Transfer Case Shift Control Switch
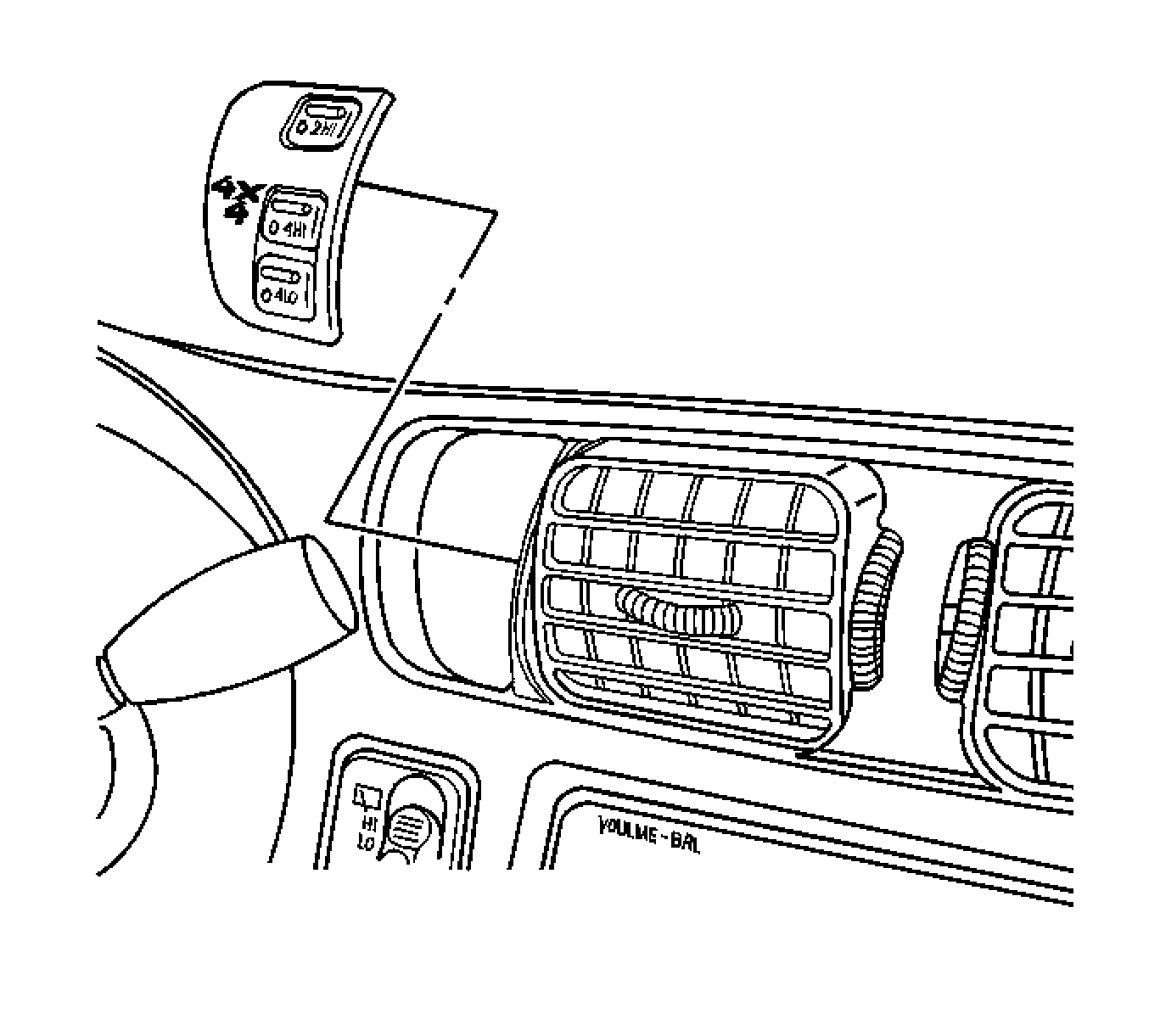
The NVG 236 transfer case features a 4 button shift control switch located on the instrument panel. When the vehicle has the ignition key in the RUN position, the transfer case shift control module starts monitoring the transfer case shift control switch to determine if the driver desires a new mode/gear position. At a single press of the transfer case shift control switch, the lamp of the new desired position begins flashing, to inform the driver that the transfer case shift control module has received the request for a new mode/gear position. The lamp continues to flash until all shifting criteria has been met and the new mode/gear position has been reached, or has been engaged. Once the new mode/gear position is fully active, the switch indicator lamp for the new position will remain ON constantly.
During normal driving situations, the transfer case can operate in the Auto 4WD mode. In the Auto 4WD mode, the transfer case shift control module monitors rear wheel slip speed, based on the inputs from both the front and rear propshaft speed sensors. When the vehicle experiences a rear wheel slip condition, the transfer case shift control module sends a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal to an electronic motor, which is the transfer case encoder motor. This motor rotates the transfer case sector shaft, applying a clutch pack. This clutch pack is designed to deliver a variable amount of torque, normally delivered to the rear wheels, and transfers it to the front wheels. Torque is then ramped up to the front wheels until the front propshaft speed sensor matches that of the rear propshaft speed sensor. Torque is then ramped down until torque is completely removed from the front wheels or until rear wheel slip is once again detected. The process would then repeat.
The NVG 236 transfer case has the added feature of also providing the driver with 3 manual mode/gear positions:
| • | 4HI - 4 Wheel Drive high range |
| • | 2HI - 2 Wheel Drive high range |
| • | 4LO - 4 Wheel Drive low range |
The driver may choose to select any of these mode/gear positions while driving the vehicle. However, the transfer case will not allow a shift into or out of 4LO unless the following criteria has been met:
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The automatic transmission is in NEUTRAL, clutch depressed on manual transmissions. |
| • | The vehicle speed is below 5 km/h (3 mph). |
This transfer case also has a NEUTRAL position. A shift to the NEUTRAL position allows the vehicle to be towed without the rear axle rotating the transfer case input shaft and the transmission output shaft. NEUTRAL position may be obtained only if the following criteria has been met:
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The automatic transmission is in NEUTRAL, clutch depressed on manual transmissions. |
| • | The vehicle speed is below 5 km/h (3 mph). |
| • | The transfer case is in 2HI mode. |
Once these conditions have been met, press and hold both the 2HI and 4LO buttons for 10 seconds. When the system completes the shift to NEUTRAL, the red neutral lamp illuminates.
The NVG 236 case halves are high-pressure die-cast magnesium. Ball bearings support the input shaft, the front output shaft, and the rear output shaft. A thrust bearing is located inside of the input shaft gear to support the front of the rear output shaft. The transfer case requires Auto Trac® II Fluid GM P/N 12378508 (Canadian P/N 10953626), which is blue in color. The fluid is designed for smooth clutch application. An oil pump, driven by the rear output shaft, pumps the fluid through the rear output shaft oil gallery to the clutch and bearings.
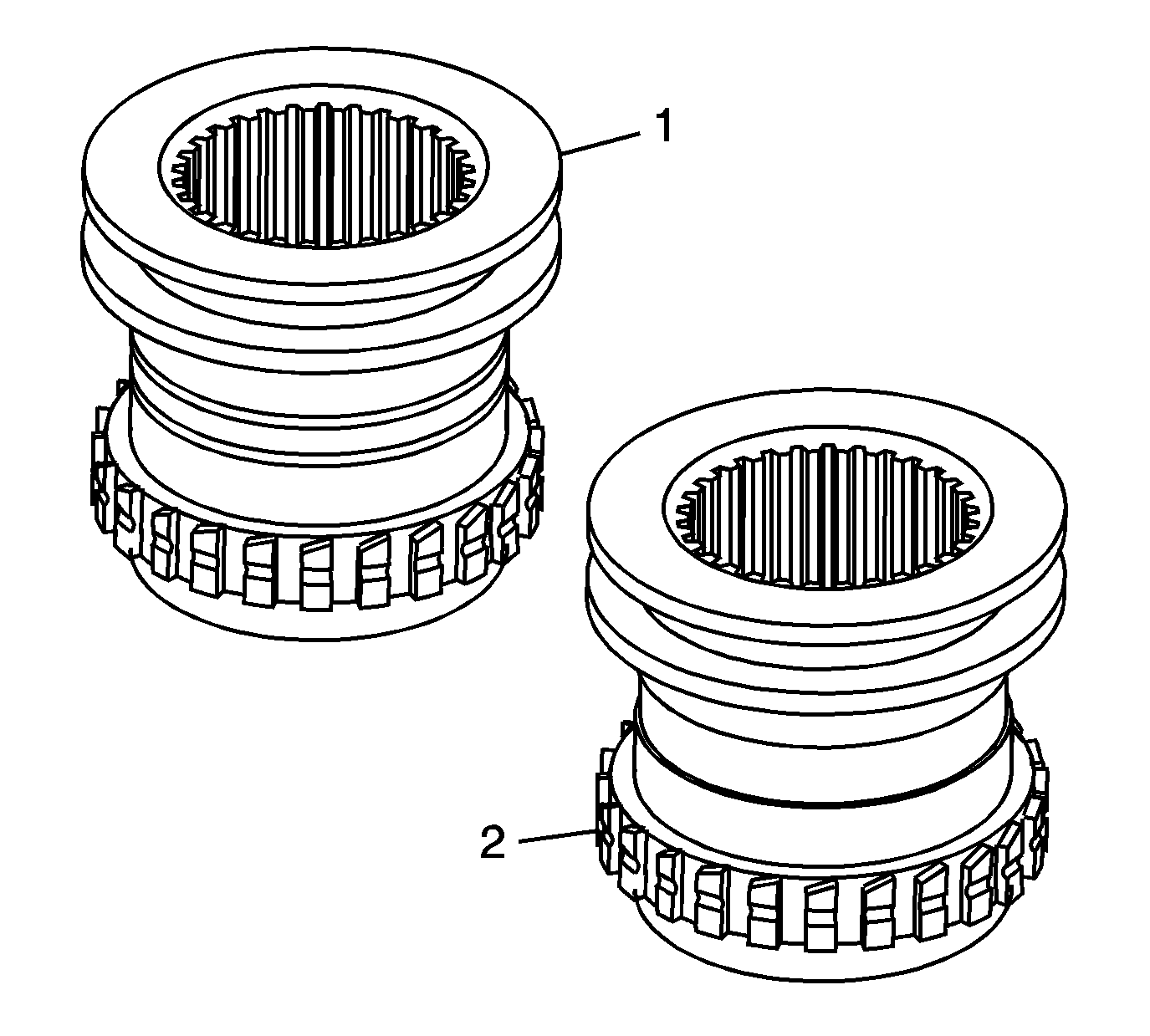
Some of the changes to the transfer case, that will take place during this model year, include the following components to the high/low range shifting mechanism:
| • | The range shift fork pads change from a Peak® 3-piece design to a Vespel® 2-piece design. |
| • | The 3 notches in the high/low range shift fork are deeper for the Vespel® pads. |
| • | The high/low range sleeve collar is wider for the Vespel® pads. |
| • | The high/low range sleeves can be identified by the grooves in the collar. |
| - | The 1st design high/low range sleeve (1) that uses the Peak® 3-piece pads has 2 narrow grooves in the collar. |
| - | The 2nd design high/low range sleeve (2) that uses the Vespel® 2-piece pads has 1 wide groove in the collar. |
2WD Power Flow
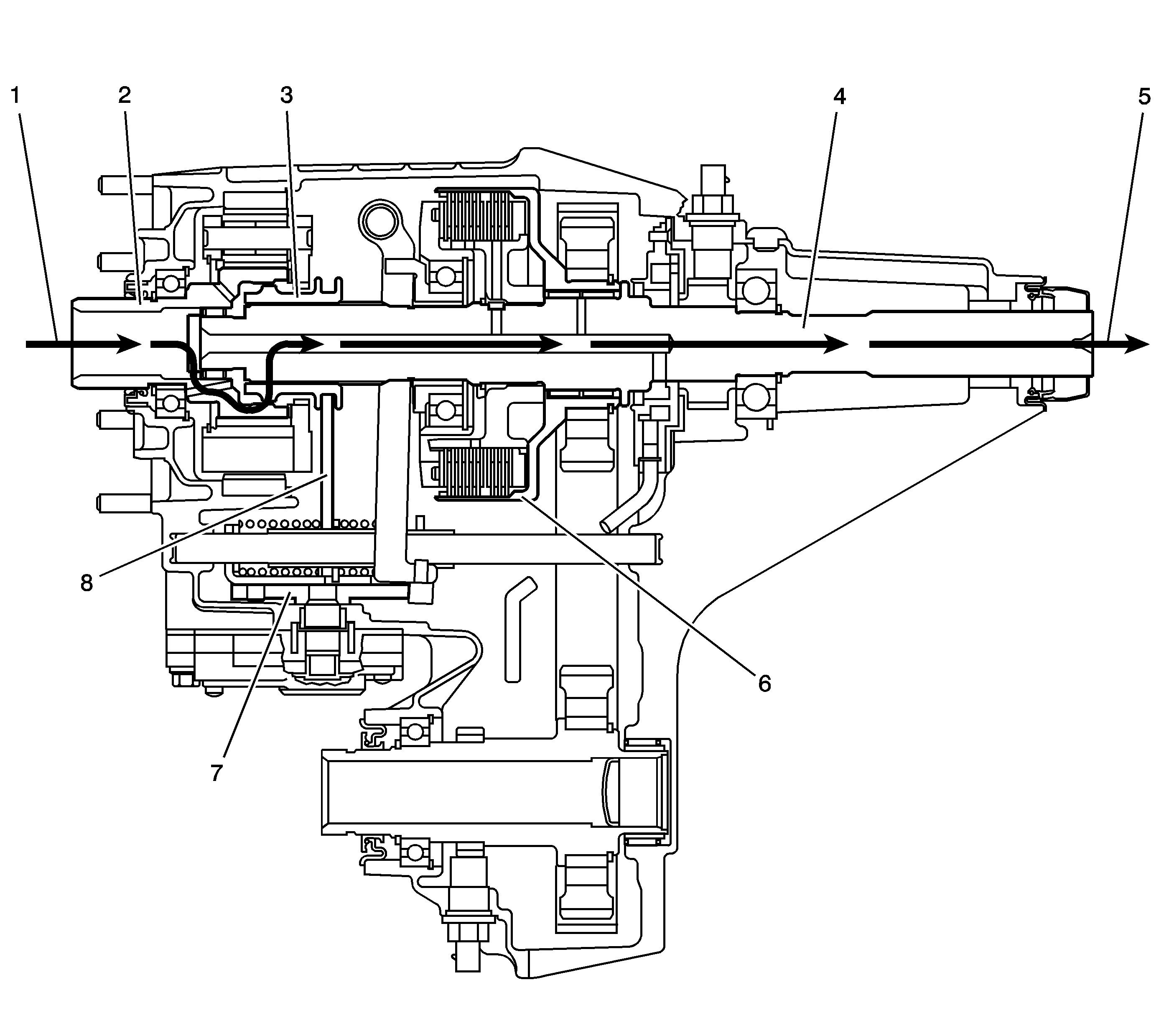
When the NVG 236 is in the 2HI mode, the power flows from the transmission (1) to the input shaft gear (2). The input shaft gear (2) is connected to the rear output shaft (4) by the high/low range sleeve (3). The range sleeve (3) outer teeth are engaged with the input shaft gear (2) inner, high-speed position teeth. At the same time the range sleeve is slip splined to the rear output shaft (4). The rear output shaft (4) delivers the power flow to the rear propshaft (5). The position of the control actuator lever shaft (7) allows no clutch (6) engagement. The high/low range shift fork (8), is in the high-speed position on the control actuator lever shaft (7).
4HI and AWD Power Flow
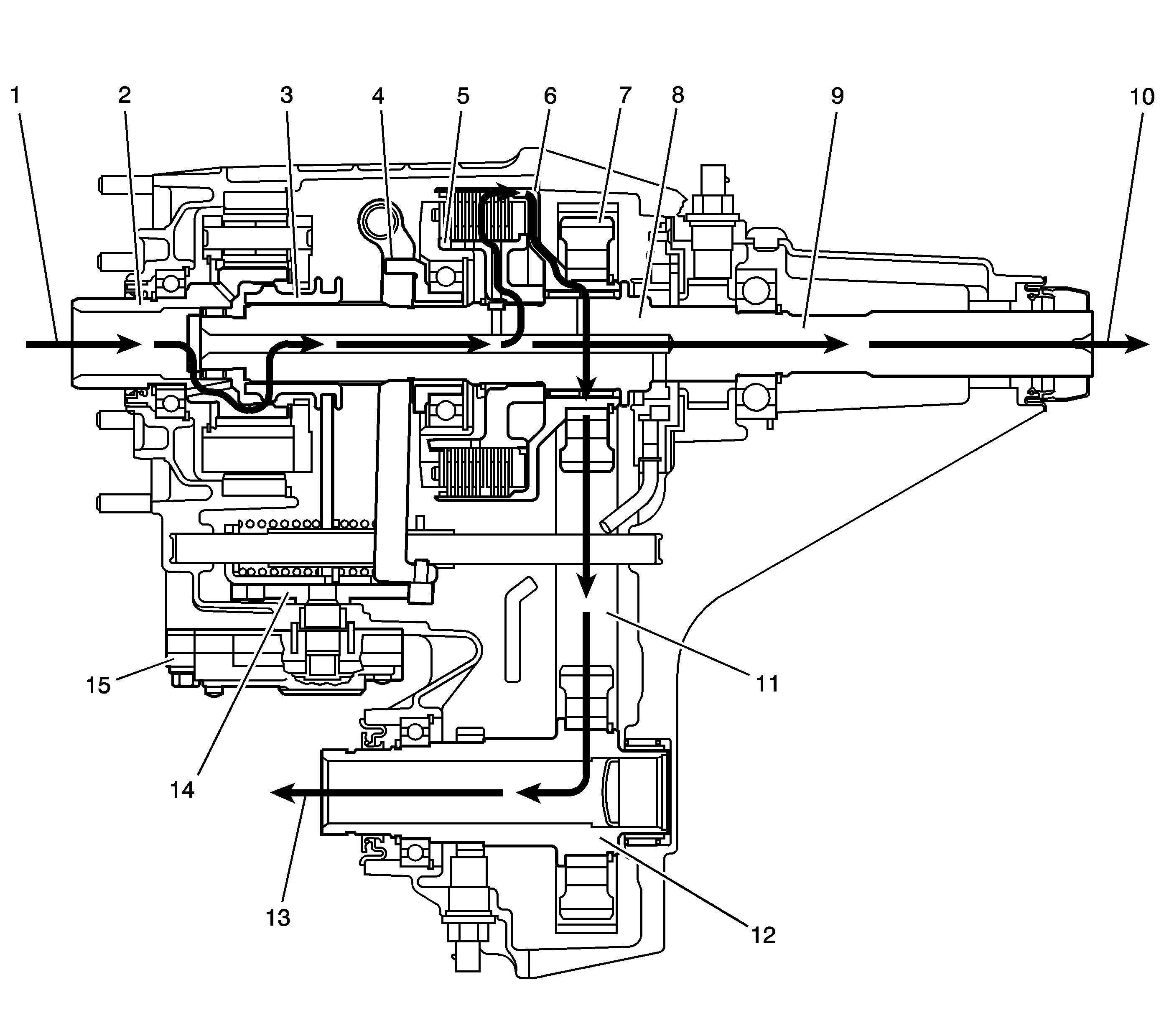
In the 4HI mode, the power flow to the rear propshaft (10) is the same as it is in the 2HI mode. To deliver power flow to the front propshaft (13) during the 4HI position, the transfer control module commands the encoder motor (15) to apply the clutch to a calibrated torque. The encoder motor (15) turns the control actuator lever shaft (14). A brake in the encoder motor (15) holds the control actuator lever shaft (14) in the full clutch position. The control actuator lever shaft (14) is cam designed and the cam action moves the clutch lever (4). The clutch lever (4) pivots on the clutch lever pivot studs and moves toward the clutch apply plate, to engage the clutch. As more pressure is applied to the clutch apply plate, the clutch discs are compressed. Using inner clutch discs, which are engaged with the clutch hub (5), and the outer clutch discs, which are engaged with the clutch housing (6), the power flow is delivered to the clutch housing (6). The clutch hub (5) is splined to the rear output shaft (9), and the clutch housing (6) rotates on a needle bearing on the rear output shaft (9). The chain drive sprocket (7) is splined to the clutch housing (6). The power flows from the drive sprocket (7), through the chain (11), to the chain driven sprocket. The driven sprocket is splined to the front output shaft (12). The power flow is delivered to the front propshaft (13) through the front output shaft (12).
During the Auto 4WD mode, the power flow is the same as it is in the 4HI mode. Except, during the Auto 4WD mode, the encoder motor (15) rotates the control actuator shaft lever (14) to the correct torque level positions. Rotating the control actuator (14) to the various positions changes the clutch torque level. When a difference of front propshaft (13) to rear propshaft (10) speed is recognized, the transfer case control module commands for more or less clutch torque.
4LO Power Flow
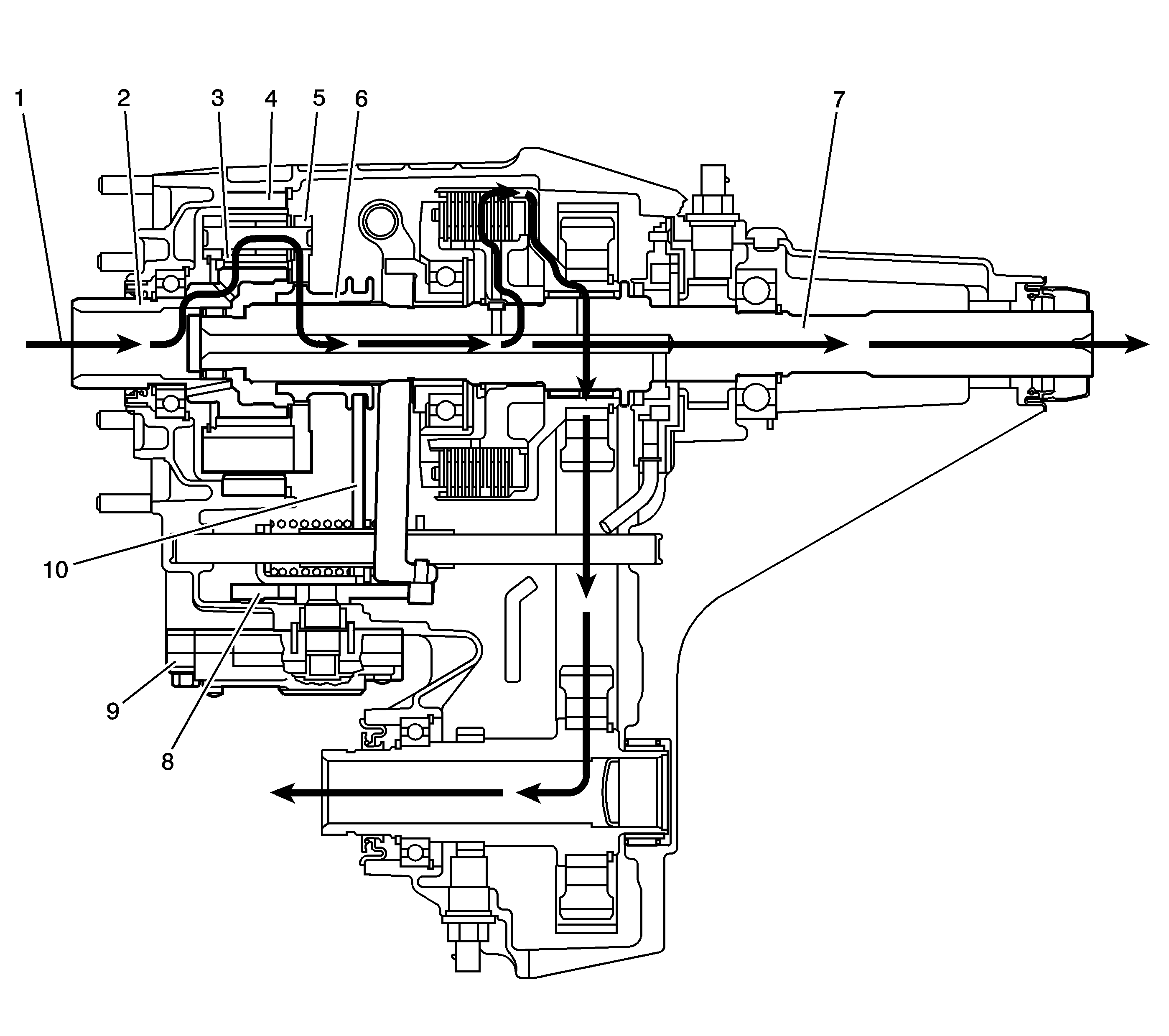
When shifting the transfer case to the 4LO mode, it commands the encoder motor (9) to turn the control actuator lever shaft (8), to move the high/low range shift fork (10). The shift fork (10) moves the high/low range sleeve (6), which is slip splined on the rear output shaft (7) toward the rear of the transfer case. The range sleeve (6) outer teeth disengage from the input shaft gear (2) inner teeth. The range sleeve (6) outer teeth then engage in the planetary carrier (5) teeth. The power flow is now from the input shaft gear (2) planetary teeth to the planetary gears (3) in the carrier. Rotating the planetary gears (3), which are engaged in the annulus gear (4), the planetary carrier (5) rotates. The planetary carrier (5) engaged to the range sleeve (6), drives the rear output shaft (7), providing a 2.72:1 reduction to the speed of the rear output shaft (7). The power flow to the front propshaft is the same as it is in the 4HI.
A NEUTRAL position is obtained when the range sleeve (6) is not engaged to the input shaft gear (2) or the planetary carrier (5). NEUTRAL position is used for towing the vehicle.
Transfer Case Electrical Components
View the list of major components that make up the automatic transfer case (ATC) system below.
SERVICE 4WD Indicator
The SERVICE 4WD indicator is an integral part of the cluster and cannot be serviced separately. This lamp is used to inform the driver of malfunctions within the ATC system. The SERVICE 4WD indicator is controlled by the transfer case shift control module via a Class 2 message or by a Service Indicator Control circuit.
Transfer Case Encoder
The encoder is mounted to the transfer case encoder motor assembly and is replaced only as an assembly. The encoder converts the sector shaft position, representing a mode or range, into electrical signal inputs to the transfer case shift control module. The module detects the position the transfer case is in by monitoring the 4 encoder channels, P, A, B, and C. These inputs translate into AUTO 4WD, 2HI, 4HI, NEUTRAL, and 4LO or whether the motor is still in transition between gears. The transfer case encoder channel circuits may be monitored using a scan tool.
Transfer Case Encoder Motor
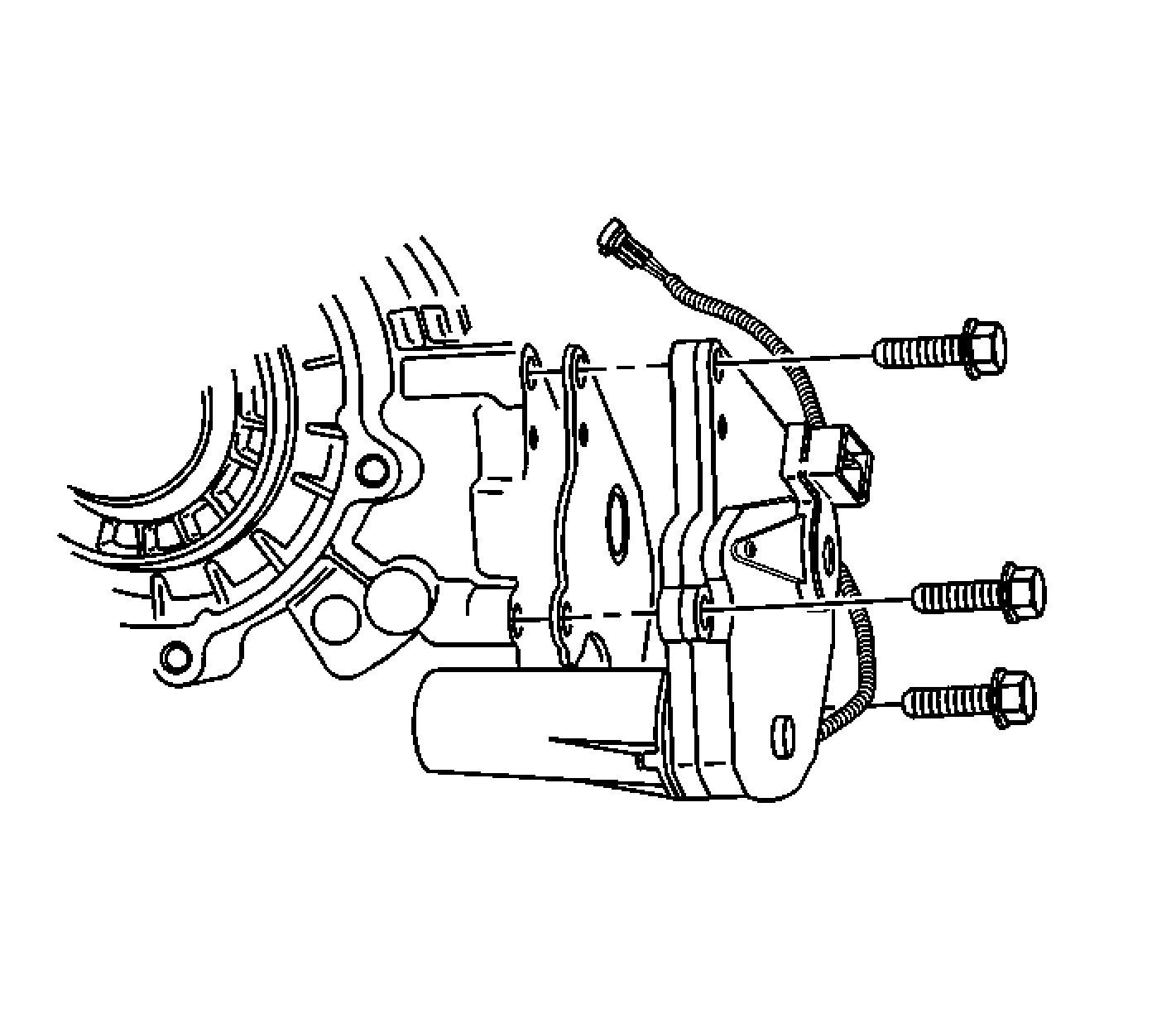
The transfer case encoder motor consists of a permanent magnet (PM) DC motor and gear reduction assembly. It is located on the left hand side of the transfer case. When activated, it turns the sector shaft of the transfer case clockwise or counterclockwise to shift the transfer case and to apply the clutch that applies torque to the front propshaft. The encoder motor is controlled with a PWM circuit provided by the transfer case shift control module. This circuit consists of a driver on both the Motor Control A and Motor Control B circuits. The encoder motor is bi-directional to allow the motor to shift the transfer case from 2HI or 4HI to NEUTRAL and 4LO positions. The transfer case encoder motor can be turned ON and OFF using a scan tool. You may also monitor Motor Control A and B circuits using a scan tool.
Transfer Case Motor Lock
The transfer case motor lock is used to prevent the transfer case from changing mode/gear positions or popping out of position when the vehicle is in 2HI, 4HI, and 4LO. When the lock circuit is energized, the transfer case encoder motor is allowed to rotate. When the transfer case is placed 2HI, 4HI, or 4LO, the motor lock circuit has no voltage provided to it, applying the lock, which assures that the transfer case remains in the current mode/gear position. When AUTO 4WD is selected, the motor lock remains applied until an adaptive mode, torque being applied to the front propshaft, is required. During an adaptive mode, the motor lock circuit is energized, the locking mechanism is released, enabling the encoder motor to turn and apply torque to the front propshaft. The transfer case motor lock circuit can be turned ON and OFF using a scan tool. You may also monitor the lock circuit using a scan tool.
Transfer Case Shift Control Module
The transfer case shift control module uses the VIN information for calculations that are required for the different calibrations, based on axle ratio, transmission, tire size, and engine. The system does not know which calibration to use without this information. This information is provided to the transfer case shift control module via Class 2 data bus from the powertrain control module (PCM). The transfer case shift control module monitors front and rear propshaft speed, as well as controlling the operation of the transfer case encoder motor assembly and the engaging and disengaging of the front axle.
Transfer Case Speed Sensors
There are three speed sensors mounted on the transfer case. 2 speed sensors are mounted on the rear output shaft and one on the front output shaft. Each speed sensor is a PM generator. The PM generator produces a AC voltage. The AC voltage level and number of pulses increases as speed increases.
Front Propshaft Speed Sensor
The transfer case shift control module converts the pulsating AC voltage from the front transfer case speed sensor to front propshaft speed in RPM to be used for calculations, and to monitor the difference between the front and rear sensor speed. It is also used in the AUTO 4WD mode to determine the amount of slip and the percent of torque to apply to the front axle. The front propshaft speed can be displayed with a scan tool.
Rear Propshaft Speed Sensor
The transfer case shift control module converts the pulsating AC voltage from the rear transfer case speed sensor to a rear propshaft speed in RPM to be used for calculations. The rear propshaft speed can be displayed with a scan tool.
Vehicle Speed Sensor
One of the two speed sensors on the rear output shaft is the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) input to the PCM. The PCM sends this information to the transfer case shift control module via the Class 2 serial data bus.
