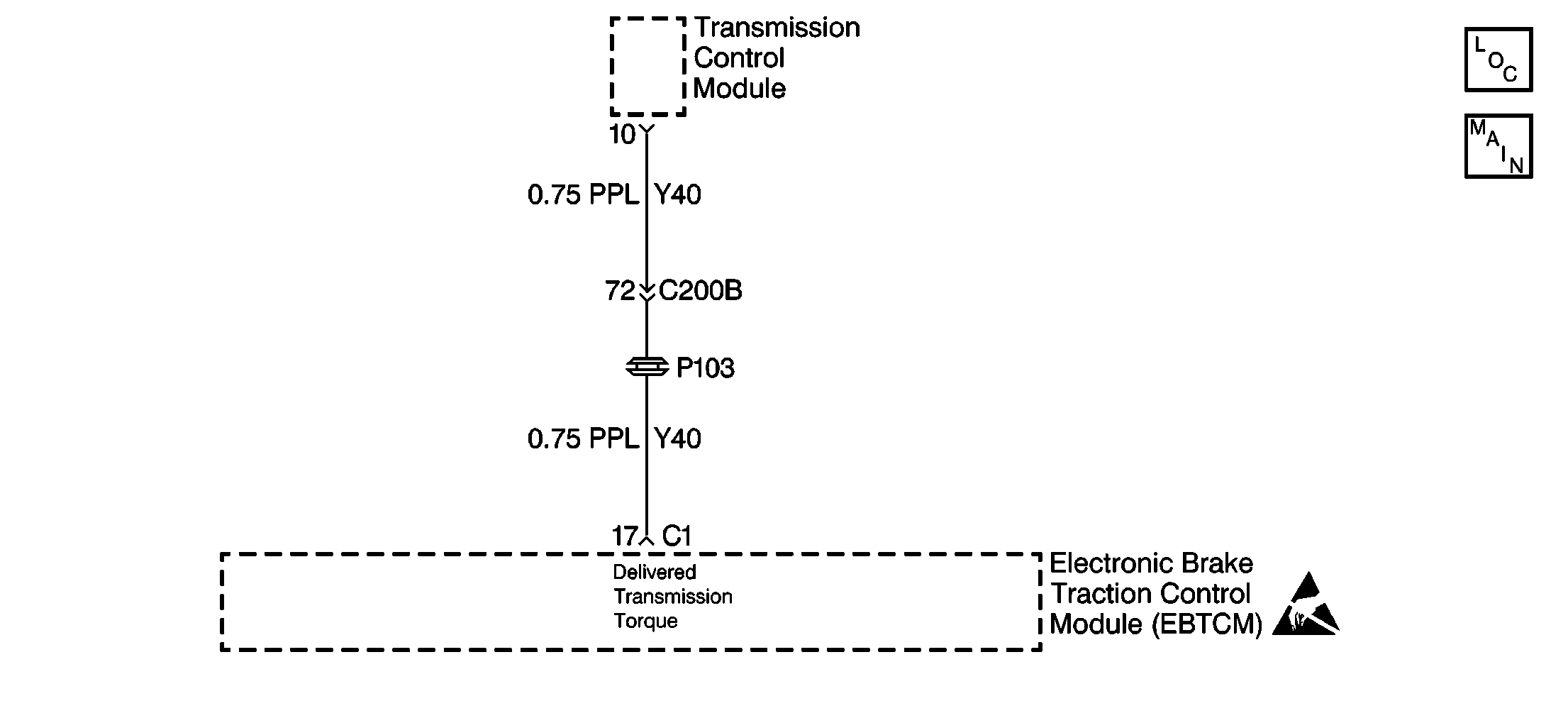
Circuit Description
The traction control system primarily uses the ECM fuel and the ignition controls to limit drive wheel slippage during acceleration. In addition to engine torque reduction, the TCM monitors the requested engine torque circuit from the EBTCM. When the EBTCM sends a torque request to the ECM and the TCM via a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal, this commands the TCM to prevent transmission down shift thus limiting drive wheel slippage during acceleration. The TCM then provides a delivered torque PWM signal informing the EBTCM how much actual torque is produced by the transmission.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The EBTCM does not receive 2 delivered transmission torque signals within 250 milliseconds of each other, 2 seconds after initialization. |
| • | There is an open in the circuit. |
| • | There is a short to ground in the circuit. |
| • | There is a short to voltage in the circuit. |
| • | The EBTCM must detect an engine RPM greater than 480 RPM to set the DTC. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC is stored. |
| • | The TC indicator lamp is turned on. |
| • | The TCS is disabled. |
| • | The ABS remains functional. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition for the DTC is no longer present. |
| • | The scan tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles have passed with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following can cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection can cause an intermittent malfunction. |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation can cause an intermittent malfunction. |
| • | A wire that is broken inside the insulation can cause an intermittent malfunction. |
Check for the following in any circuit suspected of causing an intermittent malfunction:
| • | Check for backed out terminals. |
| • | Check for improper mating. |
| • | Check for broken locks. |
| • | Check for improperly formed terminals. |
| • | Check for damaged terminals. |
| • | Check for poor terminal to wiring connections. |
| • | Check for physical damage to the wiring harness. |
Perform a thorough inspection of the wiring. Perform a thorough inspection of the connectors. Failure to carefully and fully inspect the wiring and the connectors may result in misdiagnosis. Misdiagnosis causes part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
It is very important to check ground G103. Corrosion or a loose connection at this point may cause a malfunction in the PWM signal.
-
The scan tool can be used to check the delivered transmission torque signal from the Transmission Control Module. It should remain generally steady with the gear selector in drive.
-
This test checks the presents of a pull-up voltage from the EBTCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Check that ground G103 is clean and check that ground G103 is torqued to the proper specifications. Refer to Ground Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for ground specifications and ground locations. Are the following signs evident:
| -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the percent of delivered torque within the specified range? | 20-30% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the voltage measured equal to or greater than the specified voltage? | 10 V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Is the voltage measured within the specified range? | 0-2 V | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Are the following signs evident:
| -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 | Use a J 39200 DMM to measure the resistance between the J 39700 terminal 17 and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Are the following signs evident:
| -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Did DTC 71 reset? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 |
Did DTC 71 reset? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
12 | Repair the short to voltage in the delivered transmission torque circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13 | Repair an open or repair a high resistance in the delivered transmission torque circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
14 | Repair a short to ground in the delivered transmission torque circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 | Replace all the terminals or replace the connectors that exhibit signs of the following:
Refer to Connector Repairs or Repairing Connector Terminals in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 | Suspect TCM. Refer to On-Board Diagnostic System Check in Automatic Transaxle - 4L30-E. Is the diagnosis complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17 | The malfunction is intermittent or the malfunction is not present at this time. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for more information. Is the diagnosis complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
18 | Repair the ground as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems if the ground terminal requires replacement. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
19 | Replace the EBTCM. Refer to EBTCM Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to A Diagnostic System Check | -- |
