Purpose
The distributor ignition system controls the fuel combustion by providing
a spark to ignite the compressed air/fuel mixture at the correct time. In
order to provide improved engine performance, fuel economy, and control of
the exhaust emissions, the ECM controls the distributor spark advance (timing)
with the Ignition Control (IC) system.
Only the IC system is described here. Additional information on the
ignition system is in Engine Electrical.
System Operation
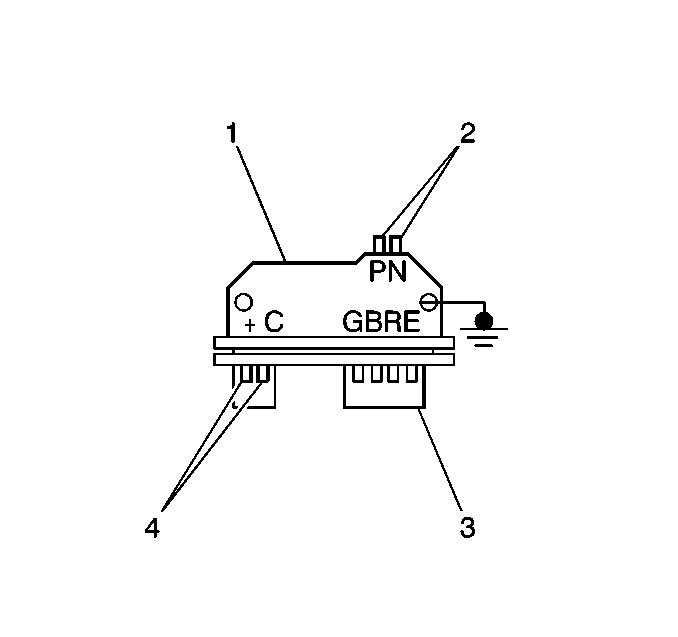
The distributor ignition system
has a distributor ignition control module (1) with four terminals for the
IC system (3) that are connected by the ECM. The ICM has terminals to the
Ignition Coil (4) and the Pick-Up Coil (2).
In order to properly control ignition/combustion timing, the ECM needs
to know the following items:
| • | The crankshaft position. |
| • | The engine speed (RPM). |
| • | The engine load (manifold pressure or vacuum). |
| • | The atmospheric (barometric) pressure. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature. |
The system consists of the distributor ignition control module, the
ECM, and the connecting wires. The four terminals for IC are lettered in the
module. The distributor four terminal connector is lettered A-B-C-D. These
circuits perform the following functions:
| • | Terminal A -- IC Reference Low -- This wire is grounded
in the distributor and makes sure the ground circuit between the module and
ECM has no voltage drop which could affect the performance. If the circuit
is open, terminal A may cause poor performance. |
| • | Terminal B -- IC Bypass -- At about 400 RPM,
the ECM applies 5 volts to this circuit in order to switch the ignition
control from the module to the ECM. An open or grounded bypass circuit will
set a DTC 42. The engine will run at base timing, plus a small amount
of advance built into the module. |
| • | Terminal C -- IC Reference High -- This terminal provides
the ECM with the RPM and the crankshaft position information. |
| • | Terminal D -- IC Control -- This circuit triggers the
module. The ECM does not know what the actual timing is, but the module does
know when it receives the reference signal. The ECM then advances then advances
or retards the spark from that point. If the base timing is set incorrectly,
the engine spark curve will be incorrect. |

