Standard Rear Axle
The solid rear axle is a semi-floating hypoid rear axle, which is designed
for use with the following components:
| • | An exposed one-piece or two-piece propeller shaft. |
The rear axle has a hypoid type differential ring gear. The centerline of the
differential drive pinion gear is located below the centerline of the hypoid type
differential ring gear. The rear axle housing encloses all of the components that
are necessary for transmitting power from the propeller shaft to the rear wheel and
tire assemblies. Bolts attach the rear axle housing cover to the back of the rear
axle housing. The rear axle housing cover is removable in order to permit service
of the differential case without removing the entire axle from the vehicle.
A universal joint connects the rear end of the propeller shaft to the drive
pinion gear yoke. The drive pinion gear yoke has a splined end that fits over the
drive pinion gear. The splined end of the drive pinion gear yoke also drives the
pinion gear. Two preloaded tapered drive pinion gear bearings support the drive pinion
gear in the rear axle housing. The races of the following components are press fit
into the rear axle housing:
| • | The inner drive pinion gear bearing press fits onto the drive pinion
gear. |
| • | The outer drive pinion gear bearing combines a light press fit to a close
sliding fit on the yoke end of the drive pinion gear. |
The races of the inner drive pinion gear bearing and the outer pinion gear
bearing press against shoulders which are recessed in the rear axle housing.
Tightening the drive pinion gear nut compresses a collapsible drive pinion
gear spacer. This bears against the following components:
| • | The outer drive pinion gear bearing |
| • | A shoulder on the drive pinion gear |
The drive pinion gear spacer performs the following actions:
| • | Enables automatic bearing preload adjustment. |
| • | Maintains a preload on the inner drive pinion gear bearing. |
| • | Maintains a preload on the outer drive pinion gear bearing. |
Enable the adjustment of the fore-and-aft position of the drive pinion gear
by placing selective drive pinion gear shims between the following components:
| • | The head of the drive pinion gear |
| • | The inner drive pinion gear bearing |
The differential case is one piece. Two differential side bearings support
the differential case in the rear axle housing. The differential side bearings are
preloaded by the insertion of differential bearing shims between the following components:
| • | The differential side bearings |
Varying the shim thickness from side to side positions the differential case
for proper backlash between the differential ring gear and the differential drive
pinion gear.
Bolts attach the differential ring gear to the differential case. The following
components have splined bores used for driving the axle shaft:
| • | The left differential pinion gear |
| • | The right differential pinion gear |
The position of these pinion gears permits the gears to turn in counterbored
cavities of the differential case. The following components have smooth bores:
| • | The upper differential pinion gear |
| • | The lower differential pinion gear |
The differential pinion gear shaft holds these pinion gears in position. The
differential pinion gear shaft mounts and locks in the differential case. All four
of the gears mesh with each other.
The following components turn freely on the pinion gear shaft:
| • | The upper differential pinion gear |
| • | The lower differential pinion gear |
These pinion gears act as idler gears when the rear wheels turn at different
speeds.
The following components back the differential pinion gears:
| • | Differential pinion thrust washers |
| • | Differential side gear thrust washers |
Vehicles that are equipped with the standard rear axle and the Antilock Brake
System (ABS) only, have a single reluctor wheel mounted on the differential carrier
behind the ring gear. A wheel speed sensor is bolted to the top of the rear axle
housing opposite the reluctor wheel. This sensor provides wheel speed information
to the electronic brake control module (EBCM)
Vehicles that are equipped with the limited slip rear axle, ABS, and Traction
Control System (TCS) have rear wheel speed sensors mounted on the axle shafts just
behind the axle flange. The axle mounted reluctor wheels are an integral part of
the rear axle shaft and cannot be replaced separately.
Limited Slip Rear Axle
Limited slip rear axles have several definite operating characteristics. An
understanding of these characteristics is necessary in order to aid diagnostics.
The rear axle limited slip differential that is used --is the Zexel Torsen®
rear axle. The Zexel Torsen® axle utilizes parallel axis helical gearing to develop
side gear separating force in an axial direction and planetary gear separating force
in a radial direction.
A thrust block is used in the Zexel Torsen® differential for retention
of the C-clip.
The Zexel Torsen® limited slip differential is non-serviceable. Diagnosis
is limited to the inspection of the unit for excessive wear to the helical gears or
the differential case. The differential should not be disassembled nor should the
helical gears be removed. The differential cases of the 2 vehicles are not
interchangeable. The following procedures are the same for both the Torsen® limited
slip differential case and the standard rear axle differential case:
| • | Removal of the differential |
| • | Replacement of the differential |
| • | Service of the side bearings |
| • | Service of the ring and pinion gear set |
| • | All backlash and tooth contact pattern procedures |
Operation
When the vehicle turns a corner, the differential allows the outer rear tire
and wheel assembly to turn faster than the inner tire and wheel assembly.
The inner tire and wheel assembly moves more slowly than the outer tire and
wheel assembly. The inner tire and wheel assembly slows its side differential pinion
gear. The side differential pinion gear is slowed because the axle shaft is splined
to the side gear.
The differential pinion gears roll around the slowed side differential pinion
gear. This action causes the other differential pinion gear and the tire and wheel
assembly to move faster.
Rear Axle Identification
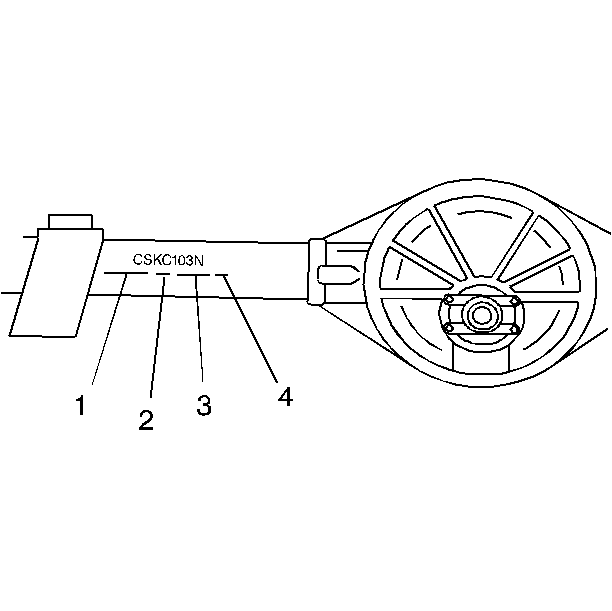
The following information is stamped onto the forward side of the right axle
housing tube or on a metal tag on the housing cover:
| • | The rear axle identification code (1) |
| • | The manufacturer's code (2) |
This information is necessary in order to repair or adjust the differential.
The RPO codes for the rear axle are also printed on the service parts identification
label.

