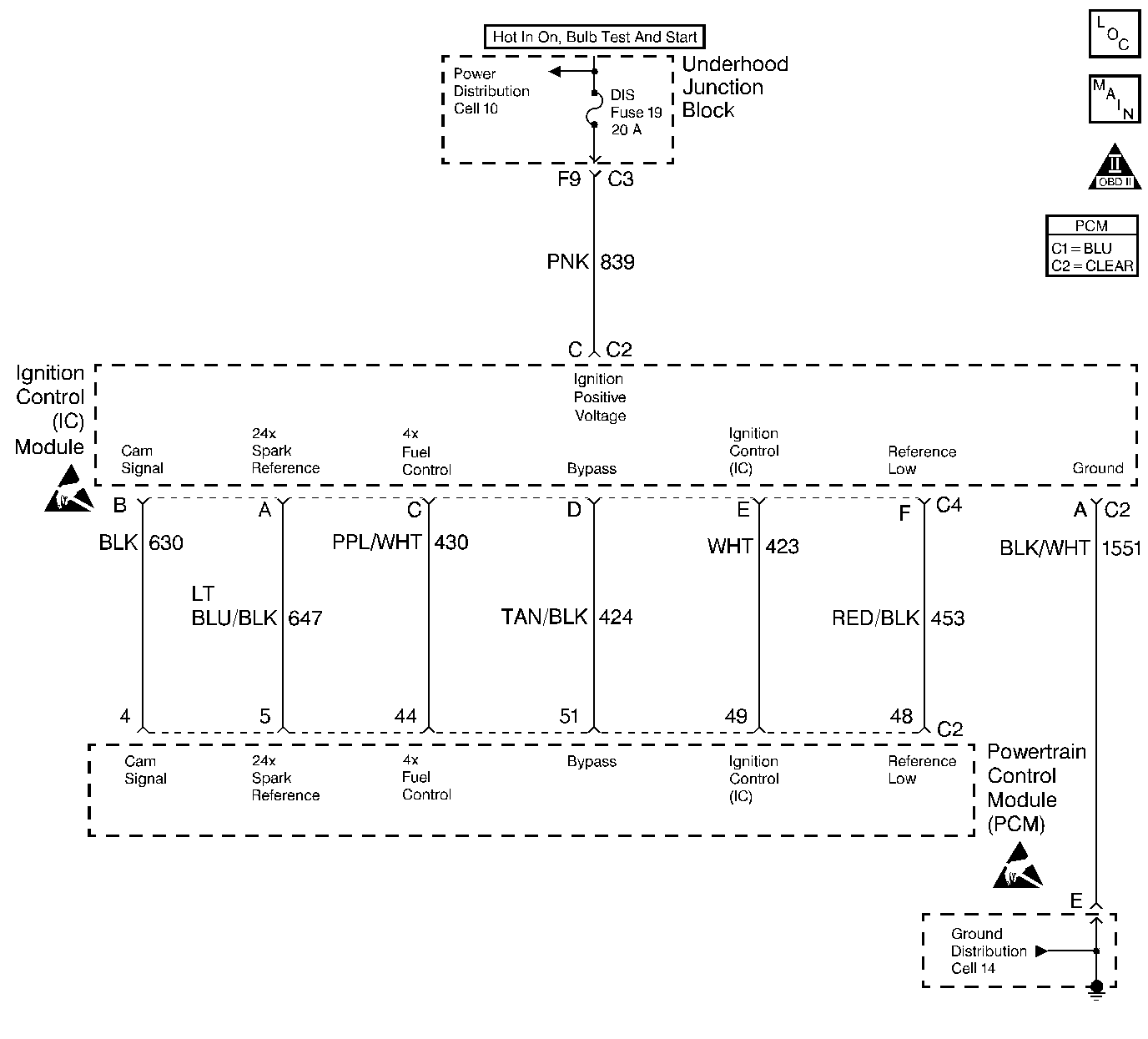
Circuit Description
This diagnostic test is used to detect misfires in any cylinder. A misfire occurs when there is a complete lack of or poor combustion in the cylinder. A misfire will cause a fluctuation in crankshaft revolution speed. The PCM uses the time between 4X reference pulses to determine when these fluctuations occur. At lower engine speeds, fluctuations in crankshaft speed are measured each reference pulse to detect misfire. At higher engine speeds, fluctuations in crankshaft speed are monitored over two engine revolutions and fluctuations in crankshaft speed at each half revolution are compared to compute a balance number. The 4X reference pulses originate in the ignition control module and vary with RPM.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTC(s) P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0340 and P0502 are not current or have not set since last key ON. |
| • | Coolant is between -7°C (19°F) and 128°C (262°F). |
| • | Engine speed running for at least 5 seconds. |
| • | Engine speed is less than 2500 rpm. |
| • | Traction control is not present. |
| • | Cylinder shut down is not present |
| • | Ignition voltage is between 9 and 16 volts. |
| • | Throttle angle 0.3 degrees or more. |
| • | Vehicle speed is less than 45 mph. |
| • | During a 12.5 millisecond time period change in throttle angle stays less than 1 degree. |
| • | During a 100 millisecond time period change in throttle angle stays less than 1.28 degrees. |
| • | Delta MAP diagnostic not in progress. |
| • | Number of consecutive positive delta revolution mode indexes less than 20. |
| • | Number of consecutive negative delta revolution mode indexes less than 20. |
| • | A/C compressor clutch has not changed states in the last engine cycle. |
| • | Slip speed is at least -64 rpm. |
| • | 18 engine cycles have occurred since any of above conditions were not met. |
| • | Rough road indication is not considered present. |
| • | 30 engine cycles have occurred since power-up. |
| • | 16 engine cycles have occurred since both the reference mode and revolution mode were disabled. |
| • | 8 engine cycles have occurred since a CAM error, or an ignition system error. |
| • | Scan tool not controlling any devices. |
| • | 10 engine cycles have occurred since desired torque less than 95.3%. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A misfire has been detected.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will turn on the SERVICE ENGINE SOON MIL under the following conditions.
| • | Impending catalytic converter damage |
| - | If a cylinder misfires at a sufficiently high rate for at least 800 engine revolutions, a catalytic converter damaging misfire level is considered present and the Service Engine Soon MIL will flash until the catalyst damaging condition is no longer present, at which time the MIL will remain on steady. |
| - | Disable TCC if either the number of emission misfires or number of catalyst damaging misfires exceeds 2. |
| • | Excessive exhaust emissions |
| - | If a cylinder misfires 15 times in 200 revolutions for 10 out of 16 200 revolution tests in each of two consecutive trips (engine run cycles which meet specific criteria), an excessive exhaust emissions condition is considered present and the Service Engine Soon MIL will be turned on. |
| - | Disable TCC if either the number of emission misfires or number of catalyst damaging misfires exceeds 2. |
The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the DTC sets. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips within the same driving parameters that set the DTC and the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A Last Test Failed (current) DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after eighty drive cycles within the same driving parameters that set the DTC with no failures of any emission related diagnostic test. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear DTCs. |
| • | Interrupting PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes in PCM Description and Operation. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If more than one cylinder showed a history of misfire, look for something in common between the cylinders such as, shared coil, etc. If only one cylinder showed a history of misfire look for a possible vacuum leak at that cylinder, etc. |
| • | If fault cannot be duplicated, wet secondary ignition system and operate vehicle under conditions that the DTC set. |
| • | It is possible to set DTC P0300 if the vehicle has run out of or is very low on fuel. |
| • | To quickly determine the cylinder(s) that are misfiring, use the scan tool and observe Misfiring Cyl. in the Misfire data list. This will display the primary and secondary misfiring cylinders. |
| • | Due to the potentially destructive nature that engine misfire has on the exhaust catalyst always check for proper catalytic converter operation after a misfire has been repaired. This can be accomplished in the following ways: |
| Drive the vehicle under the Test Conditions for DTC P0420 and ensure that the DTC runs and passes. |
| • | It is possible to set a DTC P0300 if engine oil is the improper type or viscosity. Lifter pump up, caused by improper oil can create conditions that set the DTC. Check for proper oil type and viscosity. |
| • | Anything that can effect the crank to cam speed relationship can induce a DTC P0300. This includes the serpentine belt and driven accessories, flex plate, torque converter, fuel delivery, poor fuel quality ect. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
If other DTCs are set, diagnose them first because other problems may be causing the misfire.
-
Checking if multiple cylinders are misfiring. If there is a single cylinder misfiring, the diagnosis is much easier.
-
Checking for causes of a single cylinder misfire.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Are any other DTCs set? | -- | Go to DTCs that are set | ||
Are any of the counters incrementing? | -- | |||
Does spark jump the tester gap and is spark consistent? | -- | |||
5 |
If the Injector Coil Test Procedure finds no fault, review diagnostic aids and refer to Engine Mechanical for diagnosis. Do the spark plugs appear to be okay or are only gas fouled (not oil or coolant fouled)? | -- | Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test . | |
6 | Are the spark plugs oil or coolant fouled? | -- | Refer to Engine Mechanical for diagnosis | |
7 | Do the spark plugs show any signs of being cracked, worn or improperly gapped? | -- | Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test . | |
8 | Replace or re-gap spark plugs. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
9 |
Is the wire resistance less than the value shown? | 15K ohms | ||
10 | Remove the affected coil(s). Is the coil free of carbon tracking? | -- | ||
11 |
Does spark jump the tester gap and is spark consistent? | -- | ||
12 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
13 | Replace the faulty wires. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
14 | Replace the Ignition Control Module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | -- |
15 |
Are any of the counters incrementing? | -- | ||
16 |
Do more than 3 cylinders show a high misfire rate? | -- | ||
17 |
Did any of the checks require a repair? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Refer to Diagnostic Aids |
18 | Check the vehicle for proper vent operation, vacuum leaks or an intermittent rich or lean condition. Did any of the checks require a repair? | -- | Go to Powertrain Control Module Diagnosis for Verify Repair | Refer to Diagnostic Aids |
