We recommend that you regularly inspect your vehicle's tires, including the spare tire, for signs of wear or damage. See When It Is Time for New Tires for more information.
Tires should be rotated every 5,000 to 8,000 miles (8 000 to 13 000 km). See Scheduled Maintenance .
The purpose of a regular tire rotation is to achieve a uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. This will ensure that your vehicle continues to perform most like it did when the tires were new.
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires as soon as possible and check wheel alignment. Also check for damaged tires or wheels. See When It Is Time for New Tires and Wheel Replacement for more information.
Four-Tire Rotation Pattern
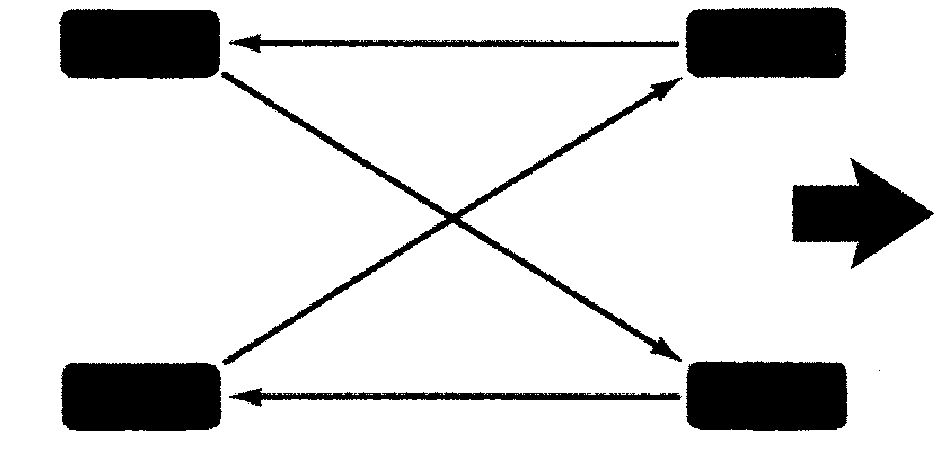
If your vehicle has a compact spare tire, it should not be included in the tire rotation process. Use the four-tire rotation pattern shown .
Five-Tire Rotation Pattern
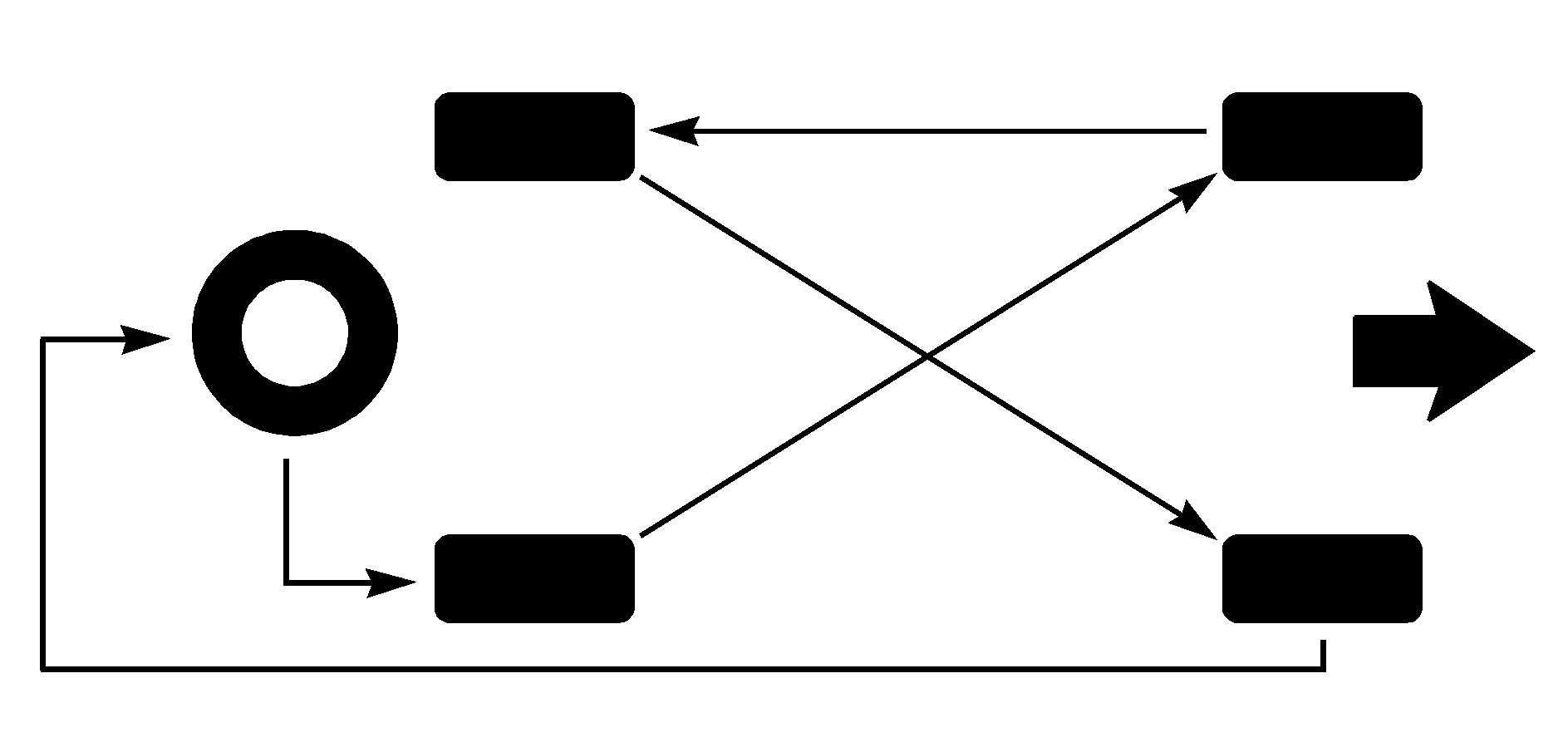
A five-tire rotation pattern may be used for your professional vehicle, if it has a full-size spare tire and wheel assembly that matches the original equipment tires and wheels in size, type and brand. The correct five-tire rotation pattern is shown.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and rear inflation pressures as shown on the Tire and Loading Information label. See Loading the Vehicle .
Vehicles that have the Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPMS) will need to have the sensors reset after a tire rotation is performed. See Tire Pressure Monitor System .
Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly tightened. See "Wheel Nut Torque" under Capacities and Specifications .
Caution: Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose after time. The wheel could come off and cause an accident. When you change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle. In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a scraper or wire brush later, if needed, to get all the rust or dirt off. See Changing a Flat Tire .
