The transmission electrical
connector is an important part of the transmission operating system. Any interference
with the electrical connection can cause the transmission to set Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs) or affect proper operation.
The following items can affect the electrical connection:
| • | Bent pins in the connector from rough handling during connection
and disconnection |
| • | Wires backing away from the pins or coming uncrimped (in either
the internal or the external wiring harness) |
| • | Dirt contamination entering the connector when disconnected |
| • | Pins in the internal wiring connector backing out of the connector
or pushed out of the connector during reconnection |
| • | Excessive transmission fluid leaking into the connector, wicking
up into the external wiring harness and degrading the wire insulation |
| • | Moisture intrusion in the connector |
| • | Low pin retention in the external connector from excessive connection
and disconnection of the wiring connector assembly |
| • | Pin corrosion from contamination |
| • | Damaged connector assembly |
Remember the following points:
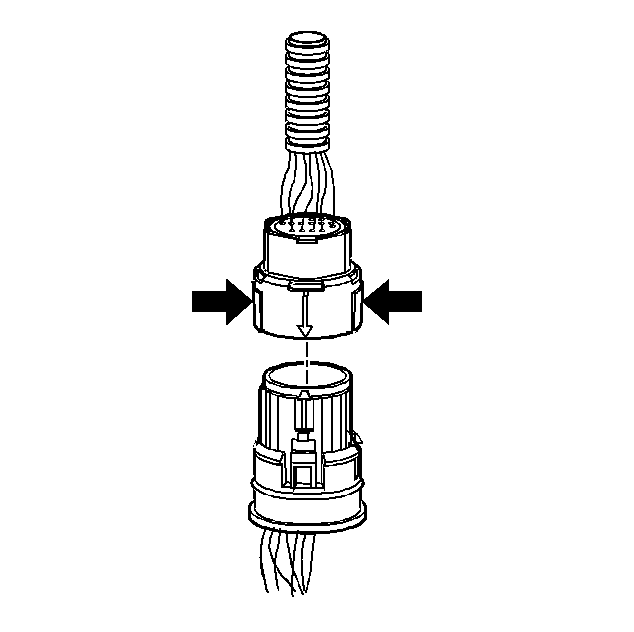
| • | In order to remove the connector, squeeze the two tabs toward
each other and pull straight up. |
| • | Limit twisting or wiggling the connector during removal. Bent
pins can occur. |
| • | Do not pry the connector off with a screwdriver or other tool. |
| • | In order to reinstall the external wiring connector, first orient
the pins by lining up the arrows on each half of the connector. Push the connector
straight down into the transmission without twisting or angling the mating
parts. |
| • | The connector should click into place with a positive feel and/or
noise. |
| • | Whenever the transmission external wiring connector is disconnected
from the internal harness and the engine is operating, DTCs will set. Clear
these DTCs after reconnecting the external connector. |

