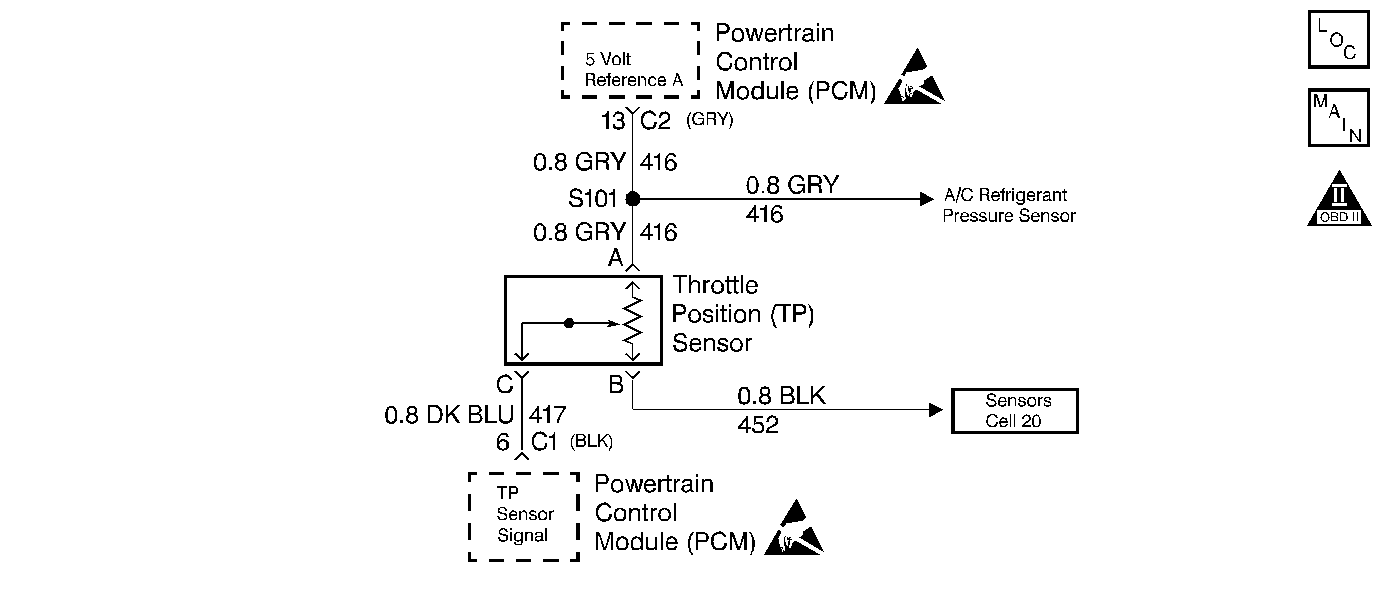
Circuit Description
The PCM supplies a 5V reference signal and a ground to the TP sensor. The TP sensor sends a voltage signal back to the PCM relative to throttle blade opening. Voltage will vary from 0.20 V at closed throttle to over 4.5 V at wide open throttle.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
| • | The TP sensor reads less than 0.19V for 5 seconds. |
| • | The engine is running. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminates. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in The Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers stores this information. |
| • | A history DTC is stored. |
| • | The TP angle will default to 0% when the vehicle speed is less than 2 mph. The TP angle defaults to 10% when the vehicle speed is greater than 2 mph. The scan tool shows the defaulted value. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will turn OFF after 3 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Whenever this DTC cannot be duplicated, use the information included in the Freeze Frame data in order to evaluate the conditions when the DTC set.
A faulty A/C sensor could set a DTC P0122. Disconnect the A/C electrical connector. If the TP reading returns to normal, replace the A/C Refrigerant Sensor.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame Data and the Failure records to the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. This information on the scan tool can be referred to later.
-
The TP sensor has an auto zeroing feature. Whenever the voltage reading is between 0.20 V and 0.90 V, the PCM will automatically assume this as closed throttle position.
-
Whenever the PCM recognizes a high voltage signal, then the PCM and wiring are OK.
-
This simulates a high voltage signal which will identify an open in the signal circuit.
-
Whenever the test lamp illuminates when probing the TP signal circuit, then the TP signal circuit is shorted to ground.
-
Before replacing the PCM, check terminals for improper mating, broken locks, or physical damage to the wiring harness. Reprogram the replacement PCM. Refer to the latest Techline information for programming procedures.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||
Is the TP sensor voltage below the specified value? | 0.2 V | |||
3 |
Is the TP sensor voltage below the specified value? | 0.2 V | ||
Is the TP sensor voltage greater than the specified value? | 4 V | |||
Is the TP sensor voltage greater than the specified value? | 4 V | |||
6 |
Was a repair made? | -- | ||
7 |
Was a repair made? | -- | ||
Was a repair made? | -- | |||
9 |
Was a repair made? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | 90°-95° C | ||
13 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
