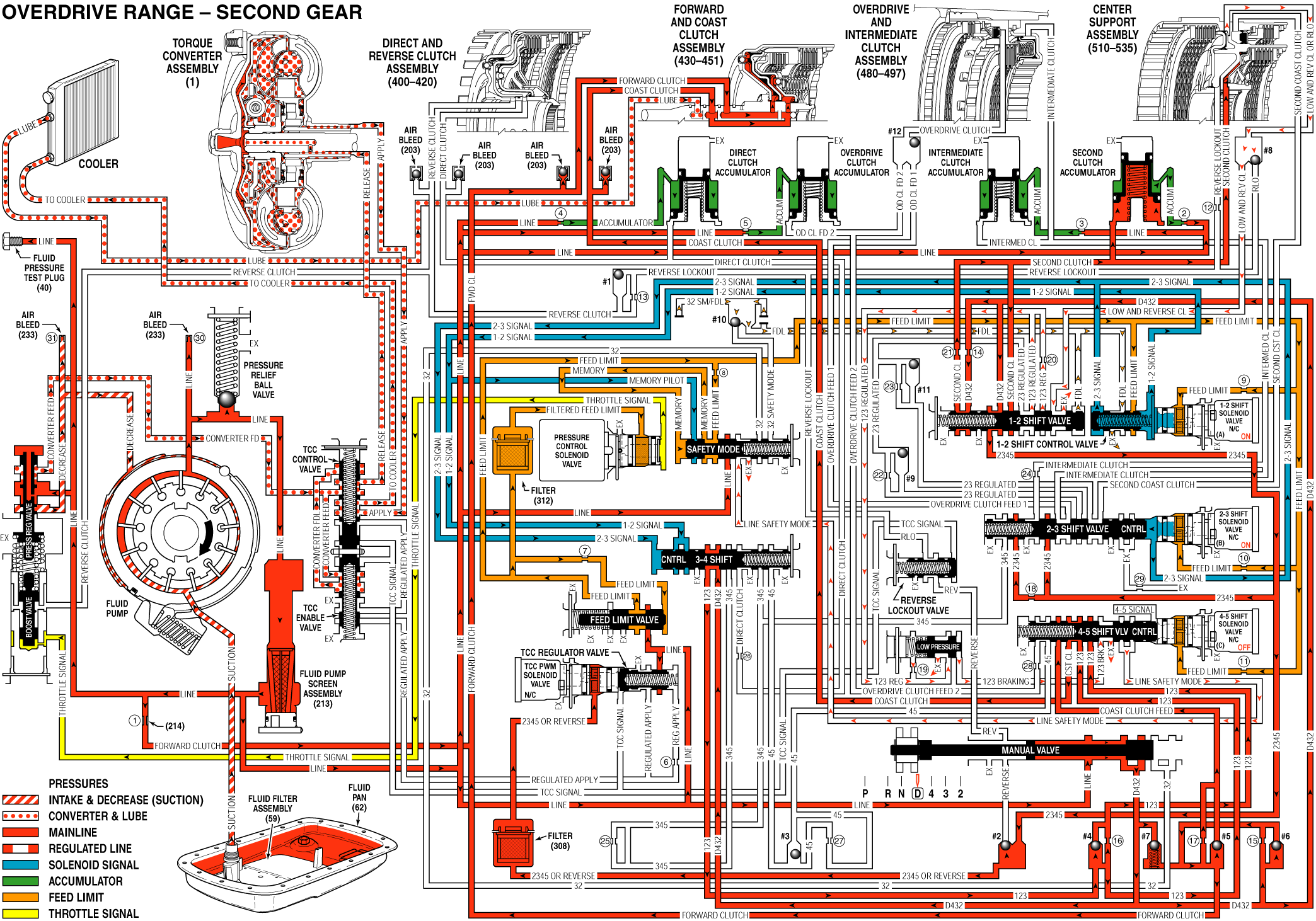
As the vehicle speed increases, TCM receives input signals from the two output and input speed sensors, TP sensor and other vehicle sensors to determine the precise moment to energize or turn ON the 1-2 SS.
Second Clutch Applies
1-2 SS Valve: 1-2 SS valve is energized to make the feed limit fluid flow into 1-2 signal fluid circuits. 1-2 signal fluid with the 1-2 shift control valve spring (367) tension overcomes 2-3 signal fluid pressure and move the 1-2 shift control valve (366) to the released position. The operation prevents the feed limit fluid from flowing into feed pipe fluid circuits.
1-2 Shift Valve: Drain the feed pipe fluid from the 1-2 shift valve (387), 1-2 shift valve spring (388) tension moves the valve to the released position to make D432 fluid flow into 2nd gear clutch and 2345 fluid circuit.
2nd Clutch: 2nd clutch fluid flows into 2nd clutch piston and applies 2nd clutch plate to shift to 2nd gear.
Shift Accumulator
2nd Clutch Accumulator: 2nd clutch fluid is also sent to 2nd Clutch Accumulator Assembly. 2nd Clutch Fluid with accumulator spring tension to make the 2nd clutch accumulator piston overcome the accumulator fluid pressure to absorb the impact when the 2nd clutch applies.
Fluid Pressure Directed in Preparation for 3rd Gear
2-3 Shift Valve: 2345 fluid is sent to 2-3 shift valve (371) and is prevented by the valve to be ready to upshift to 3rd gear.
TCC Release
#2 Ball Check Valve: 2345 fluid goes against the ball check valve to reverse fluid passage and flows into 2345 or reverse fluid circuit.
TCC PWM Solenoid Valve: 2345 or reverse fluid flows into TCC PWM solenoid valve through TCC PWM solenoid valve filter. But according to shift pattern, TCM will remain the PWM solenoid OFF to prevent the filtered 2345 or Reverse fluid flowing into TCC signal fluid passage to keep the TCC released.