Notice: Do not clean the starter motor parts in a degreasing tank. Soaking parts
will dissolve the permanent lubrication and may damage the electrical
insulation. This will shorten starter motor life.
- Clean all parts by wiping with a dry cloth.
- Inspect the bushing or the armature bearing fit in the following
locations:
| • | The shift lever housing |
| • | The drive end frame housing (If the bushings or the bearings are
damaged, install new ones) |
- Lubricate the bushings before assembling the starter motor.
| • | Avoid over lubrication. |
| • | Do not lubricate the roller bearings. |
| • | The roller bearings are permanently lubricated when manufactured. |
- Inspect the armature shaft for runout or scoring.
If the condition of the armature shaft is in doubt, install a new shaft.
- Inspect the commutator for discolored or uneven conductors.
| • | Do not turn the commutator on a lathe. |
| • | Do not undercut the insulation. |
| • | Clean the commutator with No. 240 grit emery cloth. |
| - | Blow away any copper dust. |
| - | If the commutator can not be cleaned satisfactorily, install a
new armature. |
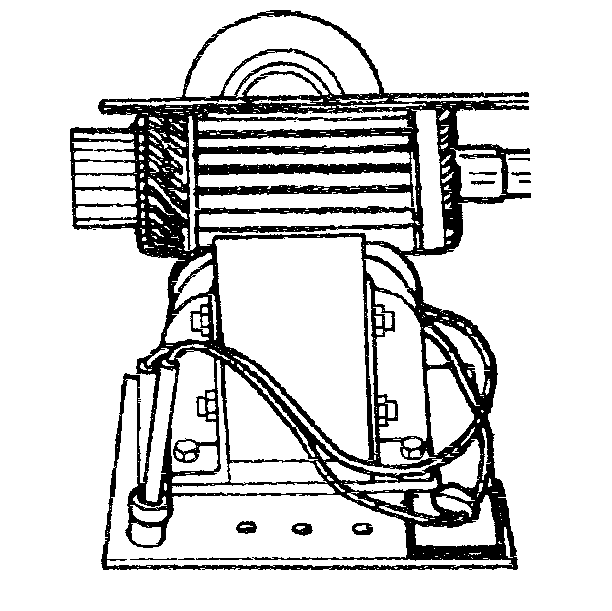
- Inspect the armature for short circuits using the following procedure:
| • | Rotate the armature in a growler. |
| • | Use a steel strip (such as a hacksaw blade) held on the armature,
parallel to the shaft. |
| • | If a short circuit is detected, the steel strip will vibrate over
the area. |
| • | Consult the growler manufacturer's instructions for more information. |
| • | Short circuits between the commutator bars can be produced by
brush dust or copper dust. |
- Inspect the armature for opens as follows:
| • | Look for loose connections where the conductors join the commutator
bars. |
| • | Poor connections cause arcing. |
| • | Arcing causes burning of the commutator. |
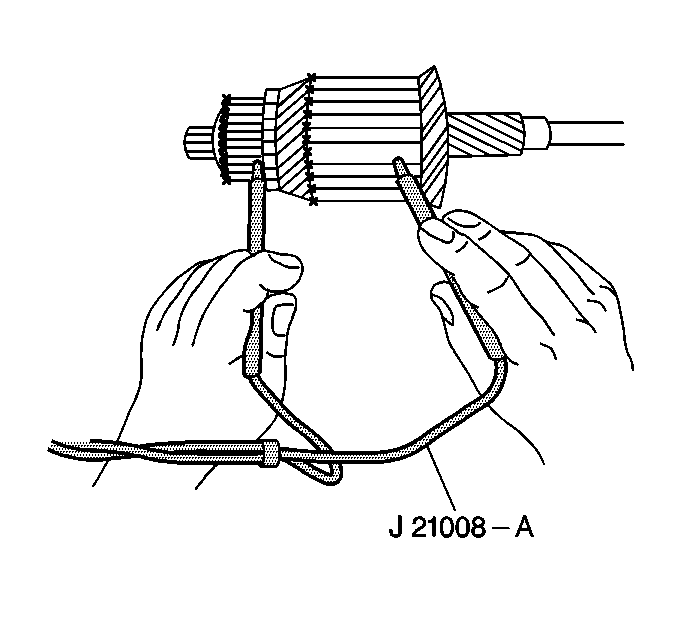
- Inspect the armature for grounds with a self-powered test lamp (continuity
tester). Use J 21008-A
.
| • | Place one test probe on the commutator. |
| • | Place the other test probe on the armature core or shaft. |
| • | If the test lamp lights, the armature is grounded. |
- Inspect the brushes for wear.
If the brushes are worn to half the size of a new brush, replace the
assembly.
- Inspect the holders for dirt or damage.
Make sure that the brushes move freely and do not bind in the holders.
- Inspect the brush springs for distortion or discoloring.
| • | Repair any damaged brush springs, as necessary. |
| • | If the brush springs are weak, bent or discolored, replace the
field and frame assembly. |
- Inspect the field coils.
| • | Look for burned or damaged insulation. |
| • | Look for damaged connections. |
| • | If the condition of the coils is doubtful, replace the field and
frame assembly. |
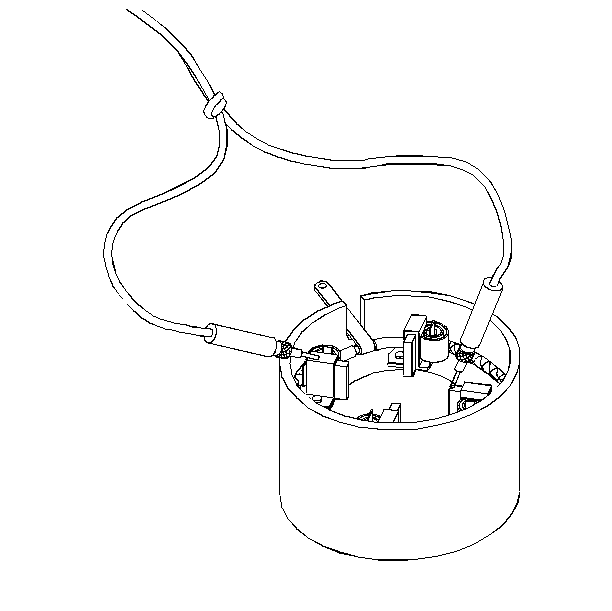
- Inspect the field coils for grounds.
| • | Connect the two leads from the growler between the field frame
and the field connector. |
| • | Be sure that the brush ends do not contact the field frame. |
| • | If the test lamp lights, the field coils are grounded. |
| • | Install a new field and frame assembly. |
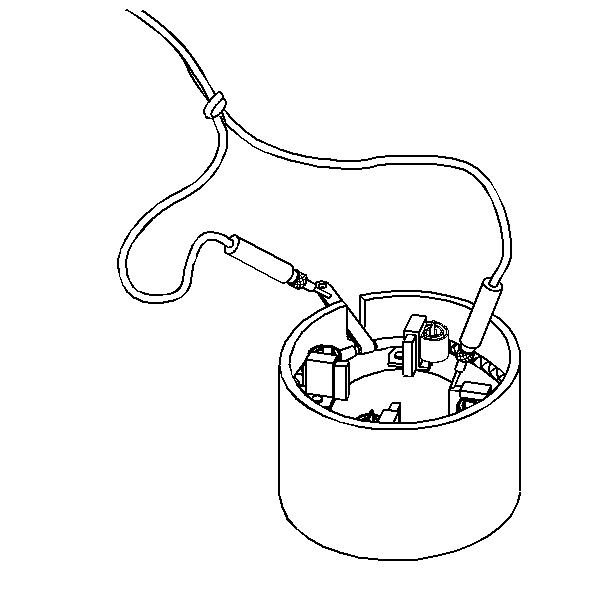
- Inspect the field coils for opens.
| • | Connect the two leads from the growler between the field connector
and each of the positive brushes. |
| • | If the test lamp does not light at both brushes, then the fields
are open. |
- Inspect the field coils for shorts.
| • | Shorts are indicated if the starter motor runs poorly after all
other inspection procedures are complete. |
| • | If shorted, the frame and field coils replace as an assembly. |
- Inspect the drive assembly (clutch) by turning the drive pinion
in the cranking direction.
| • | If the drive pinion turns roughly in the cranking direction, replace
the complete overrunning clutch assembly. |
| • | If the drive pinion slips in the cranking direction, replace the
complete overrunning clutch assembly. |
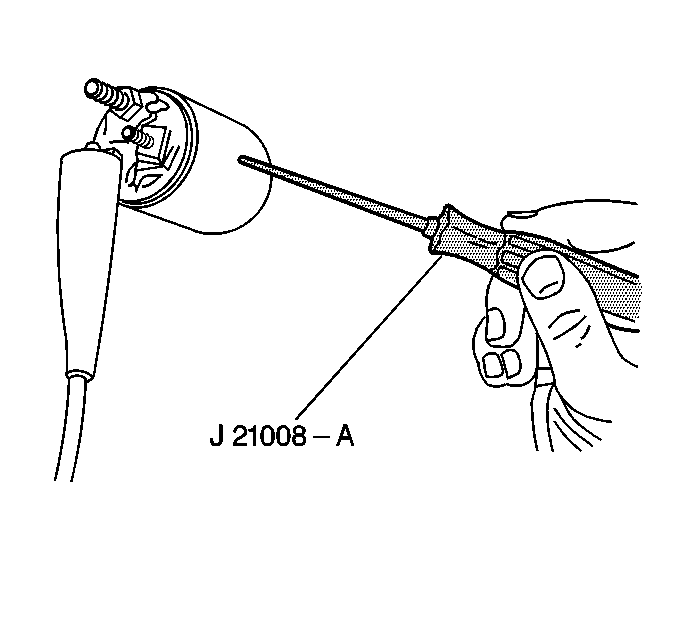
- Inspect the solenoid for grounds using a self-powered 12 V test
lamp J 21008-A
.
- If the solenoid does not pass the following tests, install a new
solenoid.
| 18.1. | Connect J 21008-A
between the BAT terminal and the metal housing (ground). |
| 18.2. | The lamp should not light, meaning that the terminal is not grounded. |
| 18.3. | Connect J 21008-A
between the (S) terminal and the metal housing. |
The lamp should light.
| 18.4. | Connect J 21008-A
between the (M) terminal and the (S) terminal, or connect the test
lamp between the (M) terminal and the metal housing. |
The lamp should light.
Notice: To prevent overheating of the solenoid pull-in winding, do not leave
the winding energized for more than 15 seconds. The current draw will decrease
as the winding temperature increases.
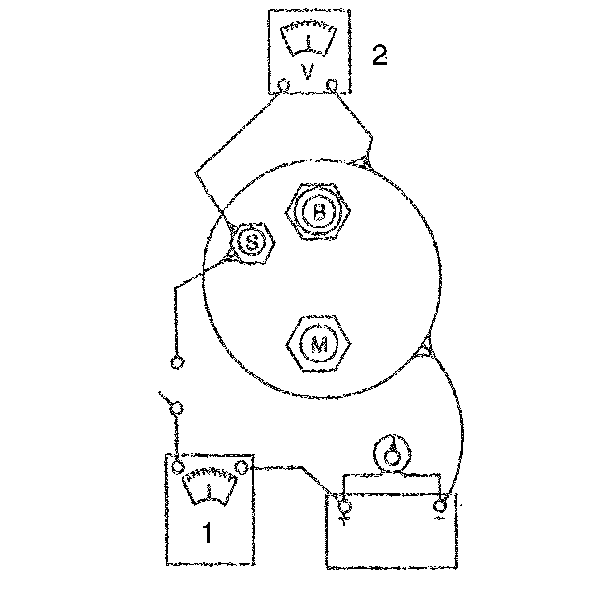
- Inspect the hold-in
winding and the pull-in winding.
Important: Before testing, the solenoid must be removed from the starter motor,
or the field lead must be removed from the terminal on the solenoid.
- In order to test both windings, perform the following procedure:
| 20.1. | Connect an ammeter in series with a 12 V battery positive
terminal, and the switch (S) terminal on the starter solenoid. |
| 20.2. | Connect a digital multimeter J 39200
to the (S) terminal on the starter solenoid and to the negative
battery terminal. |
| 20.3. | Connect the carbon pile (variable resistance) across the battery. |
| 20.4. | Ground the solenoid motor (M) terminal. |
| 20.5. | Adjust the voltage to 10 V and observe the ammeter reading. |
| 20.6. | The reading should be between 60-85 amperes. |
| • | A higher ammeter reading means that the winding is shorted or
grounded. |
| • | A lower ammeter reading means that there is excessive resistance
in the winding. |
| 20.7. | A digital multimeter J 39200
reads the winding resistance, and measures in tenths of an
ohm. |
| 20.8. | Dividing the voltagge by the amperes (voltage/amperes), determines
coil resistance. Refer to Starter Motor Usage Table. |






