SMU - Revised DTC P0146 HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1 Sensor 3

| Subject: | Revised DTC P0146 HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1 Sensor 3 |
| Models: | 1997 Chevrolet Astro Van |
| 1997 GMC Safari Van |
| with 4.3L Engine (VIN W - RPO L35) |
This bulletin is being issued to revise DTC P0146 HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1 Sensor 3 in the Engine Controls-4.3L sub-section of the Service Manual. Please replace the current information in the Service Manual with the following information.
The following information has been updated within SI. If you are using a paper version of this Service Manual, please make a reference to this bulletin on the affected page.
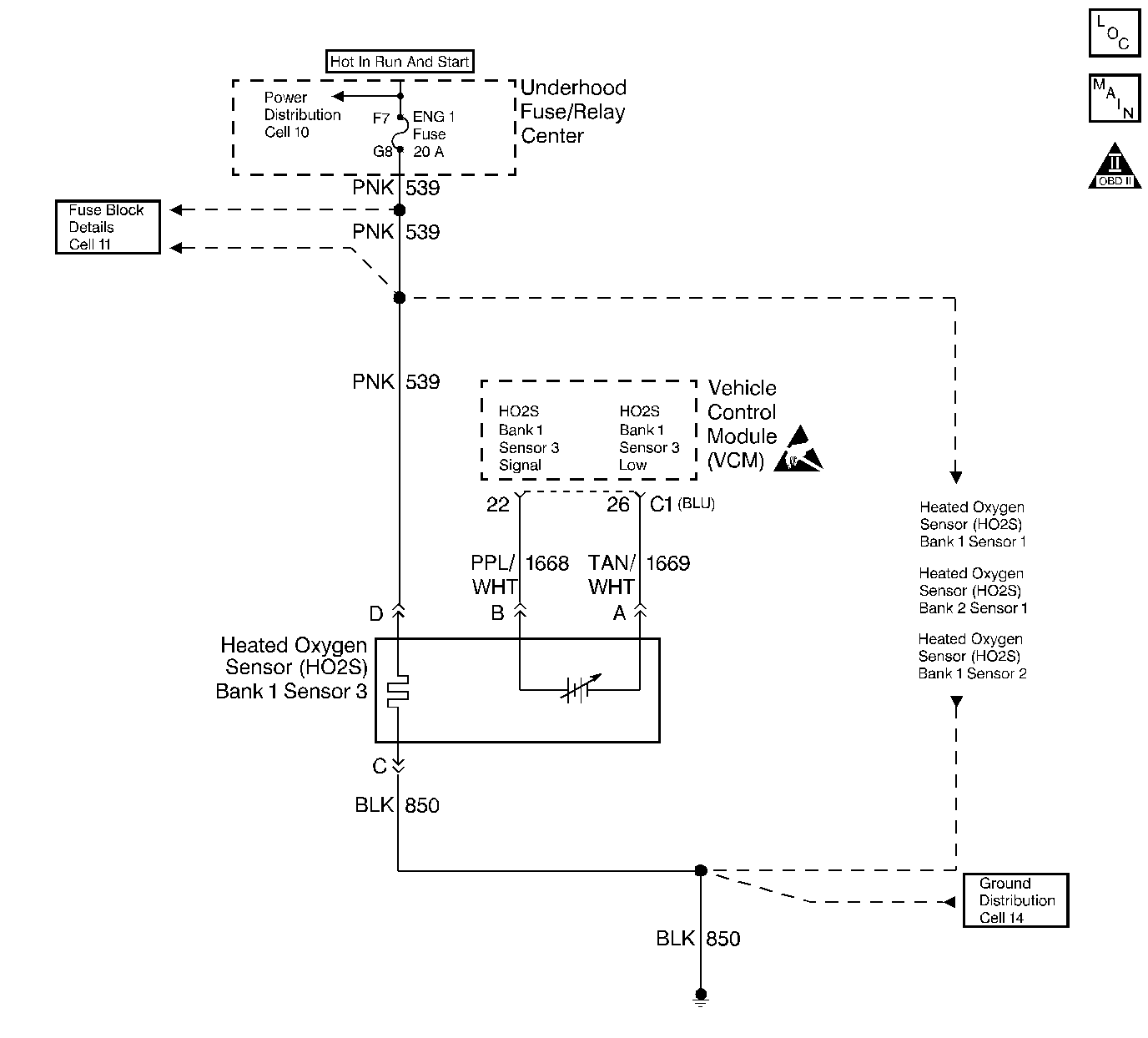
Circuit Description
Important: If the voltage is measured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, the voltage may read as low as 0.32 volt.
The VCM supplies a voltage of approximately 0.45 volts (450 mV) between the HO2S High and the HO2S Low circuits. The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) varies the voltage from approximately 1.0 volt (1000 mV) during rich conditions to 0.10 volt (100 mV) during lean conditions.
The VCM monitors the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) activity for 100 seconds after a Closed Loop. During the monitor period, the VCM counts the number of times that the HO2S switches from rich to lean and from lean to rich and adds the amount of time it took to complete all switches. With this information, an average time for all of the switches can be determined. If the average time to switch is too slow, a DTC P0146 sets.
When the HO2S temperature is below 360°C (600°F), the sensor will not produce any voltage. The sensor will also behave like an open circuit. This will result in an Open Loop operation.
The HO2S heater provides for a faster sensor warm-up which allows the sensor to become active in a shorter period of time and remain active during a long extended idle. The DTC P0146 determines if the HO2S is functioning properly by checking the response time of the sensor. This is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No EVAP DTCs |
| • | No IAT sensor DTCs |
| • | No MAP sensor DTCs |
| • | No ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No MAF sensor DTCs |
| • | No intrusive test in progress |
| • | No device controls active |
| • | The system voltage measures at least 9.0 volts. |
| • | The engine run time is at least 2 minutes. |
| • | HO2S voltage is greater than 0.351 volts (351 mV) but less than 0.473 volts (473 mV). |
HO2S Temperature Test
| • | Not in Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) mode. |
| • | ECT is at least 80°C. |
| • | MAF is at least 15 grams per second. |
HO2S Open Test Enable
| • | HO2S Temperature test has passed. |
| • | Closed Loop. |
| • | The DTC P0147 (HO2S heater) is not set. |
Action Taken When DTC Sets
The VCM turns the MIL ON after the second test failure.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connection repairs, refer to Wiring Repairs.
A intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, a rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the insulation.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection or a damaged harness: Inspect the harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection |
| - | Damaged harness |
| • | A malfunctioning HO2S heater or heater circuit: With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the HO2S voltage displayed on a scan tool should gradually drop to below 0.150 volt, indicating that the heater works properly. If not, disconnect the HO2S and connect a test lamp between the terminals C and D. If the test lamp does not light, repair the open in the HO2S ground circuit or the HO2S ignition feed circuit. If the test lamp lights, replace the HO2S. |
| • | The Intermittent test: Use a scan tool in order to monitor this HO2S signal voltage. Move the related connectors and the wiring harness with a warm engine running at part throttle in Closed Loop. If the failure is induced, the HO2S signal voltage reading changes from its normal fluctuating voltage (above 600 mV and below 300 mV) to a fixed value around 450 mV. This may help to isolate the location of the malfunction. |
Test Description
The numbers listed below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If the voltage is varying above and below the specified value, the condition is not present.
-
If the DTC does not fail, an intermittent condition exists.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check |
2 |
Did the HO2S voltage parameter change more than the specified value? | 200 mV | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
4 |
Is the HO2S voltage parameter more than the specified value? | 800 mV | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 5 |
5 | Measure the voltage from the high signal circuit of the HO2S harness connector on the engine harness side to a good ground with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0.2 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 |
6 |
Important: The sensor may be damaged if the circuit is shorted to a voltage source. Test the HO2S high signal circuit for a short to voltage with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
7 | Measure the voltage from the low signal circuit of the HO2S harness connector on the engine harness side to a good ground with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 2 V | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 9 |
8 | Test the HO2S high signal circuit for an open or high resistance with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
9 |
Is the HO2S voltage parameter less than the specified value? | 100 mV | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 10 |
10 | Test the HO2S low signal circuit for an open or high resistance with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
11 | Test the HO2S low signal circuit for a short to voltage with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 |
12 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the HO2S with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the VCM with a DVM. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 15 |
14 | Replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
15 |
Important: When replacing the VCM, the new VCM will need to be programmed. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming. Replace the VCM. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- |
16 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 17 |
17 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
