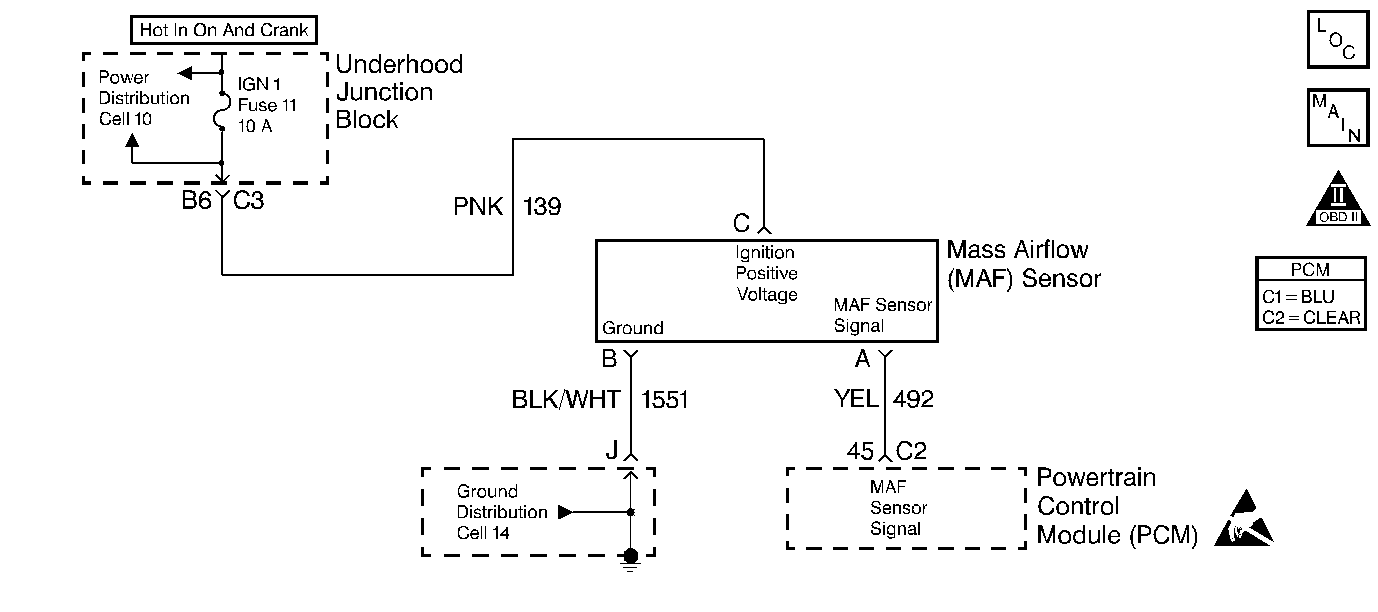
Circuit Description
This diagnostic test is used to determine if the Mass Air Flow sensor is providing proper readings to the PCM. The MAF sensor is a high frequency device that measures the rate of air flow through the throttle body. The MAF sensor outputs a series of pulses that vary in frequency with air flow. This signal is used by the PCM for fuel control. MAF readings during acceleration will be much higher than those during deceleration or idle. The PCM calculates what MAF reading should be received from the sensor under certain conditions. When the test conditions are met, the PCM will compare its calculated MAF value to the actual value received from the sensor. The calculated MAF reading is done by comparing MAP, RPM and Intake Air Temperature. The allowable difference between calculated MAF and actual MAF varies depending upon flow. If this difference is too great DTC P0101 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0102, P0103, P0106, P0107, P0108, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0560 and P1108 not set. |
| • | Ignition voltage between 11 volts and 16 volts |
| • | DTC P0101 has not previously failed this ignition cycle. |
| • | In closed loop fuel control. |
| • | Canister Purge Duty Cycle is less than or equal to 99.6%. |
| • | EGR rescaled pintle position is less than or equal to 240 counts. |
| • | DTC P0401 not testing EGR. |
| • | Traction control not active. |
| • | TPS is less than or equal to 50 degrees. |
| • | 100 msec delta MAP is less than or equal to 5 kPa. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The difference between the actual and calculated MAF has been too great.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | PCM turns ON the SERVICE EMISSION SYSTEM message. |
| • | PCM disables the EVAP control solenoid. |
| • | PCM disables long term fuel trim. |
| • | PCM substitutes calculated MAF value, based on engine speed and throttle position, for actual MAF. |
| • | PCM disables torque management. |
| • | PCM maintains transaxle shift adapts at their current levels. |
| • | PCM disables TCC. |
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A Last Test Failed (current) DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles with no failures of any emission related diagnostic test. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear DTCs. |
| • | Interrupting PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes in PCM Description and Operation. |
Diagnostic Aids
For an intermittently setting DTC P0101, compare the Freeze Frame data to the Typical Data list for the conditions under which the DTC set, looking for faulty data from other sensors which may set this DTC.
Important: An improperly installed air cleaner or a distorted /missing Intake Air Duct may cause this DTC to set. Ensure air cleaner assembly / IA duct is installed correctly and that there are no kinks, folds or damage to the IA Duct or possible debris in the air cleaner assembly or the MAF sensor inlet screen that may distort the air flow.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
To aid in finding an intermittent, wiggle the MAF sensor connector, PCM connector and the wiring harness while noting the MAF sensor display on a scan tool. With a RUNNING engine a reading of 1 or less would indicate no MAF sensor input to the PCM (an open, short, poor connection or faulty component).
-
A voltage reading of 0 volts would indicate an open circuit or disconnected ground. A voltage reading that is a half volt or more lower than the voltage noted in Step 4 would indicate high circuit resistance or a poor ground connection.
-
If the fuse is blown check for a short to ground or shorted component on the circuit. If the fuse is OK check for voltage at other components on the circuit. If other components have voltage the open is between the splice and MAF sensor. If other components have no voltage the open is between the splice and fuse.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Is MAF sensor reading more than the value specified? | 1135 Hz | Fault not present. Go to Test Descriptions | Go to Step 3 | |
3 |
Is the voltage between the values specified? | 4.7-5.3 volts | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 6 |
4 | With the key ON measure and note the voltage to ground on MAF sensor terminal C. Is the voltage in the range specified? | 10.5-15 volts | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 7 |
With the key ON measure the voltage between MAF sensor terminals B and C. Is the voltage measured within a half volt of the voltage measured in Step 4? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 | |
6 |
Was a repair made to the MAF Sensor Input circuit? | -- | Go to Step 11 | |
Repair the open or short to ground in the MAF Sensor power feed circuit. Refer to Test Descriptions. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | ||
8 | Repair the open or high resistance in the MAF Sensor ground circuit. Refer to Test Descriptions. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Step 10 | |
10 | Replace the Mass Air Flow sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
11 |
Was terminal contact repaired? | -- | Go to Step 12 | |
12 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- |
