Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
The fuel tank stores the fuel supply. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank with the fuel level sensor assembly, pumps fuel through an in-line fuel filter to the fuel rail assembly. The pump provides fuel at a pressure greater than is needed by the injectors. The fuel pressure regulator, part of the fuel rail assembly, keeps fuel available to the injectors at a regulated pressure. A separate pipe returns unused fuel to the fuel tank.
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank stores fuel for the vehicle. The fuel tank is located behind the rear wheels and is held in place by two metal straps and a cross strap attached to the underbody. The tank shape includes a reservoir to maintain a constant supply of fuel around the fuel pump strainer during low fuel conditions and aggressive vehicle maneuvers. The fuel tank is molded from high density polyethylene. When working on or near the fuel tank, be sure to observe important information molded on the bottom of the tank.
Fuel Tank Filler Pipe
The fuel tank filler pipe outlet is positioned at the rear of the vehicle. The fuel filler pipe has a built-in restrictor and deflector in order to prevent refueling with leaded fuel.
Fuel Filler Cap
The filler pipe has a threaded-type cap. The threaded part of the cap requires several turns counterclockwise to remove. A torque-limiting device prevents the cap from being over tightened. To install the cap, turn the cap clockwise until you hear a clicking noise. This indicates that the cap is correctly torqued and fully seated.
Notice: If a fuel tank filler pipe cap requires replacement, use only a fuel tank filler pipe cap with the same features. Failure to use the correct fuel tank filler pipe cap can result in a serious malfunction of the fuel system.
Fuel Sender Assembly
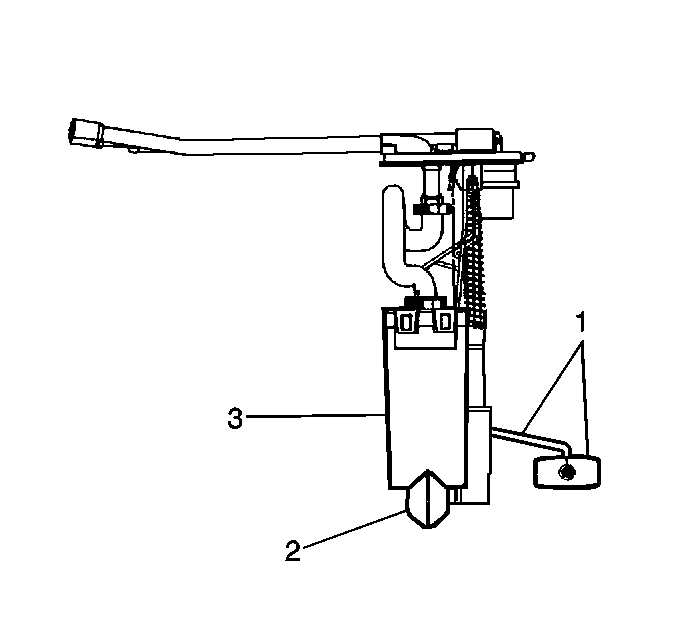
The fuel sender assembly is inside the fuel tank attached to the top of the fuel tank. The fuel sender assembly consists of the following major components:
| • | The fuel sender (1). |
| • | The fuel pump (3). |
| • | The fuel pump strainer (2). |
Fuel Sender
The fuel sender consists of a float, a wire float arm, a rheostat, and a roll-over valve. Fuel level is sensed by the position of the float and float arm which operate the 90 ohm rheostat. As the float position changes, the amount of current passing through the rheostat varies, thus changing the gauge reading on the instrument panel. The EVAP pipe of the fuel sender has a pressed in roll-over valve. The roll-over valve prevents fuel from entering the evaporative emission canister if the vehicle rolls over by shutting OFF the EVAP pipe to the canister.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump attaches to the fuel sender assembly inside the fuel tank. The fuel pump is an electric medium pressure twin turbine pump. The fuel pump pumps fuel to the fuel rail assembly at a specified flow and pressure. Excess fuel returns to the fuel tank by the return pipe. The fuel pump delivers a constant flow of fuel to the engine even during low fuel conditions and aggressive vehicle maneuvers. The PCM controls the electric fuel pump operation through a fuel pump relay.
Fuel Pump Strainer
The fuel pump strainer attaches to the lower end of the fuel pump. The fuel pump strainer is made of woven plastic. The functions of the fuel pump strainer are to filter contaminants and to wick fuel. The fuel pump strainer is self-cleaning and normally requires no maintenance. Fuel stoppage at this point indicates that the fuel tank contains an abnormal amount of sediment or water. Clean the fuel tank and replace a plugged fuel pump strainer with a new one.
In-Line Fuel Filter
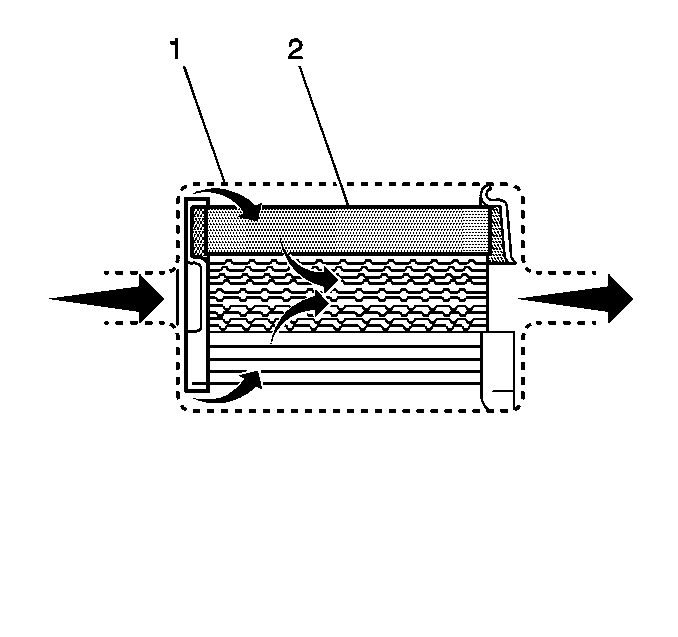
The fuel feed pipe has a steel fuel filter installed ahead of the fuel injection system. The paper filter element (2) traps particles in the fuel that may damage the injection system. The filter housing (1) is made to withstand maximum fuel system pressure, exposure to fuel additives, and changes in temperature. Quick-connect type fittings are used at both ends of the filter. There is no service interval for fuel filter replacement. Replace a restricted fuel filter.
Nylon Fuel Pipes
Caution: In order to Reduce the Risk of Fire and Personal Injury:
• If nylon fuel pipes are nicked, scratched or damaged during installation,
Do Not attempt to repair the sections of the nylon fuel pipes. Replace them. • When installing new fuel pipes, Do Not hammer directly on the
fuel harness body clips as it may damage the nylon pipes resulting in a possible
fuel leak. • Always cover nylon vapor pipes with a wet towel before using a
torch near them. Also, never expose the vehicle to temperatures higher than
115°C (239°F) for more than one hour, or more than 90°C (194°F)
for any extended period. • Before connecting fuel pipe fittings, always apply a few drops
of clean engine oil to the male pipe ends. This will ensure proper reconnection
and prevent a possible fuel leak. (During normal operation, the O-rings located
in the female connector will swell and may prevent proper reconnection if
not lubricated.)
Nylon fuel pipes are designed to perform the same job as the steel or flexible fuel pipes or hoses that they replace. Nylon pipes are constructed to withstand maximum fuel system pressure, exposure to fuel additives, and changes in temperature. There are two sizes of nylon fuel pipes used: 3/8 in ID for the fuel feed, and 5/16 in ID for the fuel return.
The fuel feed and return pipes are assembled as a harness. Retaining clips hold the pipes together and provide a means for attaching the pipes to the vehicle. Heat resistant rubber hose and/or corrugated plastic conduit protect the sections of the pipes that are exposed to chafing, high temperature or vibration.
Nylon fuel pipes are somewhat flexible and can be formed around gradual turns under the vehicle. However, if nylon fuel pipes are forced into sharp bends, the pipes will kink and restrict the fuel flow. Also, once exposed to fuel, nylon pipes may become stiffer and are more likely to kink if bent too far. Take special care when working on a vehicle with nylon fuel pipes.
Caution: In order to Reduce the Risk of Fire and Personal Injury:
• If nylon fuel pipes are nicked, scratched or damaged during installation,
Do Not attempt to repair the sections of the nylon fuel pipes. Replace them. • When installing new fuel pipes, Do Not hammer directly on the
fuel harness body clips as it may damage the nylon pipes resulting in a possible
fuel leak. • Always cover nylon vapor pipes with a wet towel before using a
torch near them. Also, never expose the vehicle to temperatures higher than
115°C (239°F) for more than one hour, or more than 90°C (194°F)
for any extended period. • Before connecting fuel pipe fittings, always apply a few drops
of clean engine oil to the male pipe ends. This will ensure proper reconnection
and prevent a possible fuel leak. (During normal operation, the O-rings located
in the female connector will swell and may prevent proper reconnection if
not lubricated.)
Quick-Connect Fittings
Quick-connect fittings provide a simplified means of installing and connecting fuel system components. The fittings consist of a unique female connector and a compatible male pipe end. O-rings, located inside the female connector, provide the fuel seal. Integral locking tabs or fingers hold the fittings together.
EVAP Pipes and Hoses
The EVAP pipe extends from the fuel sender assembly to the evaporative emission canister. The EVAP pipe is made of nylon pipe. The EVAP pipe connects to the fuel sender assembly and the evaporative emission canister with fuel resistant rubber hoses.
Caution: In order to Reduce the Risk of Fire and Personal Injury:
• If nylon fuel pipes are nicked, scratched or damaged during installation,
Do Not attempt to repair the sections of the nylon fuel pipes. Replace them. • When installing new fuel pipes, Do Not hammer directly on the
fuel harness body clips as it may damage the nylon pipes resulting in a possible
fuel leak. • Always cover nylon vapor pipes with a wet towel before using a
torch near them. Also, never expose the vehicle to temperatures higher than
115°C (239°F) for more than one hour, or more than 90°C (194°F)
for any extended period. • Before connecting fuel pipe fittings, always apply a few drops
of clean engine oil to the male pipe ends. This will ensure proper reconnection
and prevent a possible fuel leak. (During normal operation, the O-rings located
in the female connector will swell and may prevent proper reconnection if
not lubricated.)
