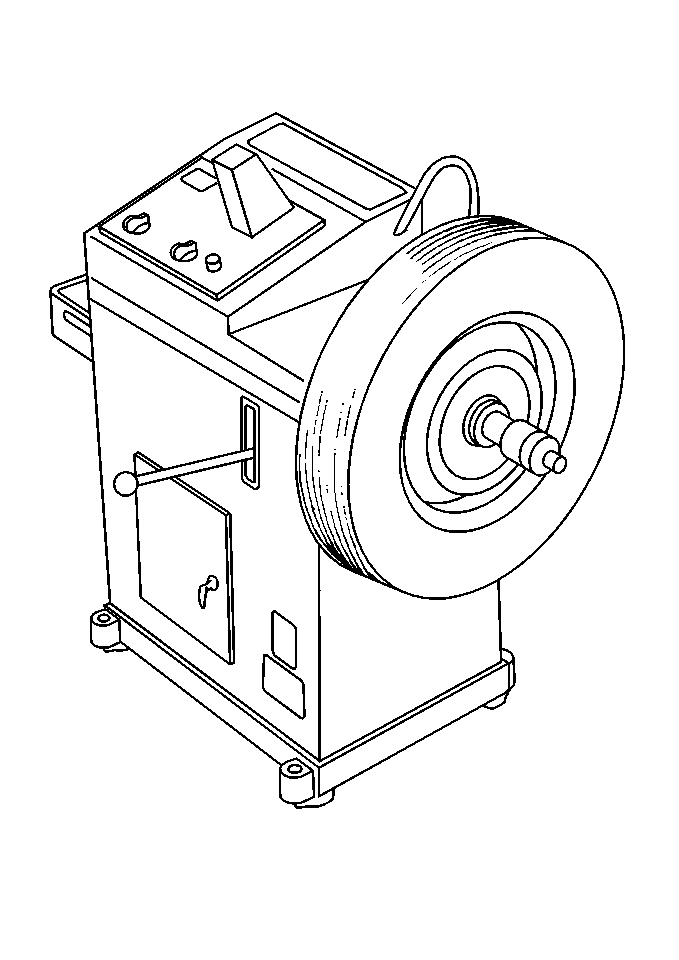
Static and dynamic balance are the two kinds of tire/wheel balance:
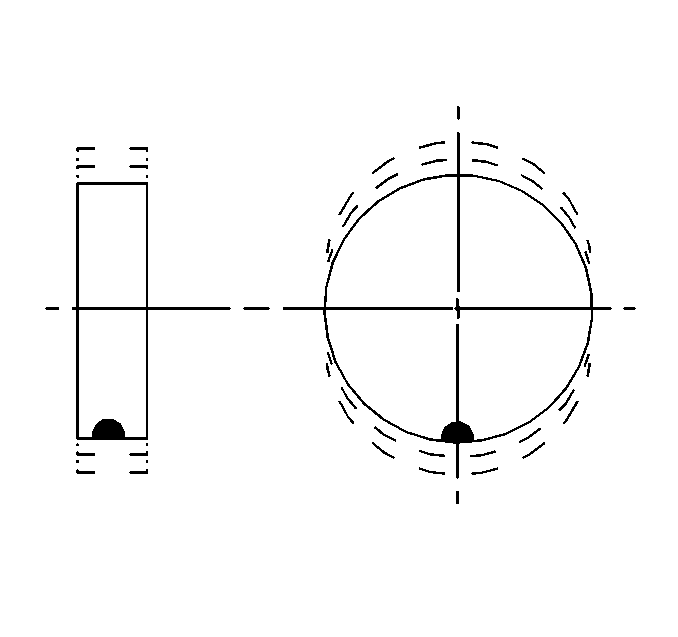
| • | Static balance, also called single plane balance, affects the distribution of weights around the wheel circumference. |
| • | Dynamic balance, or two-plane balance, affects the distribution of weight on each side of the tire/wheel centerline. |
Most off-vehicle balancers can check both types of balance simultaneously.
As a general rule, most vehicles are more sensitive to static imbalance than to dynamic imbalance. As little as 14-21 g (0.50-0.75 oz) may induce a vibration in some vehicles. Vibration induced by static imbalance will cause a vertical, or bouncing, motion of the tire.
Dynamic imbalance results in a side-to-side motion of the tire, or shimmy.
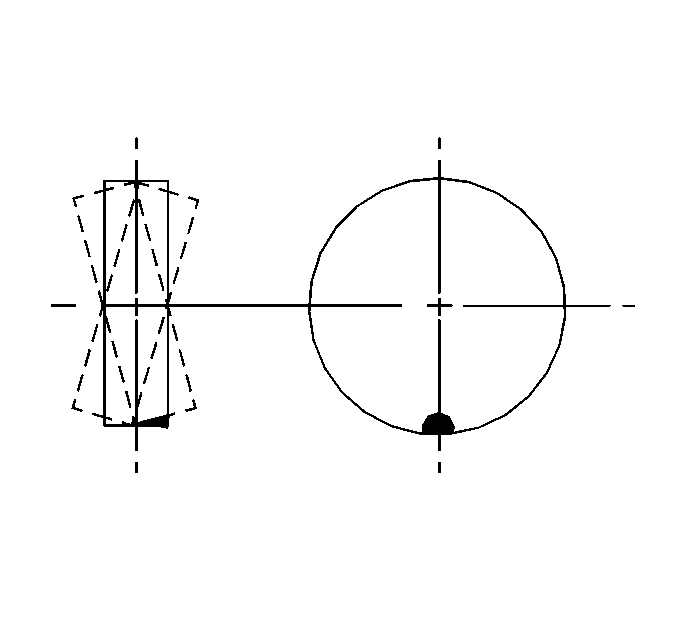
| • | Balance all 4 tires as close to ZERO as possible. |
| • | Carefully follow the wheel balancer manufacturer's instructions for proper mounting techniques for different types of wheels. |
| • | Aftermarket wheels, especially those incorporating universal lug patterns, are potential sources of runout and mounting problems. |
| • | Use the correct coated weights on aluminum wheels. |
| • | Retest the tire and wheel assemblies for excessive runout after correction and installation. |
| • | Evaluate the vehicle at the complaint speed and note if the vibration has been corrected. |
| • | If the vibration is still present, or is reduced but still unacceptable, consider these possibilities: |
| - | On-vehicle imbalance |
| - | Radial or lateral force variation |
Correcting On-Vehicle Imbalance
On-vehicle imbalance may result from components other than the tire and wheel assemblies having imbalance. An on-vehicle high-speed balance or replacement of suspected components may be necessary in order to correct the condition.
Rotors do not have a set tolerance. However, rotors with more than 0.75 ounce imbalance have the potential to cause vibration. The rotors can be inspected for imbalance using either the on-vehicle or the off-vehicle method as described below:
Checking Rotor Imbalance (Off-Vehicle)
- Measure the diameter and the width of the rotor.
- Mount the rotor on a balancer in the same manner as a wheel.
- Inspect for static imbalance and obvious deficiencies.
Important: The rotors can only be inspected for static imbalance. Ignore the dynamic imbalance reading.
