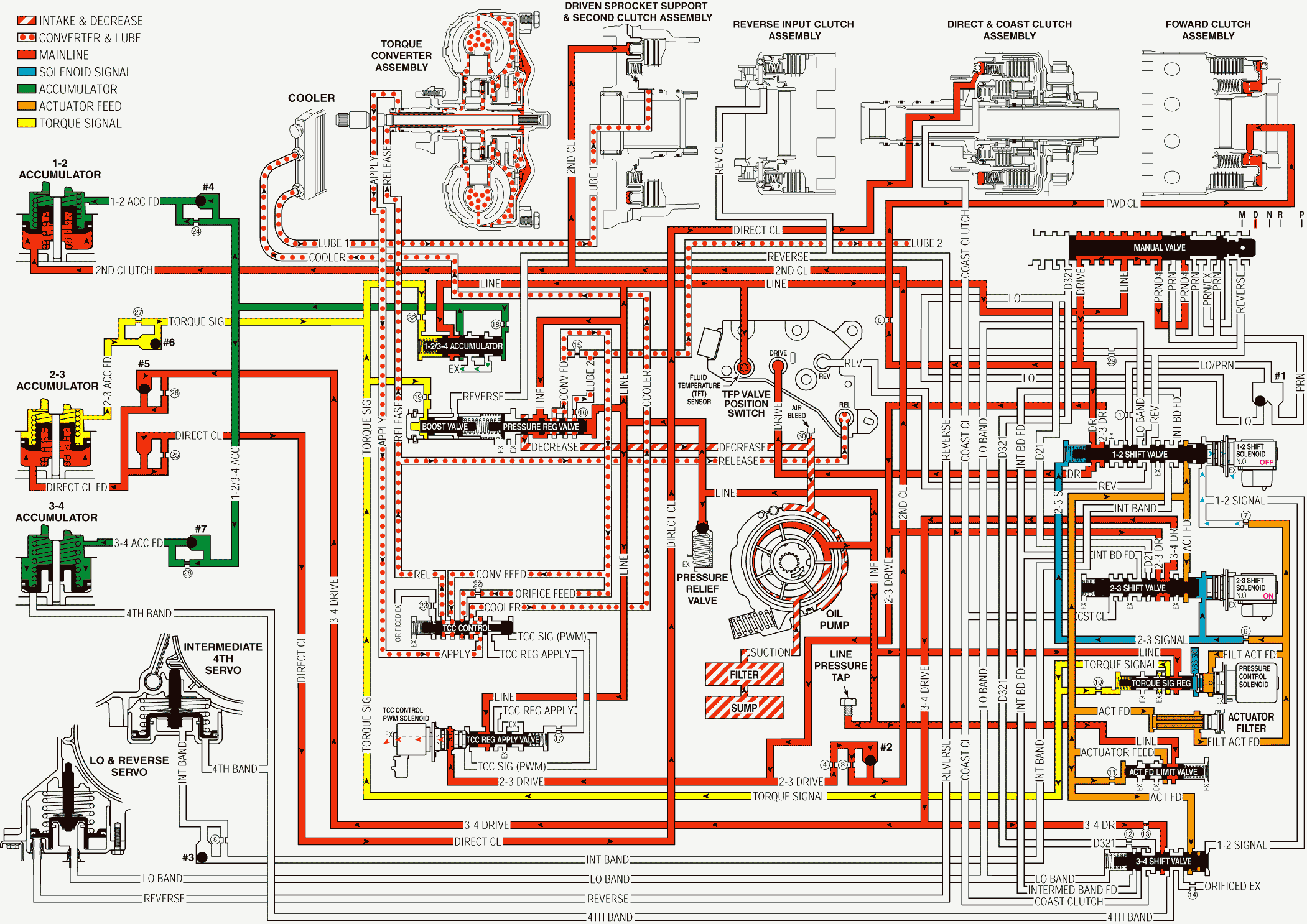
Overdrive Range, Third Gear - Torque Converter Clutch Not Applied W/O Electronic Range Select Mode
As vehicle speed increases and operating conditions become appropriate, the PCM energized the 2-3 shift solenoid valve in order to shift the transmission into Third gear. The manual valve remains in the Overdrive (D) position, and line pressure continues to feed the drive and the PRND4 fluid circuits.
Direct Clutch Applies
2-3 Shift Solenoid Valve
The PCM energizes the normally open 2-3 shift solenoid valve, which blocks the 2-3 signal fluid from exhausting. The 2-3 signal fluid pressure is routed to both of the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves.
2-3 Shift Valve
The 2-3 signal fluid pressure moves the valve against a spring force in order to initiate the 2-3 upshift. The 2-3 drive fluid is routed through the valve and into the 3-4 drive fluid circuit.
#5 Checkball (Direct Clutch Apply)
The 3-4 drive fluid pressure seats the #5 checkball, and 3-4 drive fluid is forced through the #26 orifice and into the direct clutch feed fluid circuit. the #26 orifice helps to control the direct clutch apply.
Direct Clutch
The direct clutch fluid pressure applies the direct clutch, causing the transmission to shifts into Third gear.
3-4 Shift Valve
The 3-4 drive fluid is also routed to the 3-4 shift valve in preparation for a 3-4 upshift.
Shift Accumulation
2-3 Accumulator
Direct clutch feed fluid is also routed to the 2-3 accumulator piston. This fluid pressure moves the piston against a combination of spring force and the 2-3 accumulator feed fluid pressure. This action absorbs the initial direct clutch fluid pressure in order to cushion the direct clutch apply. the movement of the 2-3 accumulator piston forces some of the fluid out of the accumulator.
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Under normal operating conditions the TCC is released in Third gear. However the TCC apply could vary depending upon the vehicle application, and the TCC may be calibrated in order to apply in Overdrive Range - Third gear.
A/T Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch (TFP Val. Position Sw.) Assembly
Release fluid pressure routed to the TFP Val. Position Sw. Assembly signals to the PCM that the TCC is released.
Overdrive Range, Third Gear - TCC Not Applied - Without Electronic Range Select Mode
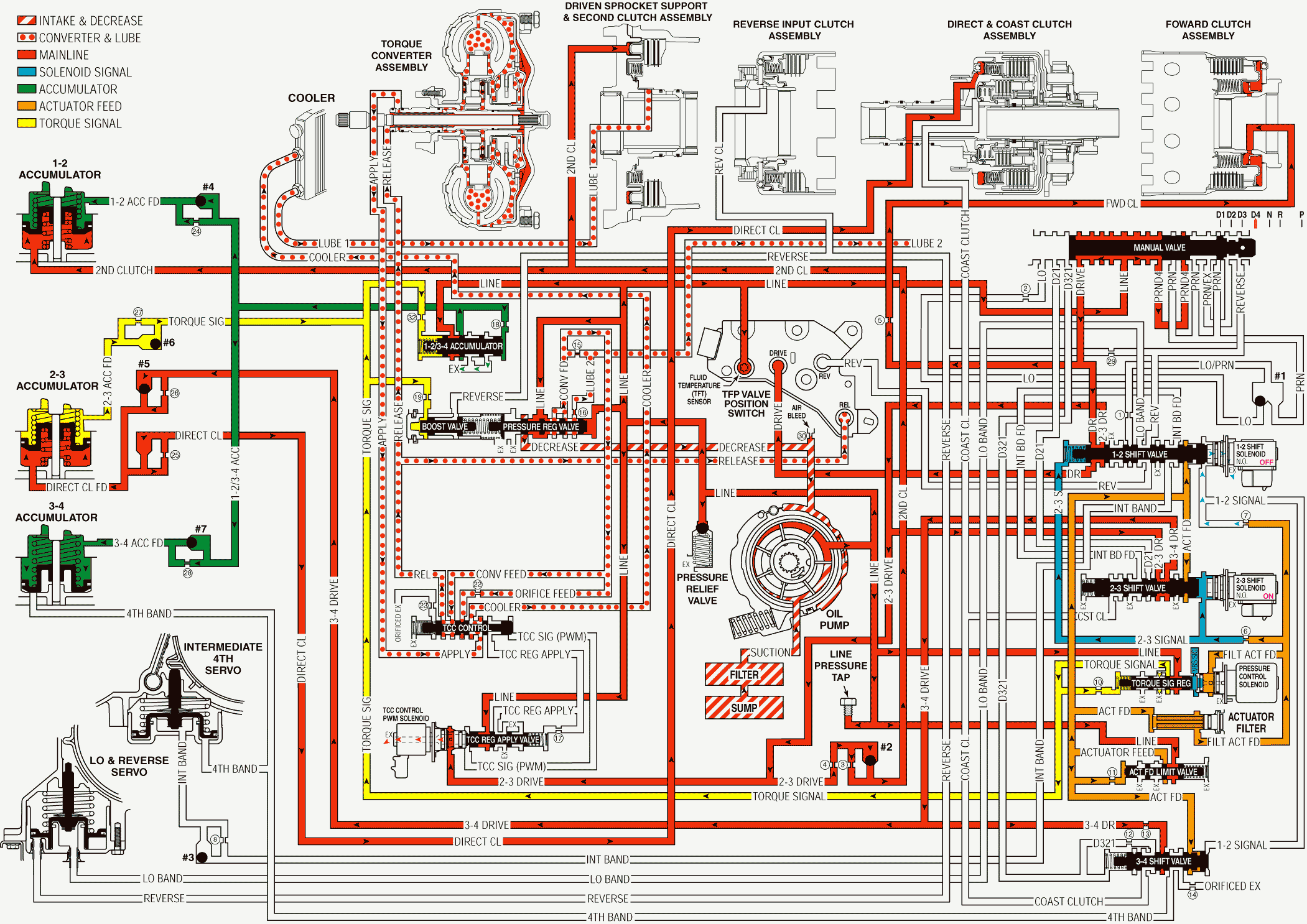
Overdrive Range, Third Gear - Torque Converter Clutch Not Applied With Electronic Range Select Mode
As vehicle speed increases and operating conditions become appropriate, the PCM energized the 2-3 shift solenoid valve in order to shift the transmission into Third gear. The manual valve remains in the Overdrive (D) position, and line pressure continues to feed the drive and the PRND4 fluid circuits.
Direct Clutch Applies
2-3 Shift Solenoid Valve
The PCM energizes the normally open 2-3 shift solenoid valve, which blocks the 2-3 signal fluid from exhausting. The 2-3 signal fluid pressure is routed to both of the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves.
2-3 Shift Valve
The 2-3 signal fluid pressure moves the valve against a spring force in order to initiate the 2-3 upshift. The 2-3 drive fluid is routed through the valve and into the 3-4 drive fluid circuit.
#5 Checkball (Direct Clutch Apply)
The 3-4 drive fluid pressure seats the #5 checkball, and 3-4 drive fluid is forced through the #26 orifice and into the direct clutch feed fluid circuit. The #26 orifice helps to control the direct clutch apply.
Direct Clutch
The direct clutch fluid pressure applies the direct clutch, causing the transmission to shifts into Third gear.
3-4 Shift Valve
The 3-4 drive fluid is also routed to the 3-4 shift valve in preparation for a 3-4 upshift.
Shift Accumulation
2-3 Accumulator
Direct clutch feed fluid is also routed to the 2-3 accumulator piston. This fluid pressure moves the piston against a combination of spring force and the 2-3 accumulator feed fluid pressure. This action absorbs the initial direct clutch fluid pressure in order to cushion the direct clutch apply. the movement of the 2-3 accumulator piston forces some of the fluid out of the accumulator.
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Under normal operating conditions the TCC is released in Third gear. However the TCC apply could vary depending upon the vehicle application, and the TCC may be calibrated in order to apply in Overdrive Range - Third gear.
A/T Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch (TFP Val. Position Sw.) Assembly
Release fluid pressure routed to the TFP Val. Position Sw. Assembly signals to the PCM that the TCC is released.
Overdrive Range, Third Gear - TCC Not Applied - With Electronic Range Select Mode