Exhaust System Description Gasoline Engines
Exhaust System
Important: Check the complete exhaust system and the nearby body areas and the trunk lid for broken, damaged, missing, or mispositioned parts, open seams, holes, loose connections, or other deterioration which could permit hazardous exhaust fumes to seep into the trunk or the passenger compartment. Dust or water in the trunk may be an indication of a problem in one of these areas. Any defects should be corrected immediately.
Notice: When inspecting or replacing exhaust system components, make sure there is adequate clearance from all points on the underbody to prevent overheating of the floor pan and possible damage to the passenger compartment insulation and trim materials.
Muffler and Resonators
If holes, open seams or any deterioration is discovered upon inspection of the front muffler and pipe assembly, the complete assembly should be replaced. The same procedure is applicable to the rear muffler assembly. Heat shields in the front and the rear muffler assembly positions, as well as for the catalytic converter and the connecting pipe, protect the vehicle and the environment from high temperatures the exhaust system develops.
Catalytic Converters (Pup Converter)
Important: The catalytic converter requires the use of unleaded fuel only, or damage to the catalyst will result. The catalytic material is very sensitive to the effects of a rich or lean fuel mixture, which may cause the temperature of the converter to rise rapidly. The catalytic converter normally operates at approximately 600°C. The catalytic converter is also sensitive to the use of leaded petrol. Using leaded fuel can cause deposits to form in the converter, which restrict exhaust flow and prevent the catalyst from working. This will result in an increase in exhaust backpressure and converter temperature.
The catalytic converter is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being changed. Engine exhaust gases contain carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx). When the exhaust gases flow through the monolith, reactions with the catalytic converter occur. CO and HC are converted by oxidation with oxygen (O2) in the exhaust gases to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). NOx is converted by reduction with CO to produce nitrogen (N2) and CO2. The converter is called a 3-way type because it simultaneously converts 3 components of exhaust gas (CO, HC and NOx) to harmless natural gases. Catalytic converter can be damaged or rendered ineffective, if the engine burns excessive amount of oil or the exhaust temperature at the converter is too high (exceeds 840°C).
Exhaust System Description Diesel Engines
Pre-Catalyst
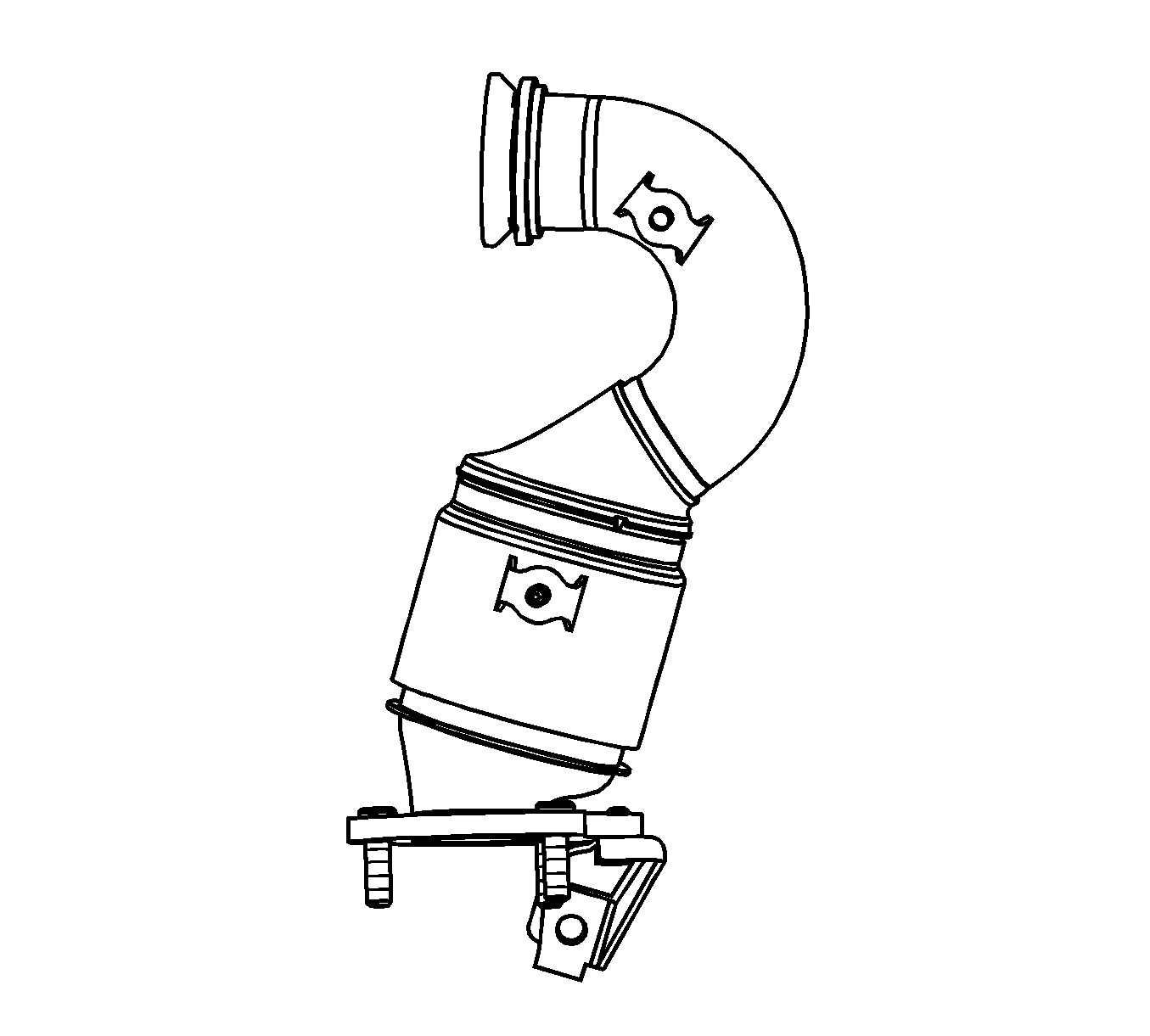
The catalyst converters are emission control devices added to the exhaust system to reduce pollutions from the exhaust pipes.
It has coating only platinum, which simultaneously lower the level of HC and CO. But NOx is able to be reduced from engine control system (example: cooled EGR system, etc).
Front Muffler
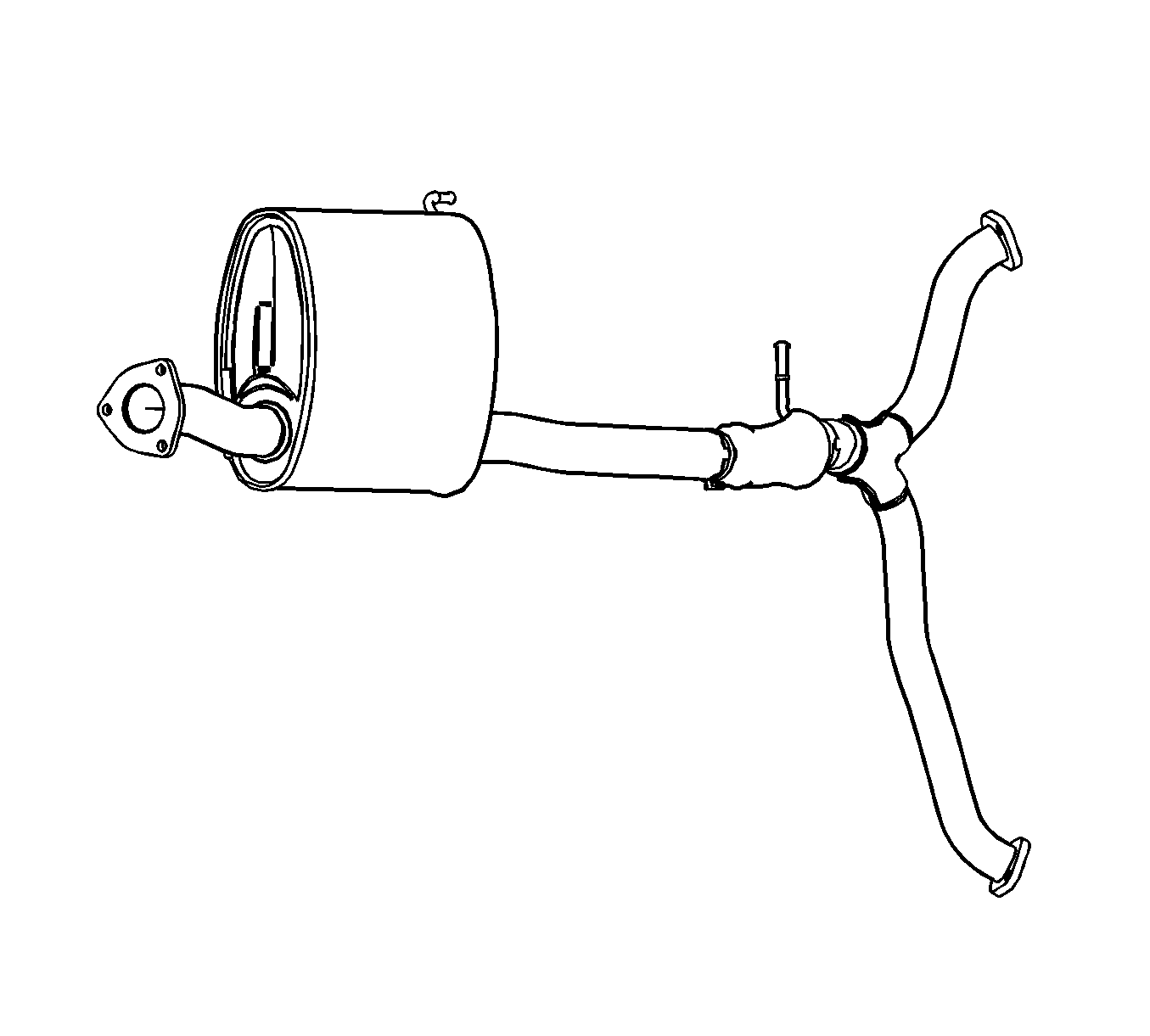
The function of the muffler is to reduce engine noise. It is made up of a series of perforated tubes and baffles to break up the sound waves and reflect them.
It is made of Stainless Steel to protect the front muffler from corrosion.
It is mounted on the middle of underbody.
Rear Muffler
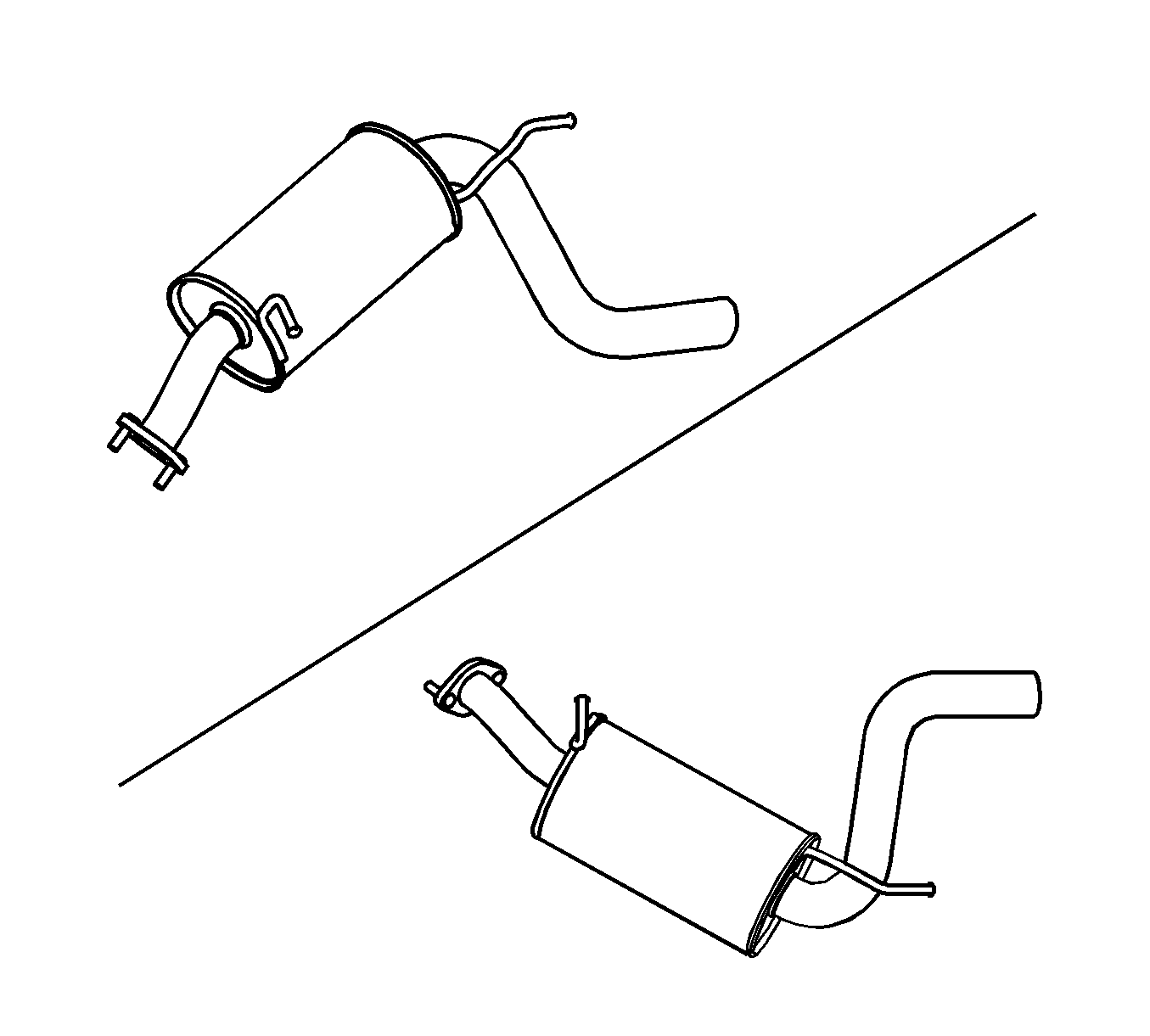
The rear muffler is to reduce broad band engine exhaust noise. It is comprised of a series of perforated tubes and baffles to break up the sound waves and reflect them. The adopted dual muffler for this vehicle improves the efficiency to reduce flow noise.
It is made of Stainless Steel to protect the front muffler from corrosion.
It is mounted behind the rear wheel.
