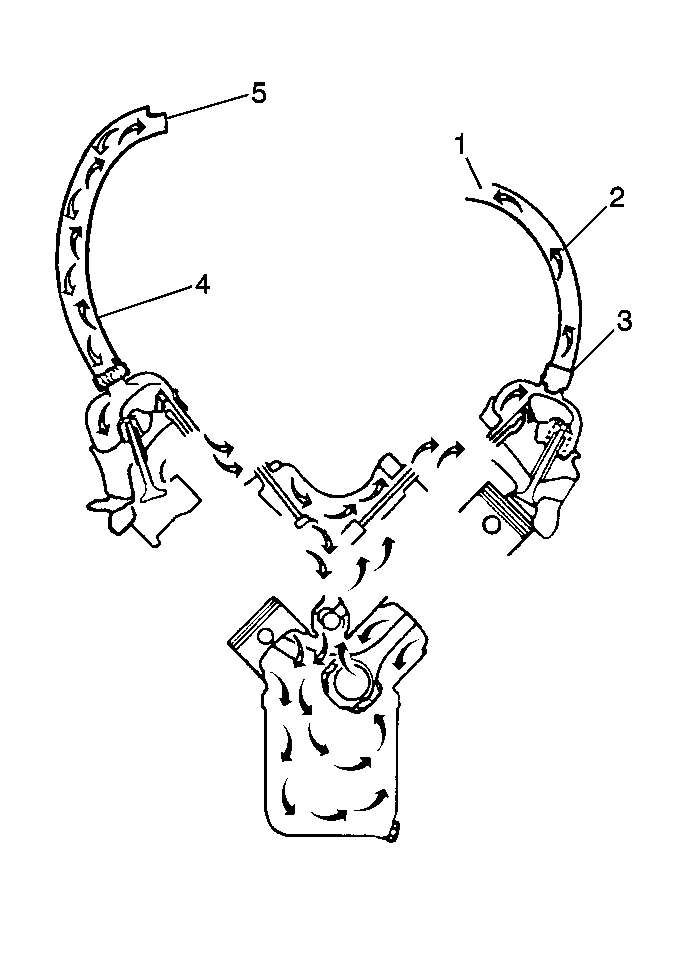
A closed crankcase ventilation system is used to provide
a more complete scavenging of crankcase vapors. Fresh air from the air cleaner
is supplied to the crankcase, mixed with blow-by gases and then passed
through a crankcase ventilation valve into the intake manifold.
Typical Crankcase Ventilation Valve Flow