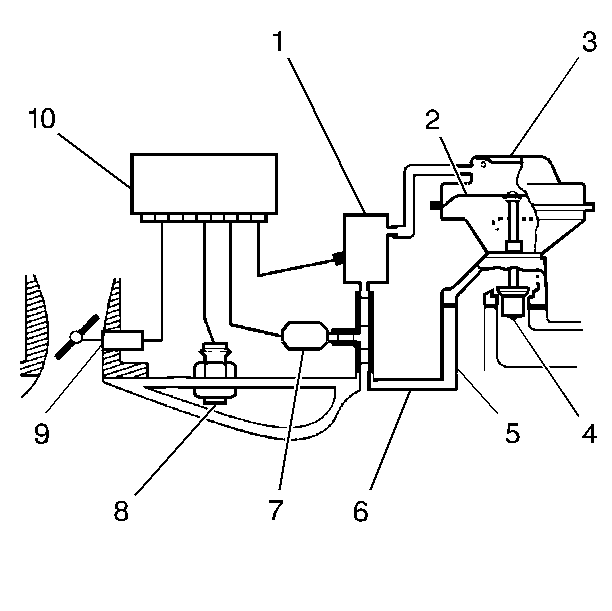
Purpose
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system lowers the NOx (Nitrogen
Oxides) emission levels caused by the high combustion temperatures. The EGR
valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber
in order to decrease the combustion temperature.
The main element of the system is an EGR valve operated by a vacuum
and mounted on the intake manifold.
Operation
A vacuum opens the EGR valve in order to let the exhaust gas flow into
the intake manifold. The exhaust gas then moves with the air/fuel mixture
into the combustion chamber. If too much exhaust gas enters, the combustion
will not occur. For this reason, the system allows very little exhaust gas
to pass through the valve, especially at idle. The system usually opens the
EGR valve under the following conditions:
EGR Control