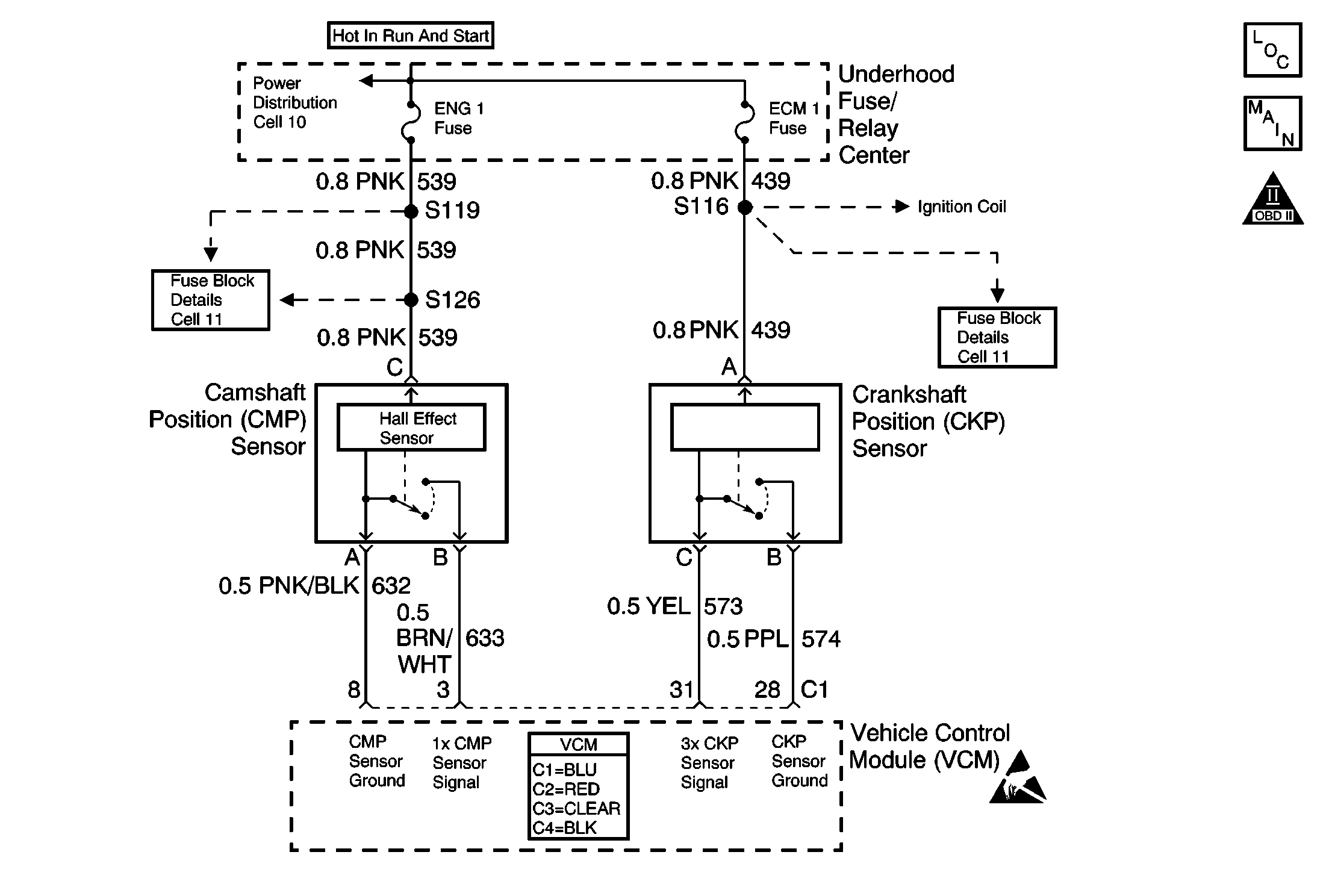
Circuit Description
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) monitors the crankshaft position (CKP) and the camshaft position (CMP) signals to determine if they are synchronized. If both signals are not observed by the control module within a narrow time window, the vehicle control module (VCM) will determine that an error has occurred.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
When the engine is running, the camshaft position sensor reference pulse is not detected at the correct position relative to the crankshaft position sensor pulse.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) the first time the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module will set the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A loose CMP sensor causing a variance in the sensor signal |
| • | Excessive free play in the timing chain and gear assembly |
| • | The distributor incorrectly installed 1 tooth off in either the advance position or the retard position |
| • | A loose distributor rotor on the distributor shaft |
| • | A loose or missing distributor hold-down bolt |
Inspect for intermittents.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the table.
-
This test will determine if this DTC is intermittent.
-
If there is a variance in the camshaft sensor signal, the variance will be detected in this step.
-
Unintentional damage to the distributor shaft may result if excessive pressure is used to rotate the distributor.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Does the engine speed fluctuate up to twice the desired RPM? | -- | ||
3 | Replace the crankshaft position sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Perform the camshaft retard offset test procedure as follows:
Important: The camshaft retard reading is not accurate at less than 1,000 RPM. Is the camshaft retard reading within the specified range? |
-5° to -17° | |||
Does the camshaft retard reading change more than the specified value? | 2° | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
With the engine at a normal operating temperature and the engine OFF, perform the following procedure:
Does the rotor turn on the distributor shaft? | -- | |||
7 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
8 | Replace the distributor. Refer to Distributor Replacement in Engine Electrical. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
10 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
