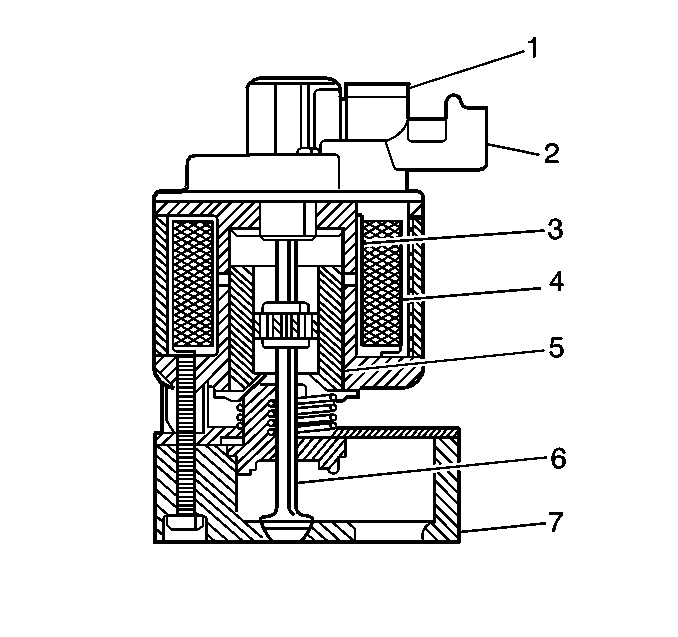
The EGR valve is designed to supply EGR to the engine. The EGR valve consists
of a sealed bobbin and coil assembly, or solenoid. Inside the solenoid is
a sleeve-armature assembly that contains a pintle and valve, two seals,
retaining washers, a seal spring, and armature spring, and a bearing. The
bearing seals the pintle valve shaft from the exhaust chamber. Also, a shield,
held in place by a compression spring, deflects exhaust gas from the shaft
and armature.