Safety Precautions
Caution: Batteries produce explosive gases, contain corrosive acid, and supply levels
of electrical current high enough to cause burns. Therefore, to reduce the risk of
personal injury when working near a battery:
• Always shield your eyes and avoid leaning over the battery whenever possible. • Do not expose the battery to open flames or sparks. • Do not allow the battery electrolyte to contact the eyes or the skin.
Flush immediately and thoroughly any contacted areas with water and get medical help. • Follow each step of the jump starting procedure in order. • Treat both the booster and the discharged batteries carefully when using
the jumper cables.
Parasitic Load Testing
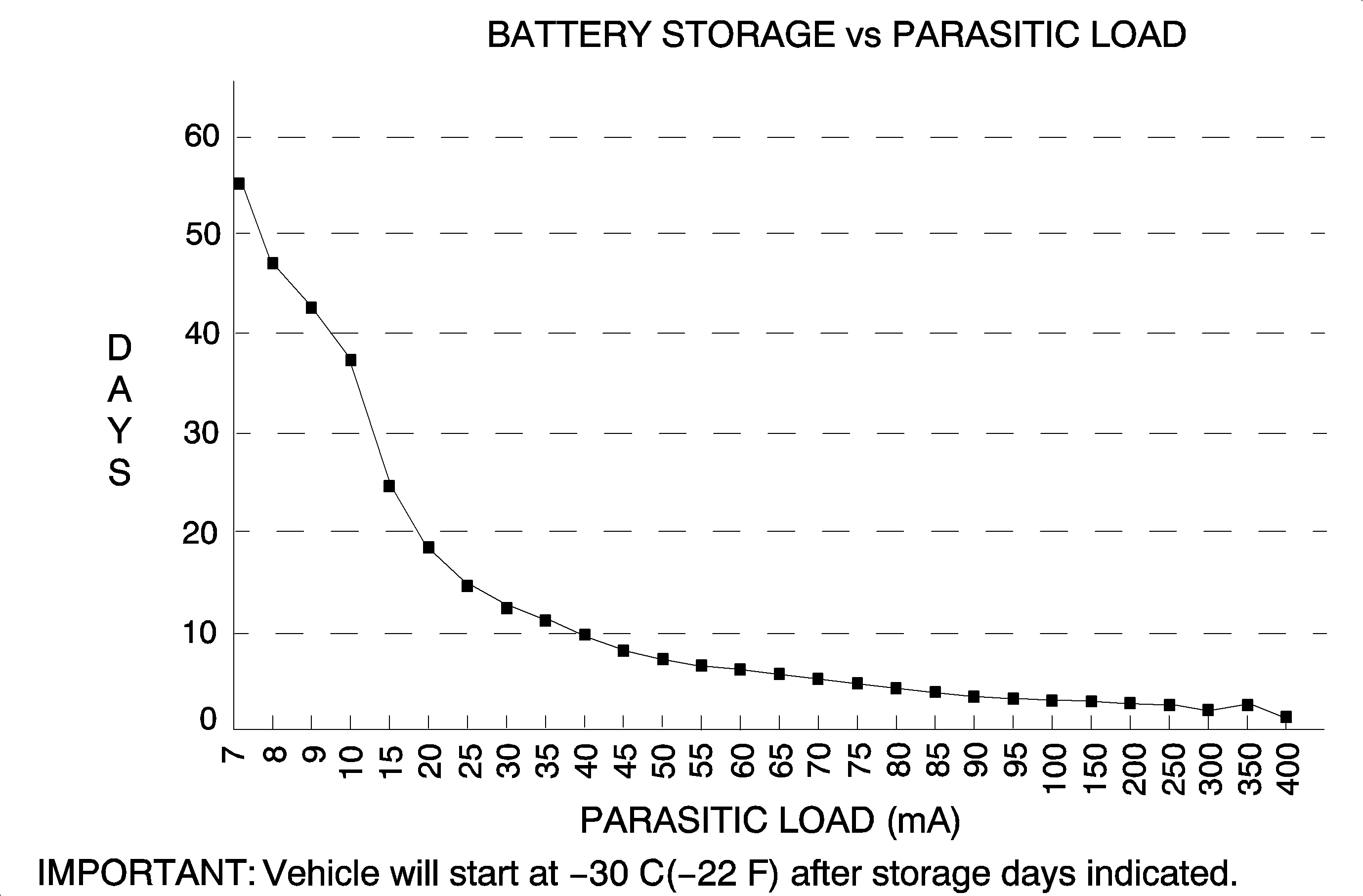
Small current drains, called parasitic drains, constantly draw current from the battery even with the ignition switch in the OFF position. These parasitic drains can discharge a battery in 4-6 weeks depending on the battery's state of charge and when the vehicle went into storage.
For normal parasitic current drain, refer to individual component parasitic loads. When testing for parasitic current draw, inspect what types of equipment the customer may have had installed on the vehicle. A cellular phone, anti-theft system, navigation system, or any device added that requires constant voltage to retain a memory, will draw current at all times. Take these added accessories into account when testing for parasitic current drain.
Saturn Parasitic Load Test Device
The parasitic load test device (SA9130Z) is used with a DMM. The test device is used to measure parasitic current drain from the battery with the ignition and all accessories OFF. The load tester, constructed with 1 ohm resistance and built-in circuit protection device, opens when the current exceeds approximately 1 amp. When the circuit is opened, the user is alerted by a red light-emitting diode (LED) indicator. The parasitic load test device is put into the circuit between the negative battery terminal and the negative battery cable so it effectively becomes a load in series with all other vehicle loads.
Important: The ignition key must be removed from the cylinder before parasitic load testing. The key-minder circuit is activated by the key cylinder switch when the key is in the ignition cylinder, which adds 20 mA of current draw.
- Install parasitic load tester between negative cable and negative battery terminal so the 1 ohm resistor of the tester is in series with battery. A top/side post adaptor must be used.
- Touch the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal, and hold them together for 20 seconds, then remove the cable from the battery. This will allow the modules on the vehicle to wake up. Verify that the LED indicator on the tester turns OFF and stays OFF.
- Set the multimeter to MILLIVOLT scale.
- Measure current across the tester by putting the multimeter probes in 2 terminals on the tester. The reading is obtained in volts. This reading is directly converted to milliampere. Should the parasitic load exceed 1 amp, the LED indicator on the tester will light. This may indicate that a vehicle accessory is ON.
- Wait 5 minutes for the modules on the vehicle to go to sleep. The current draw may be greater than 100 milliamps for the first 2-5 minutes, then it should drop to 10-30 milliamps.
| ⇒ | If the LED indicator does not stay off, verify that all vehicle accessories are OFF. Try holding the battery cable against the negative terminal again. If the LED indicator remains ON, something is drawing greater than 1 amp of current. |
| ⇒ | To find the source of excessive load, start removing fuses and modules in a systematic way. When voltage drops across the tester, the circuit or circuits protected by that fuse is the source of current drain. Also remove the fusible link from the generator to check for a voltage drop. If the voltage drop is greater than 2 volts, replace the generator. Repair the circuit and perform the parasitic load test again to verify the repair. |
Parasitic Current Drain Testing With an Ammeter
- Turn the ignition and all accessories OFF and remove the key from the ignition switch.
- Disconnect the cable from the negative battery terminal.
- Follow the manufacturers instructions for the multimeter or ampmeter being used. This could involve plugging leads into different locations on a multimeter and changing the scale to read amperage. On some testers you should start on the 10 amp scale setting, and after verifying that current drain is less than 2 mA, set the scale to 200 mA or 20 mA.
- Touch the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal, and hold them together for 20 seconds. This will allow the modules on the vehicle to wake up.
- While still holding the cable against the battery, connect the ammeter between the negative cable and the negative battery terminal so that it will be in series. Then remove the cable from the battery. Read the parasitic current drain from the battery.
- Wait 5 minutes for the modules on the vehicle to go to sleep. The current draw may be greater than 100 milliamps for the first 2-5 minutes, then it should drop to 10-30 milliamps.
- To find the source of excessive load, start removing fuses and modules in a systematic way. When voltage drops across the tester, the circuit or circuits protected by that fuse is the source of current drain. Also remove the fusible link from the generator to check for a voltage drop. If the voltage drop is greater than 2 volts, replace the generator. Repair the circuit and perform the parasitic load test again to verify the repair.
Typical Parasitic Loads
Typical parasitic load for this vehicle is 10-15 mA. If the vehicle does not have one of the following components, then subtract the parasitic load of the component for typical parasitic load of the vehicle (10-15 mA) to determine the parasitic load range for the vehicle being tested.
BCM | 3.0 mA |
CD Changer | 3.0 mA |
EBCM | 1.0 mA |
ECM/TCM | 0-1.0 mA |
Generator | 0-1.0 mA |
HVAC Delayed Blower Control | 1.0 mA |
I/P Cluster w/Security Flashing "Security" Telltale | 1.2 mA |
On-Star | 0-1.0 mA |
Radio | 2.8-4.3 mA |
Important: During CD changer initialization, parasitic current draw will fluctuate between 3 mA to 1 A. The initialization period lasts up to a maximum of 90 seconds. After initialization, the CD changer parasitic current draw will stabilize at approximately 3 mA.
If the CD changer door is open and the light is illuminated, the parasitic current draw will be approximately 65 mA. The light will remain ON for 2 minutes. After the light goes out, the CD changer parasitic current draw will stabilize at approximately 3 mA.
Typical Undesired Parasitic Loads
| • | Cigar lighter ON |
| • | Headlamps ON |
| • | Parking lamps ON |
| • | Reading lamps ON |
| • | Radio ON |
Safety Precautions
Warning: Batteries produce explosive gases, contain corrosive acid, and supply levels of electrical current high enough to cause burns. Therefore, to reduce the risk of personal injury when working near
a battery:
• Always shield your eyes and avoid leaning over the battery whenever possible. • Do not expose the battery to open flames or sparks. • Do not allow the battery electrolyte to contact the eyes or the skin. Flush immediately and thoroughly any contacted areas with water and get medical help. • Follow each step of the jump starting procedure in order. • Treat both the booster and the discharged batteries carefully when using the jumper cables.
Parasitic Load Testing
Small current drains, called parasitic drains, constantly draw current from the battery even with the ignition switch in the OFF position. These parasitic drains can discharge a battery in 4-6 weeks depending on the battery's state of charge and when the vehicle went into storage.
For normal parasitic current drain, refer to individual component parasitic loads. When testing for parasitic current draw, inspect what types of equipment the customer may have had installed on the vehicle. A cellular phone, anti-theft system, navigation system, or any device added that requires constant voltage to retain a memory, will draw current at all times. Take these added accessories into account when testing for parasitic current drain.
Saturn Parasitic Load Test Device
The parasitic load test device (SA9130Z) is used with a DMM. The test device is used to measure parasitic current drain from the battery with the ignition and all accessories OFF. The load tester, constructed with 1 ohm resistance and built-in circuit protection device, opens when the current exceeds approximately 1 amp. When the circuit is opened, the user is alerted by a red light-emitting diode (LED) indicator. The parasitic load test device is put into the circuit between the negative battery terminal and the negative battery cable so it effectively becomes a load in series with all other vehicle loads.
Note: The ignition key must be removed from the cylinder before parasitic load testing. The key-minder circuit is activated by the key cylinder switch when the key is in the ignition cylinder, which adds 20 mA of current draw.
- Install parasitic load tester between negative cable and negative battery terminal so the 1 ohm resistor of the tester is in series with battery. A top/side post adaptor must be used.
- Touch the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal, and hold them together for 20 seconds, then remove the cable from the battery. This will allow the modules on the vehicle to wake up. Verify that the LED indicator on the tester turns OFF and stays OFF.
- Set the multimeter to MILLIVOLT scale.
- Measure current across the tester by putting the multimeter probes in 2 terminals on the tester. The reading is obtained in volts. This reading is directly converted to milliampere. Should the parasitic load exceed 1 amp, the LED indicator on the tester will light. This may indicate that a vehicle accessory is ON.
- Wait 5 minutes for the modules on the vehicle to go to sleep. The current draw may be greater than 100 milliamps for the first 2-5 minutes, then it should drop to 10-30 milliamps.
| ⇒ | If the LED indicator does not stay off, verify that all vehicle accessories are OFF. Try holding the battery cable against the negative terminal again. If the LED indicator remains ON, something is drawing greater than 1 amp of current. |
| ⇒ | To find the source of excessive load, start removing fuses and modules in a systematic way. When voltage drops across the tester, the circuit or circuits protected by that fuse is the source of current drain. Also remove the fusible link from the generator to check for a voltage drop. If the voltage drop is greater than 2 volts, replace the generator. Repair the circuit and perform the parasitic load test again to verify the repair. |
Parasitic Current Drain Testing With an Ammeter
- Turn the ignition and all accessories OFF and remove the key from the ignition switch.
- Disconnect the cable from the negative battery terminal.
- Follow the manufacturers instructions for the multimeter or ampmeter being used. This could involve plugging leads into different locations on a multimeter and changing the scale to read amperage. On some testers you should start on the 10 amp scale setting, and after verifying that current drain is less than 2 mA, set the scale to 200 mA or 20 mA.
- Touch the negative battery cable to the negative battery terminal, and hold them together for 20 seconds. This will allow the modules on the vehicle to wake up.
- While still holding the cable against the battery, connect the ammeter between the negative cable and the negative battery terminal so that it will be in series. Then remove the cable from the battery. Read the parasitic current drain from the battery.
- Wait 5 minutes for the modules on the vehicle to go to sleep. The current draw may be greater than 100 milliamps for the first 2-5 minutes, then it should drop to 10-30 milliamps.
- To find the source of excessive load, start removing fuses and modules in a systematic way. When voltage drops across the tester, the circuit or circuits protected by that fuse is the source of current drain. Also remove the fusible link from the generator to check for a voltage drop. If the voltage drop is greater than 2 volts, replace the generator. Repair the circuit and perform the parasitic load test again to verify the repair.
Typical Parasitic Loads
Typical parasitic load for this vehicle is 10-15 mA. If the vehicle does not have one of the following components, then subtract the parasitic load of the component for typical parasitic load of the vehicle (10-15 mA) to determine the parasitic load range for the vehicle being tested.
BCM | 3.0 mA |
CD Changer | 3.0 mA |
EBCM | 1.0 mA |
ECM/TCM | 0-1.0 mA |
Generator | 0-1.0 mA |
HVAC Delayed Blower Control | 1.0 mA |
I/P Cluster w/Security Flashing "Security" Telltale | 1.2 mA |
On-Star | 0-1.0 mA |
Radio | 2.8-4.3 mA |
Note: During CD changer initialization, parasitic current draw will fluctuate between 3 mA to 1 A. The initialization period lasts up to a maximum of 90 seconds. After initialization, the CD changer parasitic current draw will stabilize at approximately 3 mA.
If the CD changer door is open and the light is illuminated, the parasitic current draw will be approximately 65 mA. The light will remain ON for 2 minutes. After the light goes out, the CD changer parasitic current draw will stabilize at approximately 3 mA.
Typical Undesired Parasitic Loads
| • | Cigar lighter ON |
| • | Headlamps ON |
| • | Parking lamps ON |
| • | Reading lamps ON |
| • | Radio ON |

