| Table 1: | A/C Performance Table |
| Table 2: | Refrigerant-134a Pressure-Temperature Relationship |
Important:
• Before carrying out the high/low pressure and centre vent temperature
testing, make sure that the vehicles A/C system has no visual or operational defects
and that all refrigerant recovery and recharging safety requirements are adhered to.
Refer to
Refrigerant Recovery and Recharging. • Before commencing the testing follow the vehicle set up procedure. Failure
to correctly set the vehicle up for testing will provide inaccurate diagnosis when
comparing actual pressure readings to the table below.
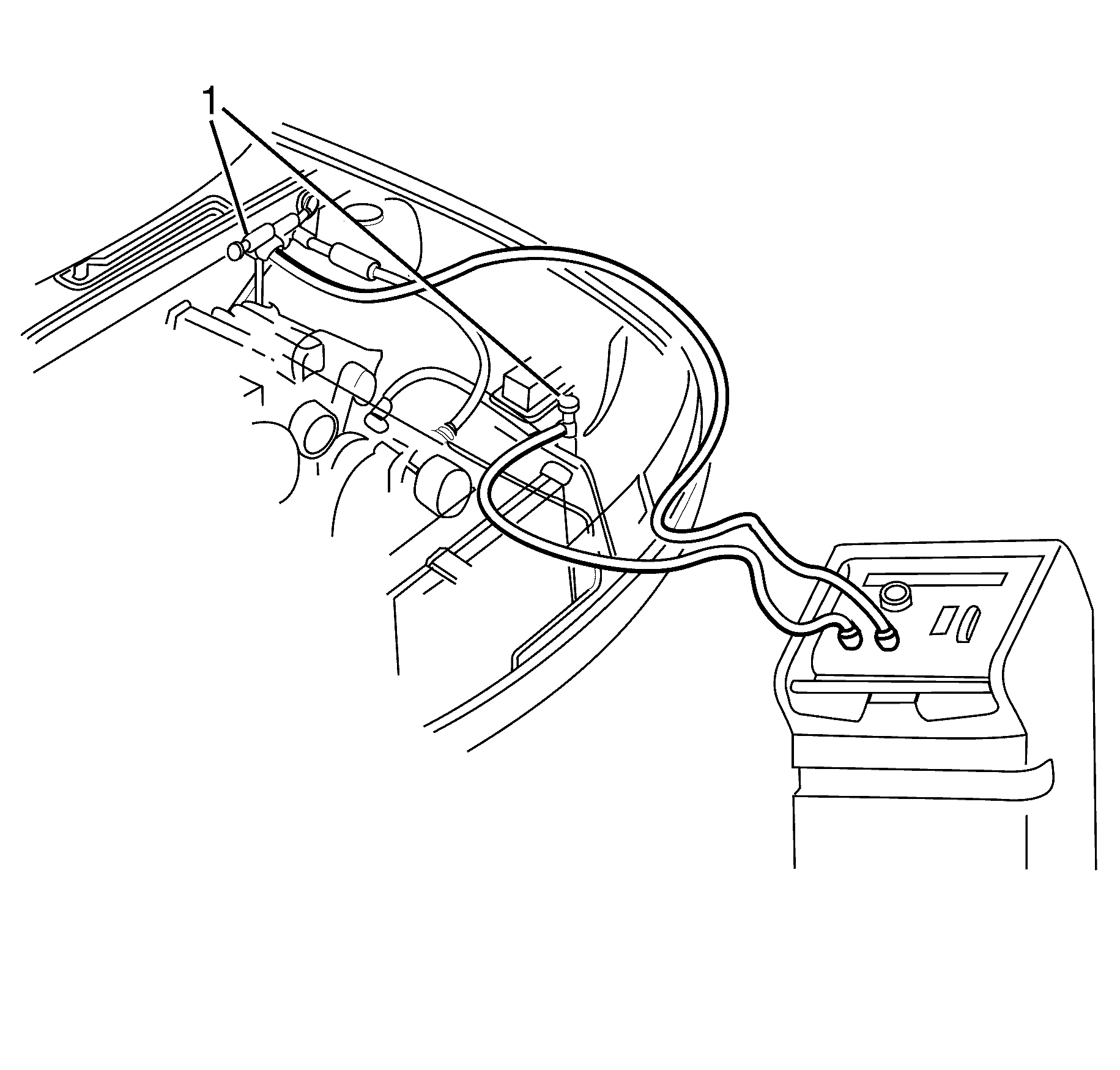
- Connect the calibrated high/low pressure gauges to the A/C system (1).
- Confirm that the static pressures (vehicle not started or A/C engaged) are correct.
- Record the ambient temperature conditions and the relative humidity at the time of the test.
- DO NOT test the vehicle with the condenser air flow restricted, such as against a wall.
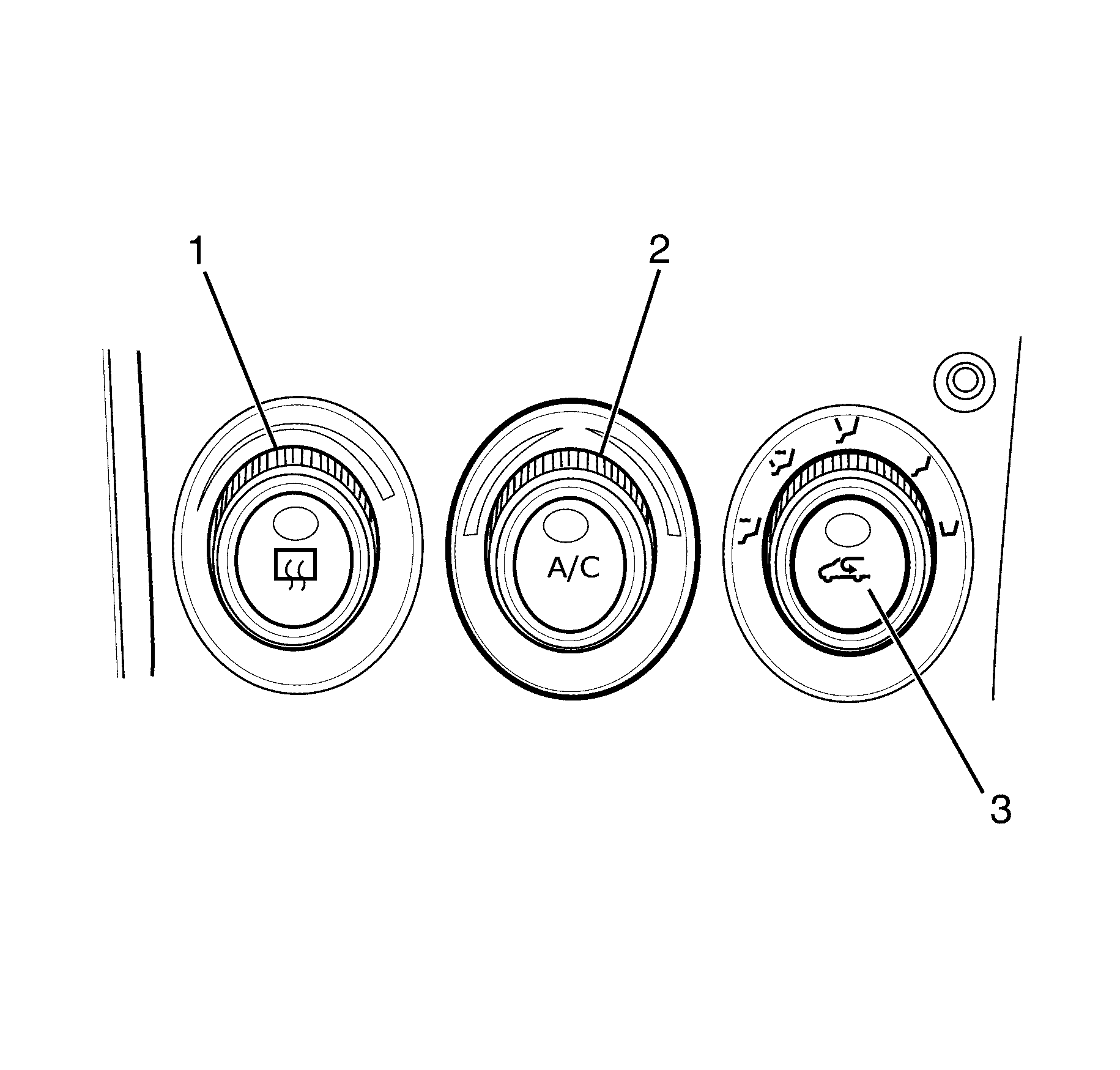
- Set the blower motor speed control (1) to the highest blower motor speed.
- Set the temperature control (2) to the maximum cold setting.
- Set the air intake mode control (3) to fresh air intake mode.
- Set the mode outlet control to the face position with the instrument panel louvres open and facing straight ahead.
- Insert a thermometer centrally into the face vent.
- Turn the engine ON and run at idle speed.
- Close all vehicle doors and windows.
- Close the vehicle engine hood.
- Make sure accurate pressure gauges are connected to the A/C system.
- Turn the engine OFF and compare the readings with the data in the A/C performance table. A normally operating A/C system should not exceed levels shown. If the readings exceed the table limits, refer to Symptoms - HVAC Systems - Manual.
Important: Both high and low pressures should be within 50kPa of each other, if not a blockage may be present in the system.
Important: When possible the vehicle should be tested in direct sunlight, especially in the case of climate control vehicles using solar sensors.
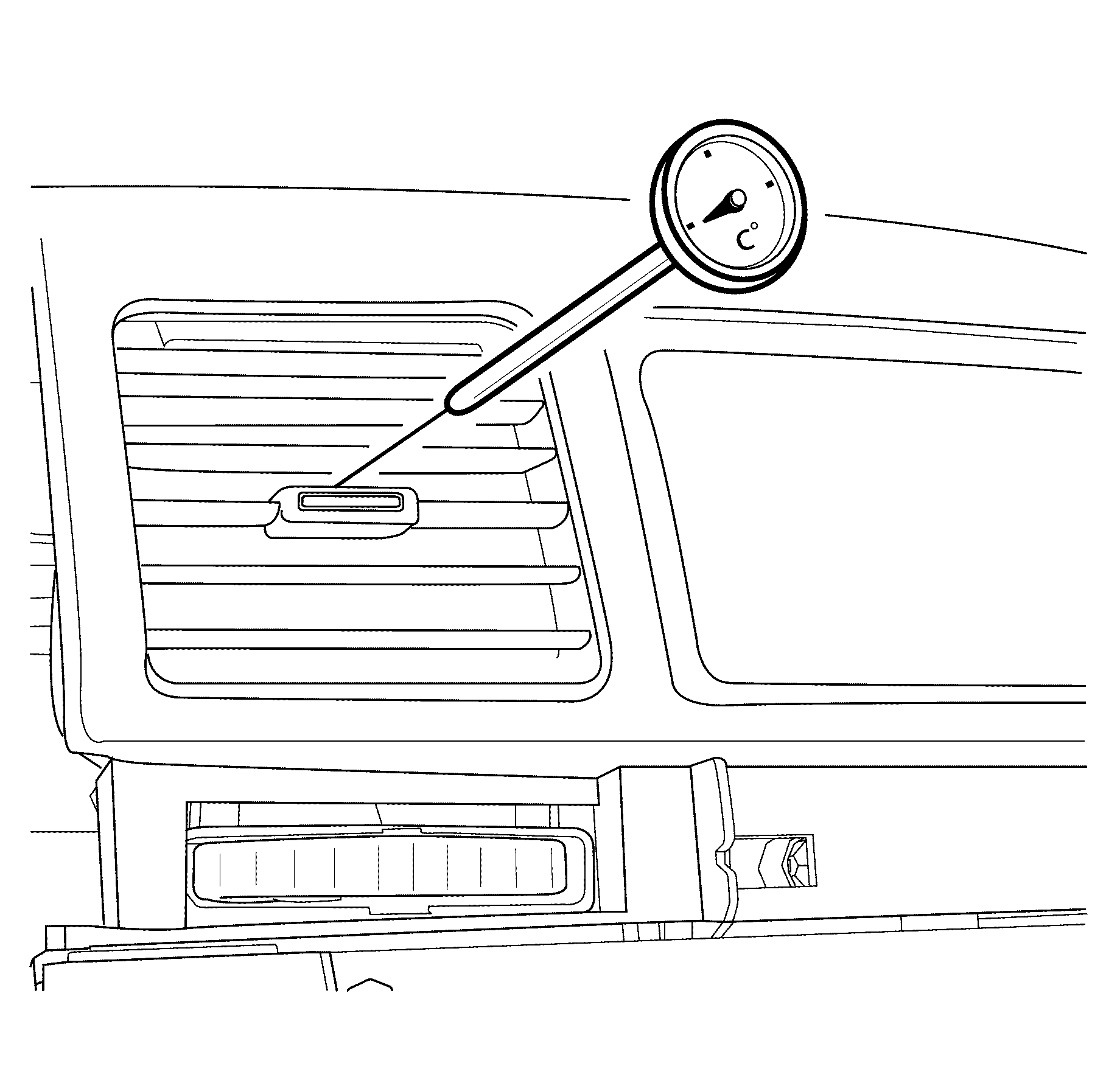
Important: Make sure that the thermometer probe is inserted to a length of approximately 50mm.
Important: For Accurate testing the relative humidity percentage (RH%) should be known, as you will see the pressures and vent temperatures alter as RH% changes. Refer to the A/C performance table below.
Engine Speed (RPM) | Relative Humidity (%) | Ambient Air Temperature | Centre Air Outlet Temperature | Gauge Pressure Low Side Pressure | Gauge Pressure High Side Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
°F | °C | °F | °C | psi | kPa | psi | kPa | ||
Idle | 20 | 59 | 15 | 37 | 3.00 | 27 | 162 | 142 | 943 |
68 | 20 | 37 | 3.00 | 31 | 185 | 168 | 1106 | ||
77 | 25 | 40 | 4.64 | 36 | 209 | 191 | 1296 | ||
86 | 30 | 47 | 8.60 | 42 | 236 | 225 | 1494 | ||
95 | 35 | 54 | 12.49 | 50 | 265 | 266 | 1653 | ||
104 | 40 | 62 | 16.45 | 58 | 300 | 304 | 1864 | ||
113 | 45 | 69 | 20.47 | 63 | 334 | 323 | 2155 | ||
40 | 59 | 15 | 37 | 3.00 | 25 | 171 | 139 | 956 | |
68 | 20 | 38 | 3.50 | 28 | 197 | 164 | 1129 | ||
77 | 25 | 44 | 6.79 | 32 | 222 | 192 | 1323 | ||
86 | 30 | 52 | 11.27 | 36 | 252 | 209 | 1445 | ||
95 | 35 | 61 | 15.94 | 42 | 288 | 248 | 1709 | ||
104 | 40 | 69 | 20.76 | 48 | 329 | 279 | 1925 | ||
113 | 45 | 77 | 25.18 | 54 | 375 | 306 | 2110 | ||
60 | 59 | 15 | 37 | 3.00 | 26 | 177 | 140 | 966 | |
68 | 20 | 40 | 4.47 | 30 | 205 | 166 | 1146 | ||
77 | 25 | 48 | 8.92 | 34 | 233 | 192 | 1326 | ||
86 | 30 | 57 | 13.93 | 39 | 269 | 215 | 1480 | ||
95 | 35 | 66 | 19.11 | 45 | 310 | 249 | 1718 | ||
104 | 40 | 76 | 24.59 | 52 | 358 | 300 | 2072 | ||
113 | 45 | 86 | 29.82 | 59 | 406 | 318 | 2196 | ||
80 | 59 | 15 | 37 | 3.00 | 27 | 186 | 142 | 976 | |
68 | 20 | 43 | 6.11 | 31 | 214 | 168 | 1160 | ||
77 | 25 | 52 | 11.15 | 36 | 250 | 191 | 1320 | ||
86 | 30 | 62 | 16.95 | 42 | 289 | 225 | 1551 | ||
95 | 35 | 74 | 23.23 | 50 | 342 | 266 | 1833 | ||
104 | 40 | 85 | 29.27 | 58 | 398 | 304 | 2096 | ||
113 | 45 | 96 | 35.65 | 63 | 436 | 323 | 2226 | ||
°C | °F | kPa | psig | °C | °F | kPa | psig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DEFINITION: This table indicates the pressure of the Refrigerant-134a at various temperatures. For instance, a drum of refrigerant at room temperature of 26.6°C (80°F) will have a pressure of 595.6 kPa (86.4 psi). If the refrigerant is heated to 51.6°C (125°F), the pressure will increase to 1278.8 kPa (185.5 psi). The refrigerant also can be used conversely in order to determine the temperature at which the Refrigerant-134a boils under various pressures. For example, at a pressure of 188.2 kPa (27.3 psi), the Refrigerant-134a boils at 0°C (32°F). | |||||||
15.5 | 60 | 392.3 | 56.9 | ||||
-23.3 | -10 | 12.4 | 1.8 | 18.3 | 65 | 438.2 | 63.6 |
-20.5 | -5 | 27.0 | 3.9 | 21.1 | 70 | 487.3 | 70.7 |
-17.7 | 0 | 43.2 | 6.3 | 23.8 | 75 | 539.7 | 78.3 |
15.0 | 5 | 60.8 | 8.8 | 26.6 | 80 | 595.6 | 86.4 |
-12.2 | 10 | 80.1 | 11.6 | 29.4 | 85 | 655.1 | 95.0 |
9.4 | 15 | 101.3 | 14.7 | 32.2 | 90 | 718.5 | 104.2 |
-6.6 | 20 | 124.3 | 18.0 | 35.0 | 95 | 785.6 | 113.9 |
-3.8 | 25 | 149.4 | 21.7 | 37.7 | 100 | 856.9 | 124.3 |
-1.1 | 30 | 176.6 | 25.6 | 40.5 | 105 | 932.3 | 135.2 |
0.0 | 32 | 188.2 | 27.3 | 43.3 | 110 | 1012.1 | 146.8 |
1.6 | 35 | 206.2 | 29.9 | 46.1 | 115 | 1096.4 | 159.0 |
4.4 | 40 | 238.0 | 34.5 | 48.8 | 120 | 1185.2 | 171.9 |
7.2 | 45 | 272.5 | 39.5 | 51.6 | 125 | 1278.8 | 185.5 |
10.0 | 50 | 309.5 | 44.9 | 54.4 | 130 | 1377.3 | 199.8 |
12.7 | 55 | 349.4 | 50.7 | 60.0 | 140 | 1589.6 | 230.5 |
