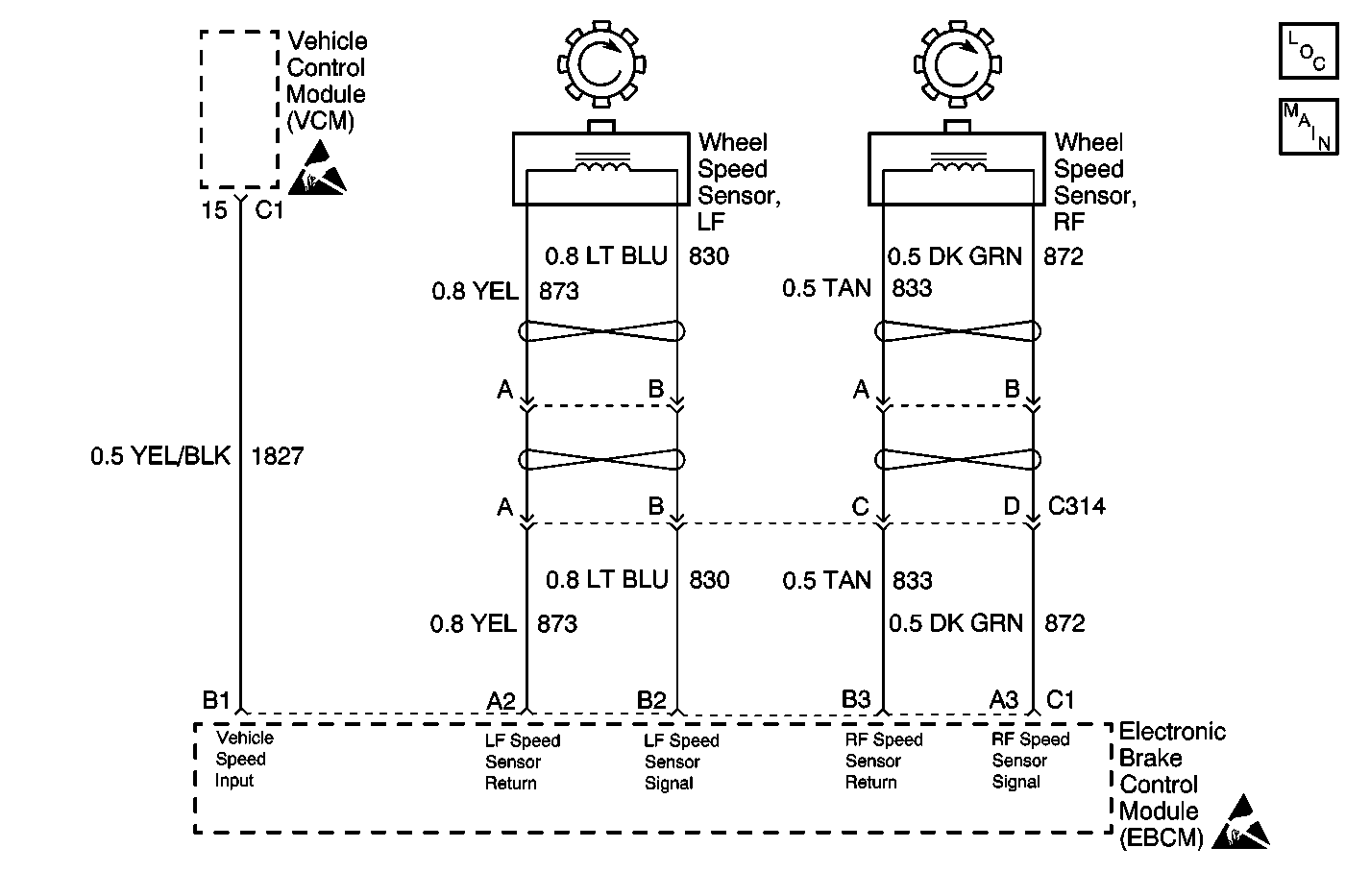
Circuit Description
The wheel speed sensor coil emits an electromagnetic field. A toothed ring on the wheel passes by the wheel speed sensor and disrupts this electromagnetic field. The disruption in the field causes the wheel speed sensor to produce a sinusoidal (AC) voltage signal. The frequency and amplitude of the sinusoidal (AC) voltage signal are proportional to the speed of the wheel. The amplitude of the wheel speed signal is also directly related to the distance between the wheel speed sensor coil and the toothed ring. This distance is referred to as the air gap.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Ignition switch in the RUN position. |
| • | All wheel speed sensor signals above 32 km/h (20 mph) with brake applied, or 19 km/h (12 mph) with brake released. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Sudden loss of both front wheel speed sensor signals 10 to 15 miliseconds. |
| • | Sudden increase in front wheel speed sensor signals for 105 miliseconds (AWD only). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on |
| • | The ABS disables |
Malfunction responses to DTC C0229 vary, depending on the affected subsystem.
| • | ABS--Ignition latched |
| • | DRP--DRP critical |
For a detailed explanation of DTC malfunction responses, refer to Self-Diagnostics
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC |
| • | Use the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function |
| • | An Ignition Latched DTC will disable ABS and DRP during the course of the current ignition cycle, (even if the cause of the DTC is intermittent). The DTC will be stored in the EBCM memory until it is repaired, and/or the DTC is cleared. After the DTC is repaired and/or cleared and the ignition is turned to ON, the ABS lamp will remain lit until the EBCM completes a power-up self test. This test concludes when the vehicle has reached a speed of greater than 13 km/h (8 mph) and the wheel speed inputs have been checked by the EBCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Any of the following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Wire insulation that is rubbed through |
| • | A wire breaks inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
When inspecting a wheel speed sensor, inspect the sensor terminals and the harness connector for corrosion. If evidence of corrosion exists, then replace the wheel speed sensor. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the numbers on the diagnostic chart.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the ABS Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
Is the harness OK and are all the connections clean and tight? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |
3 |
Did vehicle operation cause this DTC to set? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 |
4 | Make necessary repairs to the 16-way EBCM harness connector. Refer to Repairing Connector Terminals . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 7 | -- |
5 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 7 | -- |
6 | Malfunction is intermittent. Inspect all connectors and harnesses for damage which may result in high resistance when all components are connected. Refer to diagnostic aids for more information. Did you find and repair the condition? | -- | Go to Step 7 | -- |
7 | Operate the vehicle under the conditions for running the DTC as specified in the supporting text. Does the DTC set? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
