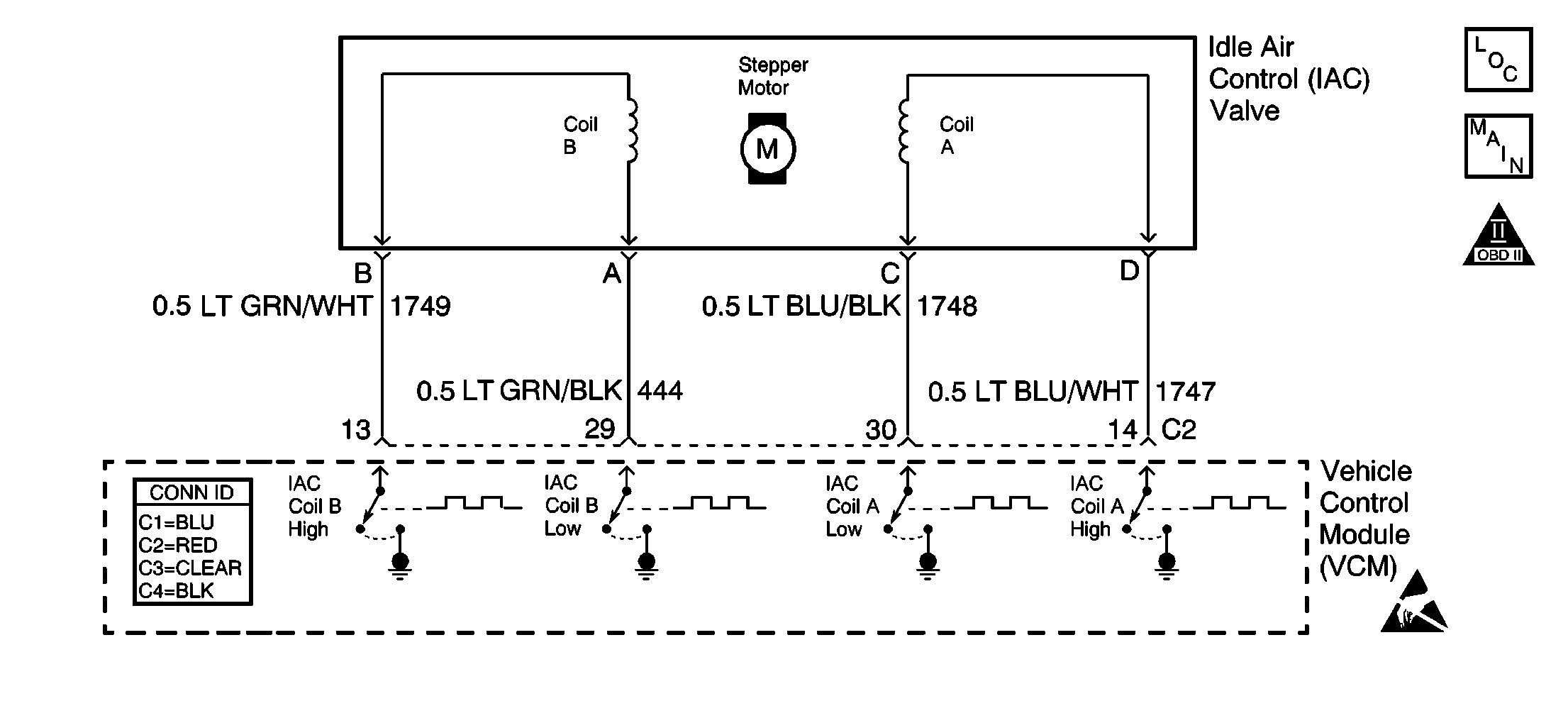
Circuit Description
The control module controls idle speed with an idle air control (IAC) valve. The desired RPM is based on sensor inputs and the actual engine RPM. Four circuits are used in order to control the IAC valve, allowing a precise amount of air into the intake manifold. In order to increase the idle RPM, the control module will command the valve pintle to move away from its seat, allowing more air to bypass the throttle plate. To decrease RPM, the control module commands the IAC pintle to move closer to its seat, causing a lower airflow to bypass the throttle plate. A scan tool will display the control module commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher the counts, the more air is allowed to bypass the throttle plate. Lower counts indicate that less air is commanded by the control module.
This DTC is designed to detect low engine RPM that is not responding to increased IAC counts.
A low idle is 75 RPM below the desired idle.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active throttle position (TP) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active vehicle speed (VSS) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor DTCs. |
| • | The ECT is more than 50°C (122°F). |
| • | The system voltage is more than 10 volts but less than 16 volts. |
| • | The IAT is more than -25°C (-13°F). |
| • | The engine has been running for more than 30 seconds. |
| • | The BARO is more than 70 kPa. |
| • | The mass air flow (MAF) is between 17.5-50 g/s. |
| • | The vehicle speed is between 25-85 mph (40-136 km/h). |
| • | Any change in throttle position is less than 1 percent. |
| • | Any change in engine speed is less than 50 RPM. |
| • | The intake air control (IAC) valve was commanded to move a specified number of counts. |
| • | The above conditions present for more than 2 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The change in MAF is more than 3 g/s.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
This DTC can be set by an IAC valve which has stopped and is not responding to the vehicle control module (VCM), a throttle stop screw that has been tampered with, or a damaged throttle or throttle linkage. A slow, unstable or fast idle may be caused by a non-IAC valve system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC valve. Out of range control IAC scan tool counts will be above 60 if idle is too low and zero if idle is too high.
Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Fuel system too lean or too rich |
| • | Throttle body bore with foreign material |
| • | Gasket leaks |
| • | IAC reset is done with the scan tool |
Refer to Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle and Stalling .
Inspect for intermittents.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The IAC Reset function used in this step only energizes the circuit for 2 seconds, so this function will have to be used repeatedly during this step. Also it is recommended that the connector test adapter kit is used during this procedure to prevent terminal damage to the IAC harness connector.
-
If the test lamp remained ON at any of the IAC valve harness connector terminals during the IAC valve reset function the circuit is shorted to voltage. If these circuits are checked before or after the IAC valve reset function it is possible that any combination of IAC circuits could light a test lamp, this would be a normal condition.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Does the engine speed correspond within 100 RPM of the commanded speeds? | 1,200 RPM 500 RPM | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
3 |
Are the resistances across terminals A and B, and terminals C and D within the specified value? | 40-80 ohms | ||
4 |
Are the resistances across terminals B and C, and terminals A and D at the specified value? | ∞ | ||
Caution: Avoid contact with moving parts and hot surfaces while working around a running engine in order to prevent physical injury. Important: Command ON the Reset IAC function for each circuit tested. This function will only flash each circuit for 2 seconds. Does the test lamp flash ON and OFF at all terminals? | -- | |||
Did the test lamp remain ON at any of the terminals during the IAC valve reset function? | -- | |||
7 | Inspect for an open or short to ground in the IAC valve circuit that did not flash the test lamp. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
8 | Inspect for a short to voltage in the IAC valve circuit where the test lamp remained ON. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
9 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
10 | Inspect for a poor connection at the VCM. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
11 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Clean the IAC valve and passages. Refer to the Cleaning and Inspection Procedure in the Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Important: The replacement VCM must be programmed. Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
16 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
