The next step after road testing the vehicle is to identify
the frequency of the duplicated and abnormal vibration. Use the EVA in order
to measure the frequency. If the EVA is not available, the frequency can
be categorized into groups according to how the vibration feels or sounds.
The majority of vibrations will fit into one of the following categories.
| • | Vibrations that can be felt: |
| • | Vibrations that make noise: |
Vibrations That Can Be Felt
Shake
The shake is a low frequency
vibration, typically 5-20 Hz. The shake is sometimes seen in
the steering wheel, the seat, or the console. The best description is the
feeling from an out-of-round or unbalanced tire. Customers may refer to shake
in one of the following terms:
In most cases, damage to or wear of the following components is to blame
for the shake:
| • | The brake rotors (vehicle-speed sensitive) |
| • | The steering tie rod ends |
| • | The suspension ball joints |
| • | The engine (engine-speed sensitive) |
Roughness
Roughness is a vibration with a slightly higher frequency than the shake,
usually 20-50 Hz. Roughness is similar to the feeling you get
from holding a jigsaw.
Buzz
Buzz is slightly higher in frequency: 50-100 Hz. A buzz
is similar to the feel of an electric razor. You may feel it in your hands
through the steering wheel, in the feet through the floor, or in the seat.
Inspect the following components for a possible cause:
Tingling
This is the highest frequency that can still be felt. Tingling may sometimes
produce a "pins and needles" sensation. Customers may say the
vibration puts their hands or feet to sleep.
Vibrations That Make Noise
Boom
Boom is a low frequency interior noise of 20-60 Hz. Sometimes
the customer complains of a pressure in their ears. Examples of similar noises
include a bowling ball rolling down an alley, deep thunder, or a bass drum.
A customer may use the following words to describe boom:
Boom may not be accompanied by a perceptible vibration (roughness).
Moan or Drone
Moan or drone is a sustained tone at a low frequency of 60-120 Hz,
somewhat higher than boom.
Examples of similar noises include a bumble bee, or blowing air across
the top of a soda bottle. Examples of words to describe moan or drone are
humming, buzzing, resonance. Moan or drone may be accompanied by a perceptible
buzzing vibration. Inspect the following systems:
Howl
Howl is a noise at mid-range frequency of 120-300 Hz. This
sounds like the wind howling.
Whine
Whine is a prolonged, high-pitched sound in the 300-500 Hz
range, and is usually related to the meshing gears or gear noise. Similar
sounds include mosquitoes, turbine engines, and vacuum cleaners.
Matching Frequency to Component Speed
At this point in the diagnosis, the vibration has been duplicated, designated
as abnormal, identified as being related to engine speed or vehicle speed,
and assigned a frequency from the EVA or categorized into a symptom group
based on how it feels or sounds.
Automotive vibrations are usually related to the rotating speed of a
component. The speed of these components will be calculated using either an
engine speed or vehicle speed method. The engine rpm readings taken during
the road test will be used in diagnosing vibrations that are engine speed
sensitive. If the vibration is vehicle speed sensitive, the rotational speed
of the tires needs to be determined. As long as the vehicle is operated at
a constant speed, the tires will operate at a constant speed. These speed
is measured in rotations or cycles per second. The reading is then compared
to the frequency of the vibration, which is also measured in cycles per second.
Calculating Tire Rotation
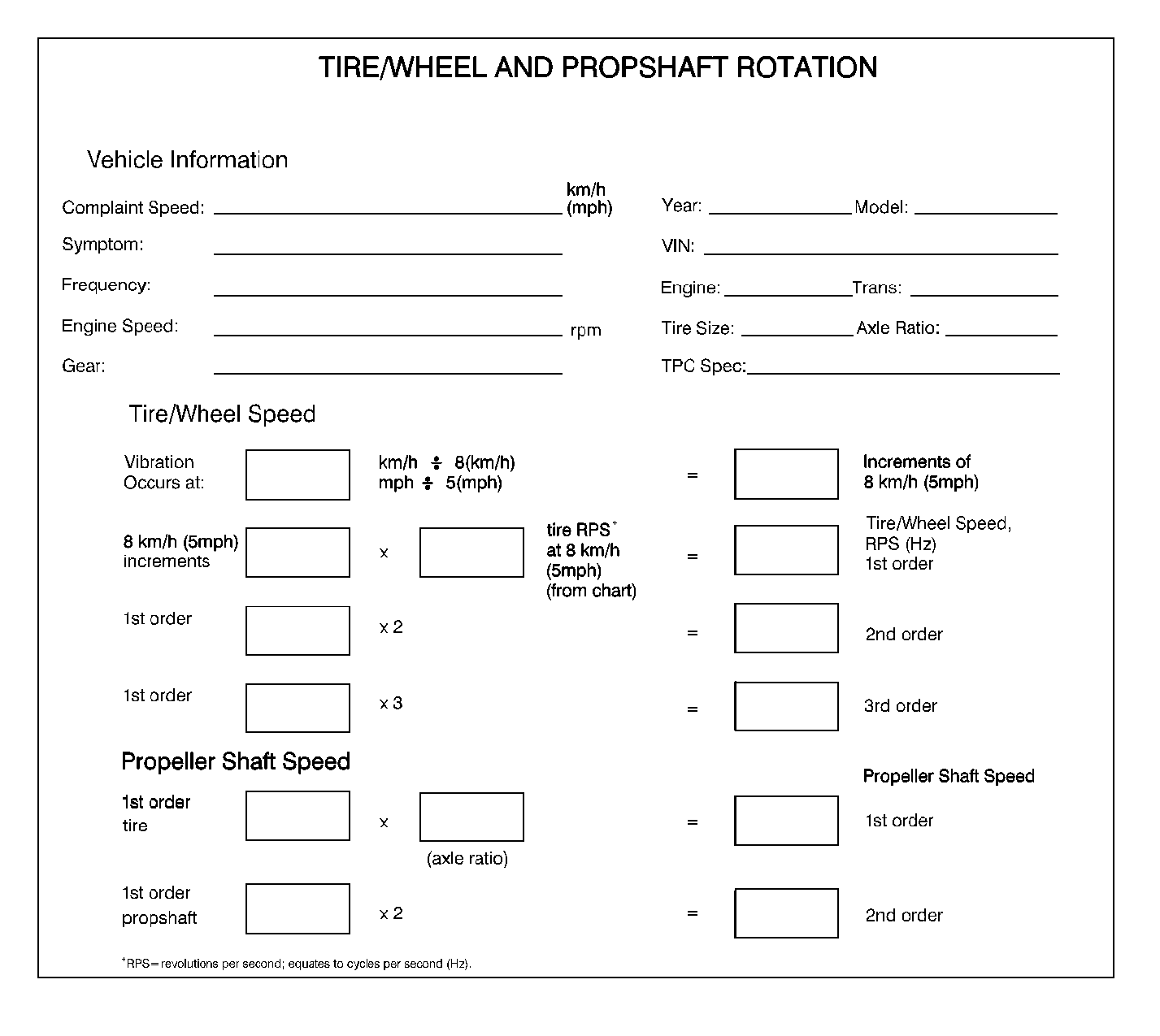
Determine the rotational
speed of the tires in revolutions per second, or Hertz (Hz), based on the
vehicle speed at which the vibration occurs. In order to determine the rotational
speed, follow this procedure:
- Determine the complaint speed -- the vehicle speed at which
the vibration occurs.
- Determine the number of 8 km/h (5 mph) increments:
| • | Divide the complaint speed by 8 when using km/h. |
| • | Divide the complaint speed by 5 when using mph. |
- Measure the tires rolling circumference.
- Divide the tires rolling circumference by 88.
- Multiply the Hertz value by the number of 8 km/h (5 mph)
increments.
- The result is the rotational speed of the tires in Hertz at the
complaint speed. If this figure matches the vibration frequency, a first-order
vibration is present in the tire and wheel assembly.
Sometimes, the tire/wheel vibration may be of a higher-order. In order
to compute possible higher-order vibrations, multiply the rotational speed
of the tires in Hertz at the complaint speed by the order number. If any
of these matches the vibration frequency, then a vibration of that particular
order is present in one of the tire and wheel assemblies.
Steering and Suspension Assembly Vibrations
Steering and suspension assembly vibrations are the first level of testing
for low-frequency vibrations that are vehicle-speed sensitive. The symptoms
if a steering/suspension first-order vibration are shimmy or shake, usually
felt in the steering wheel or in the seat. Inspect the following components
for wear or damage:
| • | The steering tie rod ends. |
| • | The suspension ball joints. |


