Tools Required
| • | J 38758 |
| • | J 39200 |
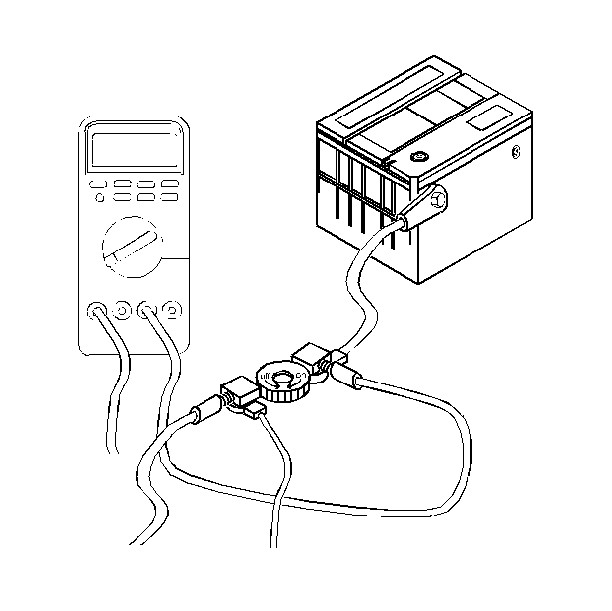
- Remove the battery cable from the battery negative terminal.
- Install the parasitic load test switch male end to the negative battery terminal.
- Turn the test switch knob to the off position.
- Install the negative battery cable to the female end of the test switch tool.
- Turn the test switch knob on the "ON" position.
- Open the trunk in order to access the trunk compartment fuse block.
- Turn the ignition switch to the "Lock" position and remove the ignition key.
- Connect the J 39200 terminals on the test switch tool.
- Turn the test switch tool knob to the "OFF" position to allow current to flow through the ammeter.
- After approx. 20 minutes check the current reading. If the current draw is above 30 millilamps the load can either be that a module on the Class 2 serial data line is not going to "sleep" or that the load is related to a traditional excessive current draw i.e. lumbar seat switch stuck on.
Notice: The parasitic load test switch should never be turned to the "OFF" position with the engine running; damage could occur to the attached ammeter or the vehicle electrical system.
Tighten
Tighten the J 38758
to 15 N·m
(11 lb ft).
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Tighten
Tighten the negative battery cable to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Diagnosing Class 2 Serial Data Line
- Pull the COMFORT, IGN0 BODY, and BATT fuse(s). If the draw goes away the most likely cause is that a module on the Class 2 serial data line is keeping the Body Control Module (PZM) "awake." Do not replace the PZM until the whole test has been completed. If the current draw does not go away, refer to the traditional excessive current draw in this procedure.
- Reinstall the COMFORT fuse. This will "wake up" the class 2 serial data line.
- Wait approx. 20 minutes.
- When the PZM goes back to sleep, monitor the current draw using J 39200 . If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the COMFORT fuse or a component that is powered by the Controlled Power Relay. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- Disconnect the RFA Module.
- Monitor the current draw using J 39200 , if the excessive current draw is removed, then the parasitic drain can be isolated to the RFA Module and its related circuits.
- Disconnect the CD Changer, if equipped.
- Monitor the current draw using J 39200 , if the excessive current draw is removed, then the parasitic drain can be isolated to the CD Changer and its related circuits.
- Disconnect the ACM.
- Wait approx. 20 minutes.
- When the PZM goes back to sleep, monitor the current draw using J 39200 . If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to the ACM and its related circuits.
- Do not replace the PZM until all of the components powered by the Controlled Power Relay have been diagnosed.
- Reinstall the IGN0 BODY fuse (equipped with a Climate Control Panel CCP).
- Monitor the current draw using J 39200 . If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the IGN0 BODY fuse. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- Reinstall the BATT fuse.
- Monitor the current draw using J 39200 . If the current draw is excessive, the cause of the parasitic drain can be isolated to a component that receives power from the BATT fuse. If no change is noted in the current draw, proceed to the next step.
- When cause of excessive current draw has been located and repaired, remove the current drain test tool and connect the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal.
Tighten
Tighten the negative battery cable to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Traditional Excessive Current Draw
- When current draw is above 30 millilamps, remove the system fuses one fuse at a time until the current draw returns to a value less than or equal to 30 millilamps.
- Repeat the parasitic current drain procedure after any repair has been completed.
- When the cause of excessive current draw has been located and repaired, remove current drain test tool and connect the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal.
Tighten
Tighten the negative battery cable to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
