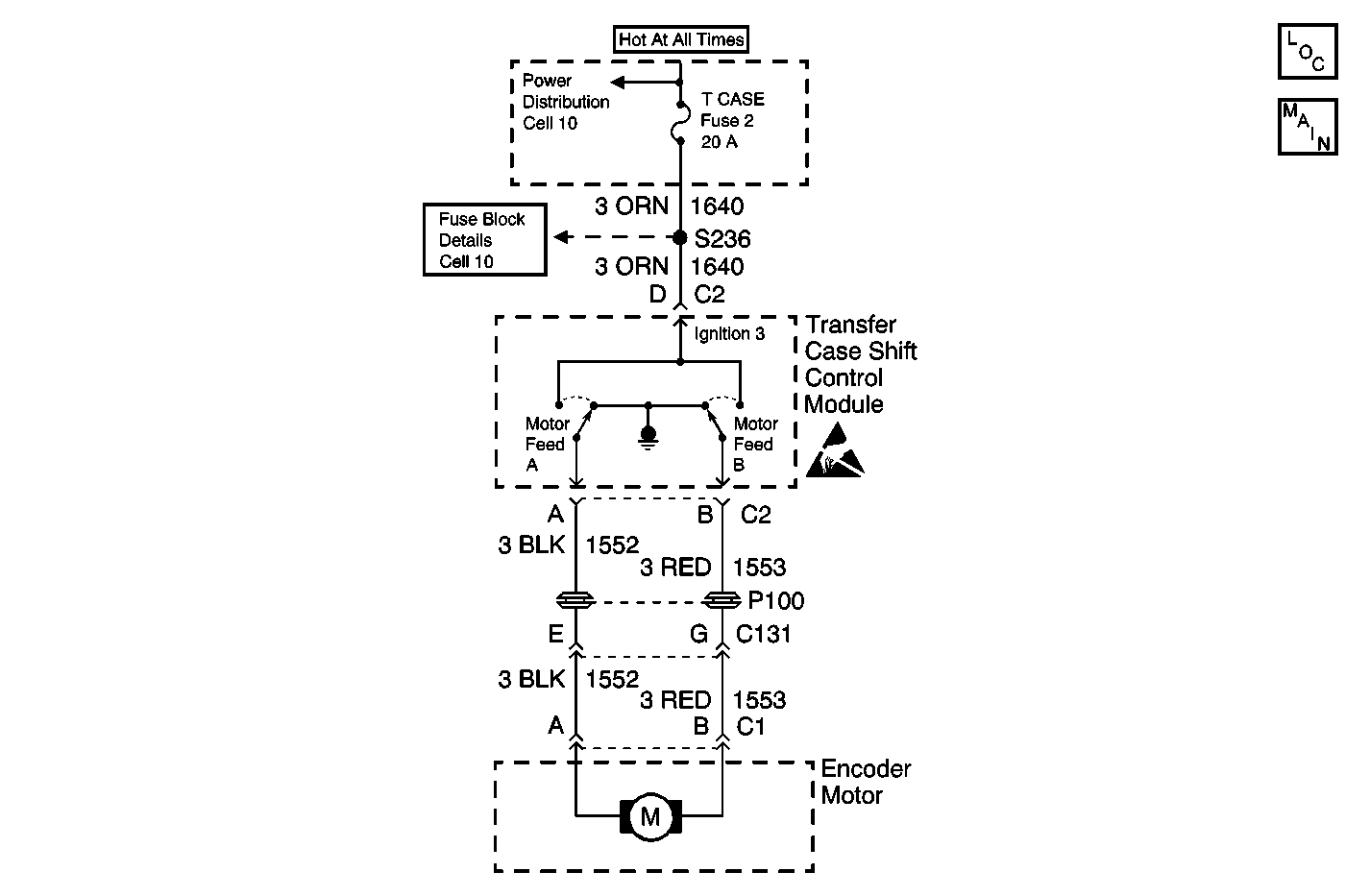
Circuit Description
The transfer case motor is a bi-directional, permanent magnet, D.C. motor. When energized, (through Motor Feed A or Motor Feed B, the ground is provided by the opposing Motor Feed circuit and then grounded through the transfer case shift control module ground circuit), the motor, through a series of gears, rotates the sector shaft which moves the mode and range forks to shift the transfer case between 4H, AUTO 4WD, 2H, N, and 4L ranges. While the transfer case motor is energized the transfer case shift control module also energizes the solenoid for the transfer case lock. The motor lock is disabled (locking action released) and free turning of the transfer case motor and sector shaft is then allowed.
This DTC detects a short to ground in Motor Feed A or Motor Feed B CKT.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The system will test the motor circuits: |
| • | First, the system checks for unwanted voltage. |
| • | Then, the system supplies voltage on one circuit and reads the voltage back on the other. |
| • | If the system detects a problem with the circuits, the DTC is logged. |
| • | The transfer case shift control module senses a low voltage return in Motor Feed A or Motor Feed B when a high voltage is expected. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | All shifting will be disabled. |
| • | The SERVICE indicator (4WD/AWD) lamp will be latched on for the remainder of the current ignition cycle. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The transfer case shift control module will clear the DTC if the condition for setting the DTC no longer exists. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 100 consecutive ignition cycles without a fault present. |
| • | History DTCs can be cleared using a scan tool. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
Listen for an audible motor noise when the encoder motor operates. Command both the ON and OFF states. Repeat the commands as necessary.
-
Tests for a short to ground in the Motor Feed A circuit.
-
Tests for a short to ground in the Motor Feed B circuit.
-
Tests for a higher than normal resistance in the Motor Feed A and B circuits through the module.
-
Tests for a short to ground in the encoder motor windings.
-
Tests for continuity across the motor circuit. Resistance readings vary depending on the location of the brush contact inside the motor assembly.
-
Tests Motor Feed A circuit for a short to ground.
-
Tests Motor Feed B circuit for a short to ground.
-
Tests Motor Feed A and B circuits for an open or high resistance.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Transfer Case Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
Does the encoder motor turn ON and OFF? | -- | Go to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections | Go to Step 3 | |
Is the resistance reading less than the specified value? | 10 K ohms | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 4 | |
Connect a DMM between the Motor Feed B circuit harness connector and ground at the transfer case. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance reading less than the specified value? | 10 K ohms | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 5 | |
Connect a DMM between the Motor Feed A and B circuit harness connector at the transfer case. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance reading greater than the specified value? | 2 ohms | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 10 | |
|
Important: The transfer case Motor Feed circuits have capacitors connected between their circuit and ground. When making resistance checks with a DMM, allow the reading to stabilize (approximately 10 seconds) before making the final measurement (as the capacitor charges it can give the indication of a short circuit). Test terminals A and B at the transfer case side of the harness for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 7 | |
Test the resistance across the motor circuit. Were the resistance readings within the specified range? | 0.5-35 ohms | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 11 | |
Was the condition found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | |
Was the condition found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | |
Was the condition found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 12 | |
11 | Replace the encoder motor. Refer to Motor/Encoder Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
12 | Replace the transfer case shift control module. Refer to Transfer Case Shift Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 13 | -- |
13 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
