Valve Guide Reaming, and Valve and Seat Grinding L98, LS2
Tools Required
J 37378-1 Valve Guide Reamer
Valve Guide Reaming
Important:
| • | Above acceptable valve stem-to-guide clearance may cause a noisy valve
train, premature valve stem oil seal wear, component damage, and/or above acceptable
engine oil consumption. |
| • | Insufficient valve stem-to-guide clearance will result in noisy or sticking
valves. Valves that are too tight may disturb engine smoothness or lead to component
damage. |
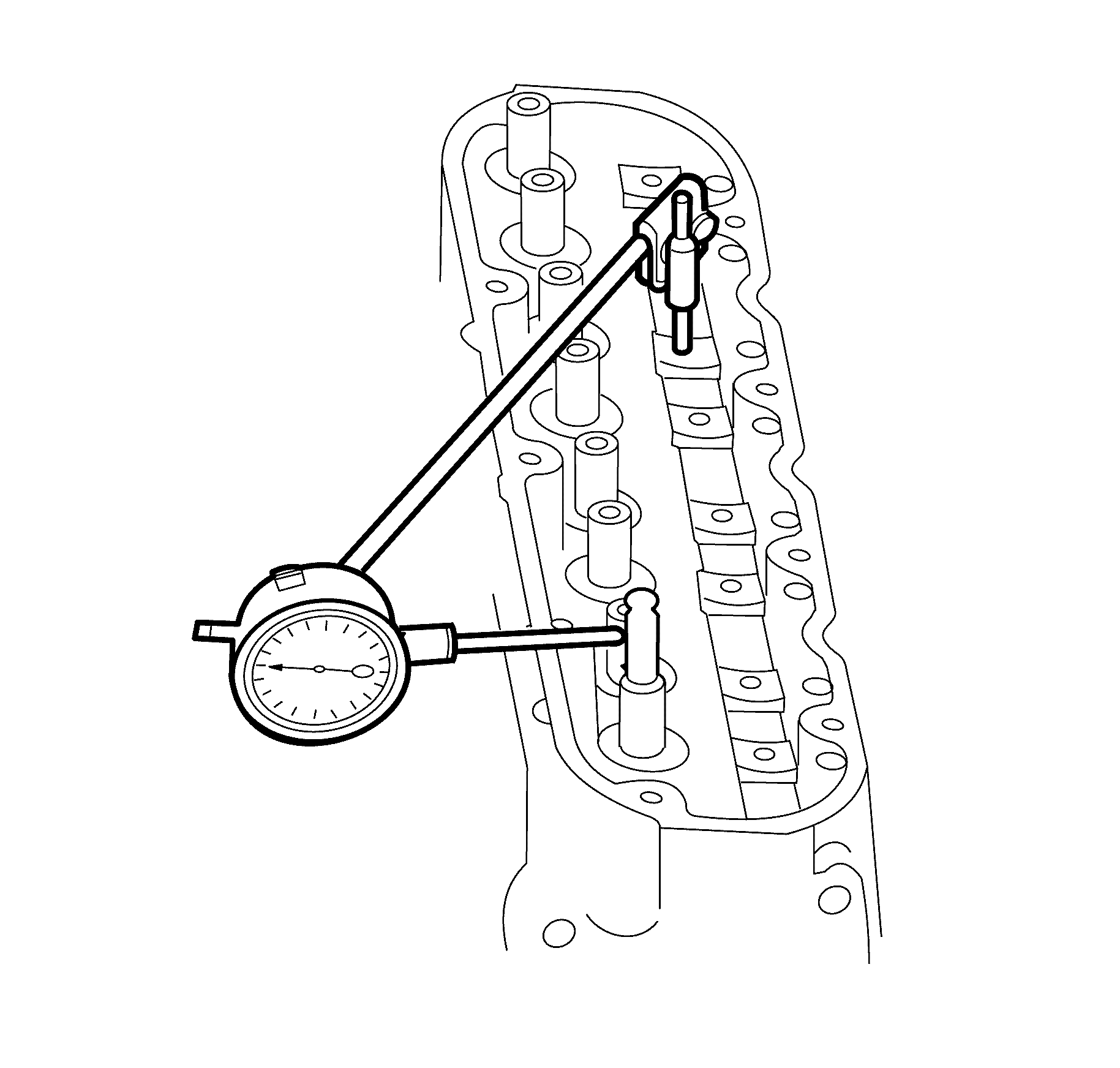
- Measure the valve stem-to-guide clearance using a dial indicator. Position the
tip of the dial indicator at the top of the valve guide.
Valve stem-to-guide
clearance may also be obtained by using a micrometer to measure the valve stem diameter
and a ball type measuring gauge to measure the guide bore.
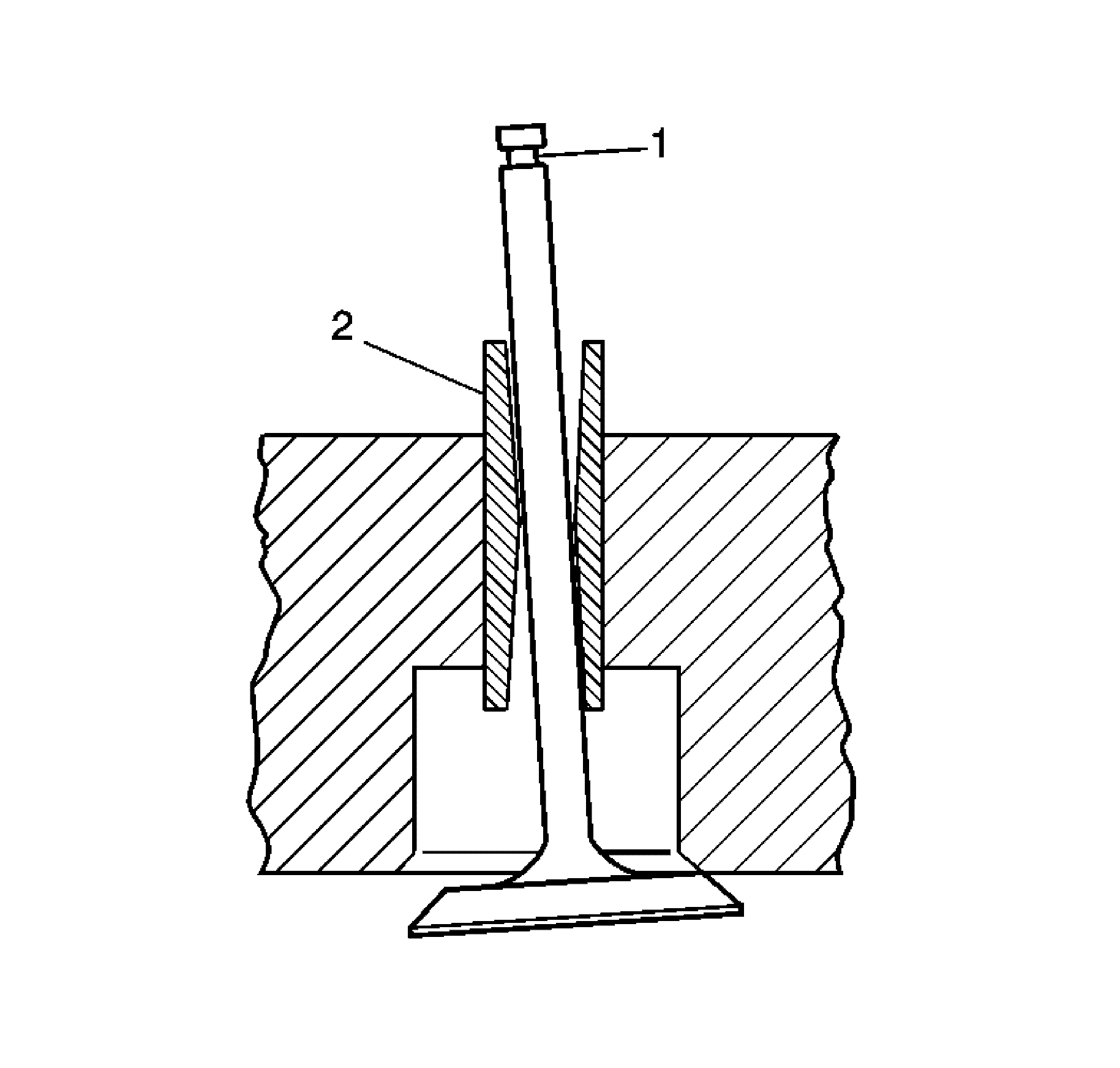
- A valve stem (1) and guide (2) with
above acceptable clearance must be replaced or the cylinder head replaced. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
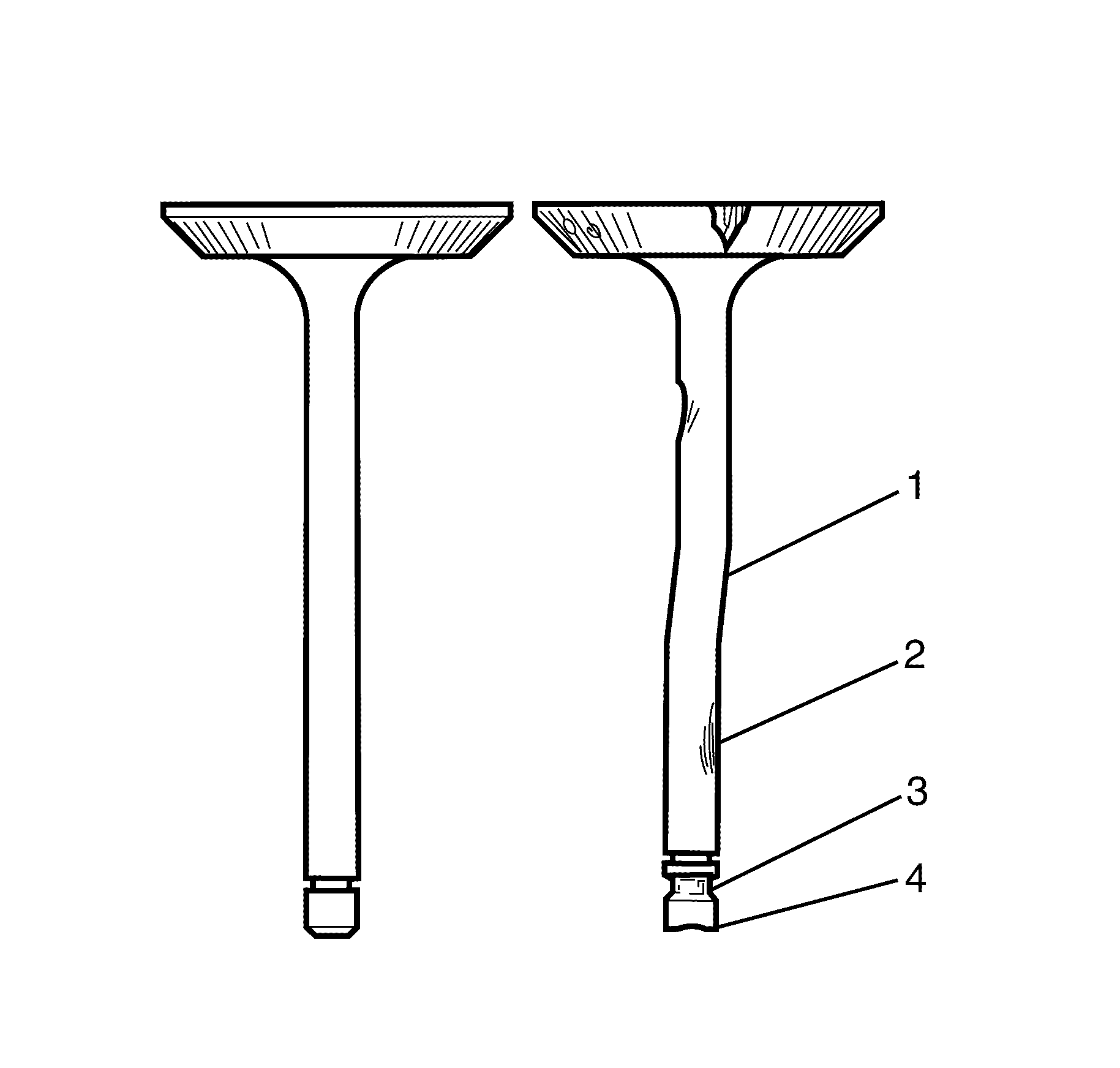
- Inspect the valve stems for above acceptable scoring,
wear, or warpage.
| • | A valve stem that has above acceptable scoring (3 or 4) or wear (4
or 6) must be replaced. |
| • | A valve guide that is worn and has above acceptable stem-to-guide clearance
should be reamed and valves with oversize stems installed. |
- Measure the valve stem diameter. A valve stem with a diameter less than
7.95 mm (0.313 in) must be replaced.
If the valve stem diameter
is within specifications, and the stem-to-guide clearance is above acceptable, the
cylinder head must be replaced.
Valve and Seat Grinding
Important:
| • | Reconditioning the valve seats is very important. The seating of the valves
must be perfect for the engine to deliver optimum power and performance. Several different
types of equipment are available for grinding valve seats. |
| • | Another important factor is the cooling of the valve head. Good contact
between the valve and the seat will ensure that heat will be correctly dissipated. |
| • | The recommendations of the manufacturer of the equipment should be followed
carefully to obtain the correct results. Regardless of what type of equipment is used,
it is essential that valve guide bores be free from carbon or dirt to ensure correct
centring of the tool pilot in the guide. |
| • | Exhaust valves that are pitted must be refaced to the correct angle. Valve
stems that show above acceptable wear, or valves that are warped above acceptable
tolerances must be replaced. When a valve head that is warped above acceptable tolerances
is refaced, a knife edge may be ground on part or all of the valve head due to the
amount of metal that must be removed. Knife edges lead to breakage, burning or pre-ignition
due to heat localizing on this knife edge. If the edge of the valve head is less than
1.25 mm (0.05 in) after grinding, replace the valve. |
| • | Several different types of equipment are available for refacing valves.
The recommendation of the manufacturer of the equipment should be carefully followed
to obtain the correct results. |
| • | DO NOT reface intake valves. Intake valves with above acceptable wear
or damage MUST be replaced. |
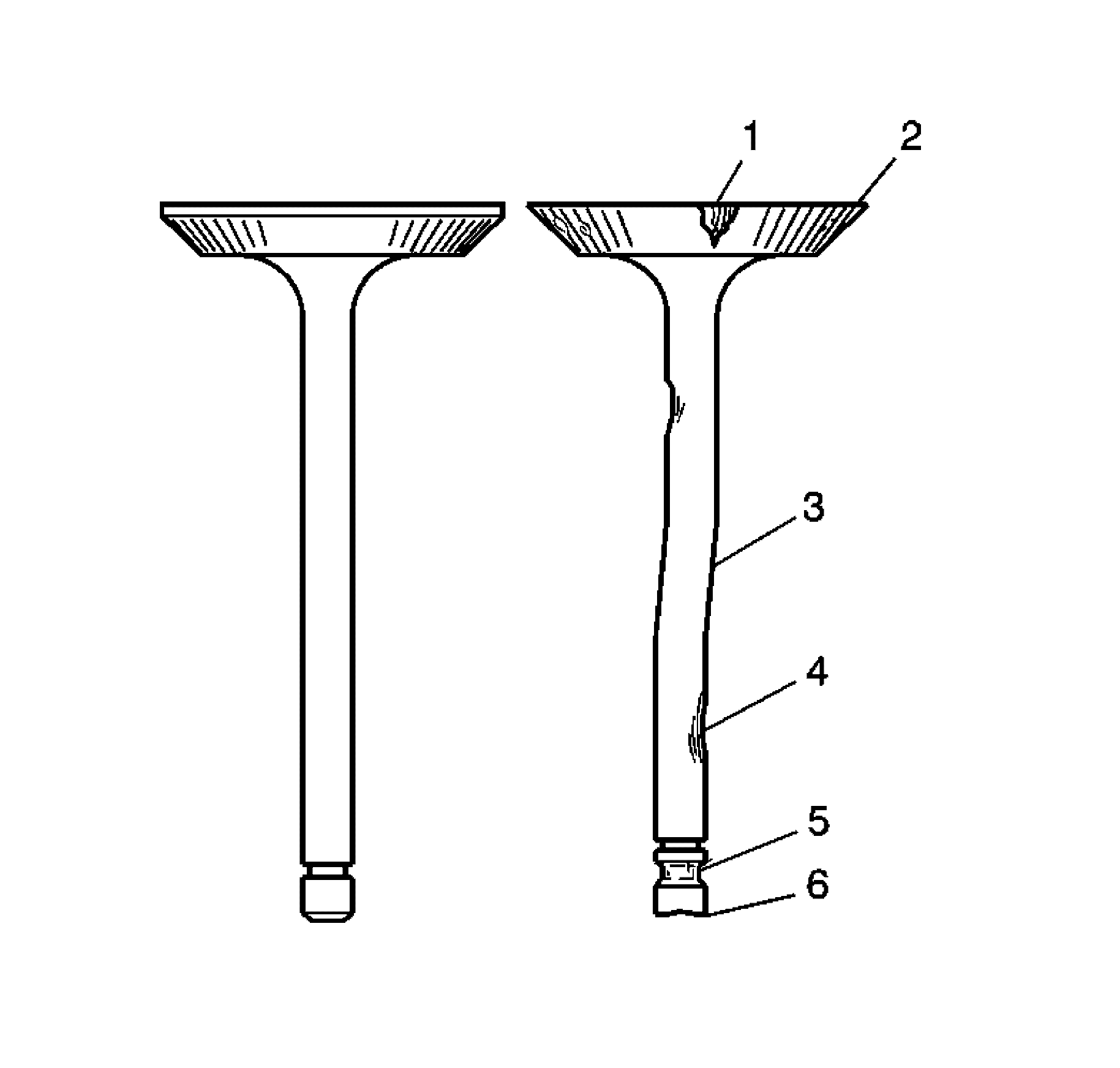
- Inspect the valve for the following conditions:
| • | Burnt or eroded areas (1) |
| • | A worn or scored stem (4) |
- Inspect the valve face for the following conditions:
| • | Worn or no margin (1 or 4) |
| • | Burnt or eroded areas (3) |
- Inspect the valve margin.
The exhaust
valve may be refaced if the margin is greater than 1.25 mm (0.05 in)
thick before grinding.
- Reface pitted exhaust valves on a suitable valve refacing machine.
- Replace the valve if the margin is less than 1.25 mm (0.05 in)
thick after grinding.
- If the valve face has been ground, it may be necessary to shim the valve
spring to obtain the correct spring installed height. Refer to
Cylinder Head Disassemble.
- Inspect for a loose valve seat in the cylinder head. The valve seat has
an interference fit to the cylinder head.
- Clean the valve guide bores with a suitable tool. Remove all carbon or
dirt from the bores.
The valve guide must be clean for the seat grinding
tool to obtain correct results.
- Grind the valve seat.
The recommendations of the manufacturer
of the equipment should be followed carefully to obtain the correct results. Regardless
of what type of equipment is used, it is essential that valve guide bores be free
from carbon or dirt to ensure correct centring of the tool pilot in the guide.
- Inspect the valve seats.
| • | The valve seats should be concentric to within 0.05 mm (0.0021 in)
total indicator reading. |
| • | If the valve seat has been ground, it may be necessary to shim the valve
spring to attain the correct spring installed height. Refer to
Cylinder Head Disassemble. |
Valve Guide Reaming, and Valve and Seat Grinding LS3
Valve Guide Reaming
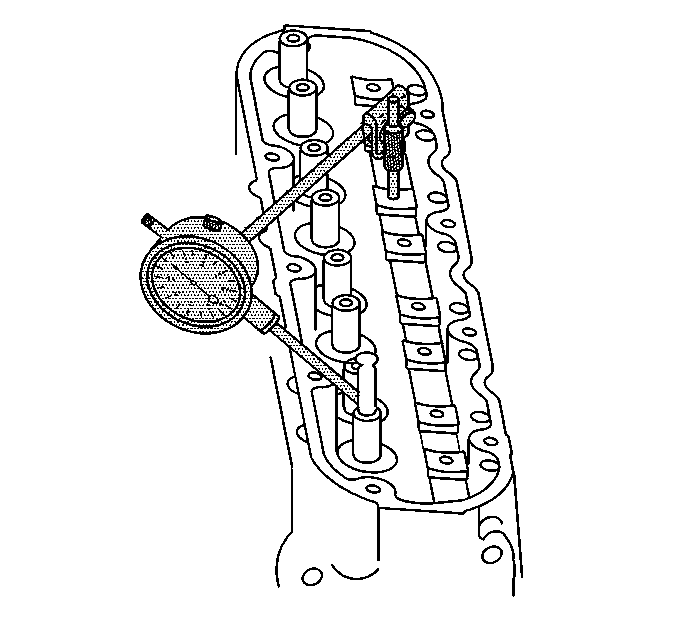
Notice: Excessive valve stem-to-guide clearance may cause a noisy valve train, premature
valve stem oil seal wear, component damage, and/or excessive engine oil consumption.
Notice: Insufficient valve stem-to-guide
clearance will result in noisy or sticking valves. Valves that are too tight may disturb engine smoothness or lead to component damage.
- Using a dial indicator, measure the valve stem-to-guide clearance. Position the tip of the dial indicator at the top of the valve guide.
Valve stem-to-guide clearance may also be obtained
by using a micrometer to measure the valve stem diameter and a ball type measuring gage to measure the guide bore.
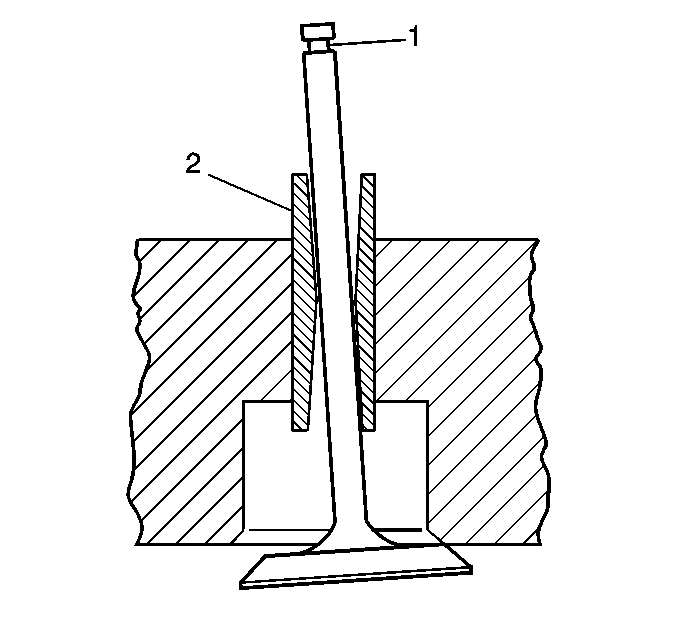
- A valve stem (1) and guide (2), with excessive clearance, must be replaced or the cylinder head replaced. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
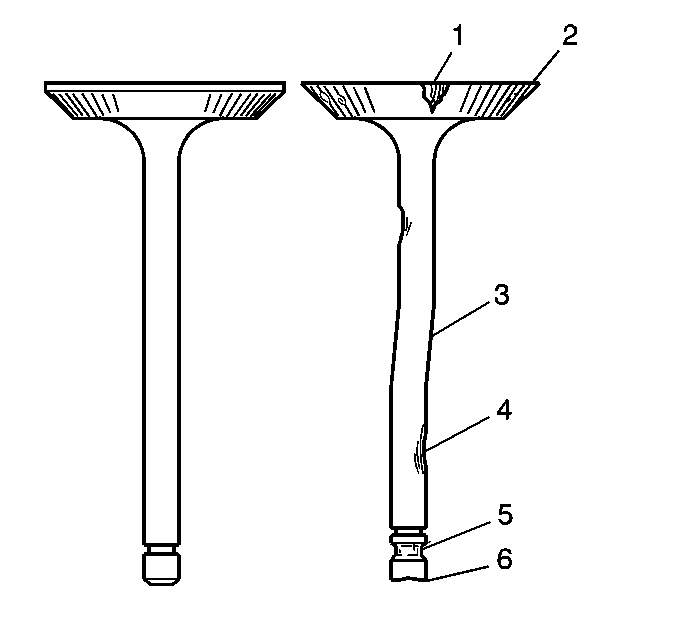
- Inspect the valve stems for excessive scoring, wear, or warpage.
| • | A valve stem that has excessive scoring (3 or 4) or wear (4 or 6) must be replaced. |
| • | If a valve guide is worn or has excessive stem-to-guide clearance, the cylinder head should be replaced. |
- Measure the valve stem diameter. A valve stem with a diameter less than 7.95 mm (0.313 in) must be replaced.
If the valve stem diameter is within specifications, and the stem-to-guide clearance is excessive,
the cylinder head must be replaced.
Valve and Seat Grinding

Important:
| • | Reconditioning the valve seats is very important. The seating of the valves must be perfect for the engine to deliver optimum power and performance. Several different types of equipment are available for grinding valve seats. |
| • | Another important factor is the cooling of the valve head. Good contact between the valve and the seat will ensure that heat will be properly dissipated. |
| • | The recommendations of the equipment manufacturer should be followed carefully to obtain the proper results. Regardless of the type of equipment used, it is essential that valve guide bores be free of carbon or dirt to ensure proper centering of
the tool pilot in the guide. |
| • | Valves that are pitted must be refaced to the proper angle. Valve stems that show excessive wear, or valves that are warped excessively must be replaced. When a valve head that is warped excessively is refaced, a knife edge may be ground on part
or all of the valve head due to the amount of metal that must be removed. Knife edges lead to breakage, burning or pre-ignition due to heat localizing on this knife edge. If the edge of the valve head is less than 1.25 mm (0.05 in) after
grinding, replace the valve. |
| • | Several different types of equipment are available for refacing valves. The recommendation of the equipment manufacturer should be carefully followed to obtain the proper results. |
| • | DO NOT reface intake valves. Intake valves with excessive wear or damage MUST be replaced. |
- Inspect the valve for the following conditions:
| • | Burnt or eroded areas (1) |
| • | A worn or scored stem (4) |
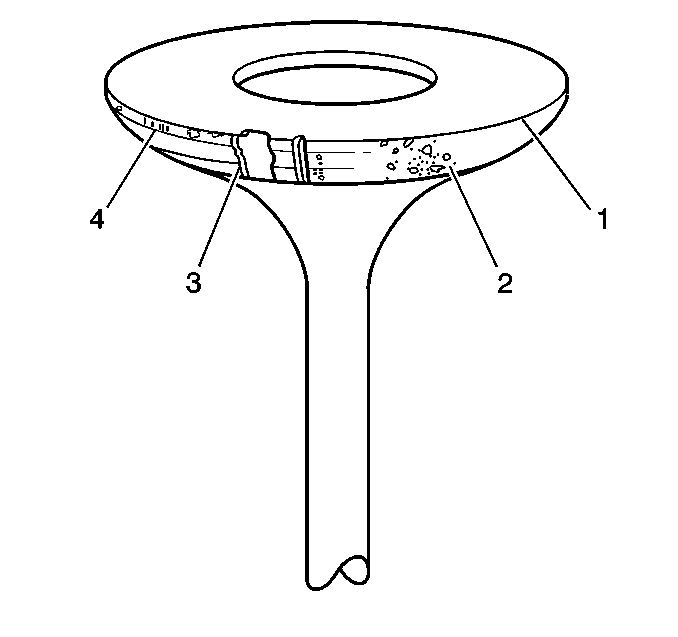
- Inspect the valve face for the following conditions:
| • | Worn or no margin (1 or 4) |
| • | Burnt or eroded areas (3) |
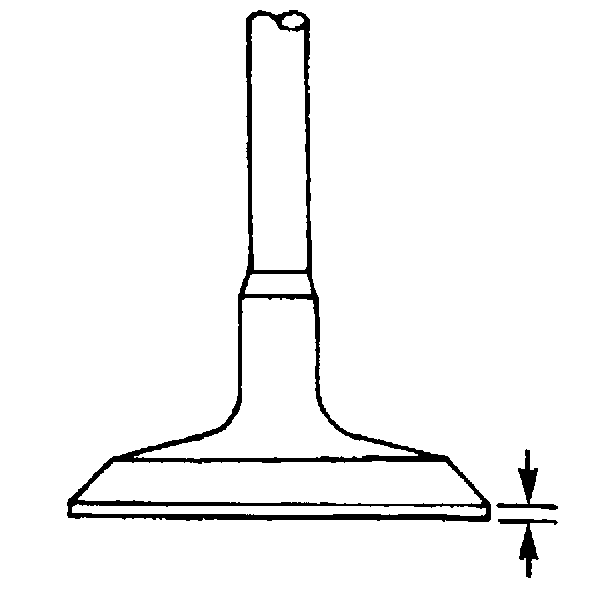
- Inspect the valve margin.
The exhaust valve may be refaced if the margin is greater than 1.25 mm (0.05 in) thick before grinding.
- Reface pitted exhaust valves on a suitable valve refacing machine.
- Replace the valve if the margin is less than 1.25 mm (0.05 in) thick after grinding.
- If the valve face has been ground, it may be necessary to shim the valve spring in order to obtain the proper spring installed height. Refer to
Cylinder Head Disassemble.
- Inspect for a loose valve seat in the cylinder head. The valve seat has an interference fit to the cylinder head.
- Clean the valve guide bores with a suitable tool. Remove all carbon or dirt from the bores.
The valve guide must be clean for the seat grinding tool to obtain proper results.
- Grind the valve seat.
The recommendations of the equipment manufacturer should be followed carefully to obtain the proper results. Regardless of the type of equipment used, it is essential that valve guide bores be free from carbon or
dirt to ensure proper centering of the tool pilot in the guide.
- Inspect the valve seats.
| • | The valve seats should be concentric to within 0.05 mm (0.0021 in) total indicator reading. |
| • | If the valve seat has been ground, it may be necessary to shim the valve spring in order to attain the proper spring installed height. Refer to
Cylinder Head Disassemble. |












