Ignition System Overview
The ignition system consists of the following components or circuits:
| • | The 8 ignition secondary wires |
| • | The 8 ignition control (IC) circuits |
| • | The camshaft position (CMP) sensor |
| • | The camshaft reluctor wheel |
| • | The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor |
| • | The crankshaft reluctor wheel |
| • | The related connecting wires |
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) |
Crankshaft Position Sensor and Reluctor Wheel
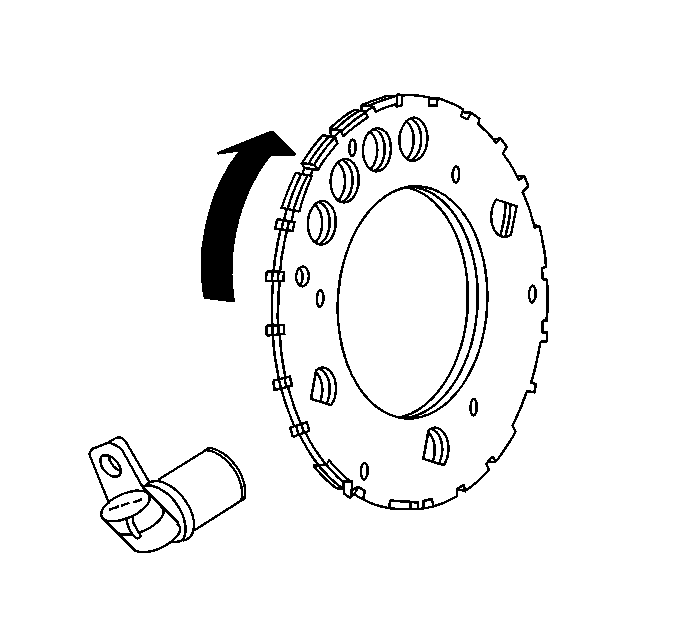
The crankshaft position
(CKP) sensor is a magneto resistive type sensor. The CKP sensor works
in conjunction with a 24X reluctor wheel. The reluctor wheel
is mounted on the rear of the crankshaft. The 24X reluctor wheel
uses 2 different width notches that are 15 degrees apart. This pulse
width encoded pattern allows cylinder position identification within
90 degrees of crankshaft rotation. In some cases this can be achieved
within 45 degrees of crankshaft rotation. The reluctor wheel also
has dual track notches that are 180 degrees out of phase, this
design allows for quicker starts and accuracy. The CKP sensor also
outputs a 4x signal for spark control, misfire diagnosis, tachometer output,
and fuel control. All CKP signals are output as a digital square waveform.
Camshaft Position Sensor
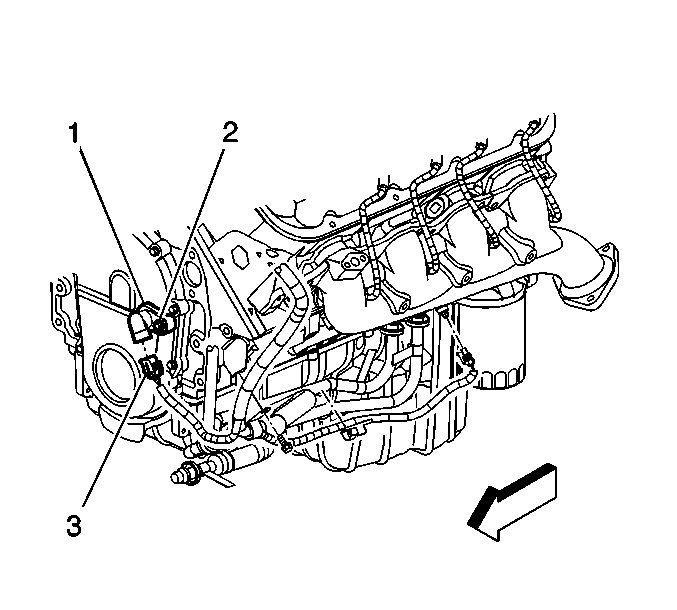
The camshaft position
(CKP) sensor works in conjunction with 1x reluctor wheel mounted at the rear
of the camshaft. The CMP is used to determine the top dead center position
of cylinder #1, and will synchronize with the 24x CKP sensor signal for
quicker starting. The PCM will detect an increase in the mass airflow (MAF)
sensor signal when the engine starts. The CMP signals are output as a digital
waveform.
Ignition Coils
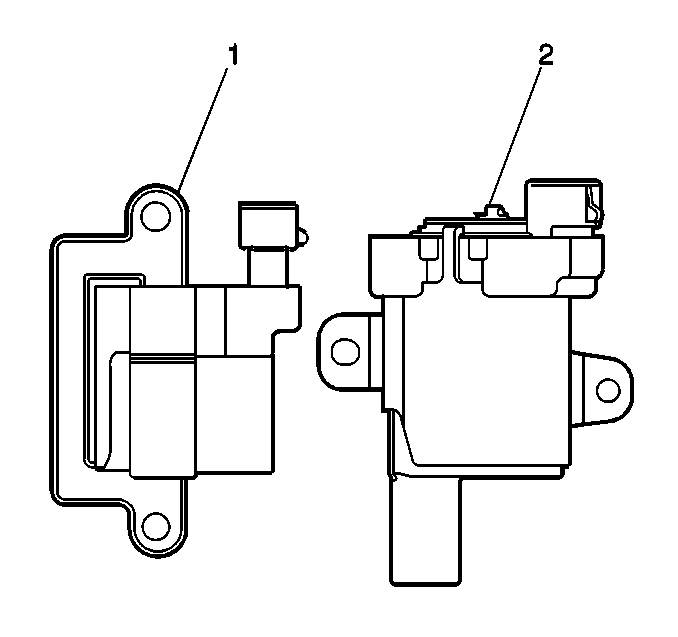
The ignition system on
this vehicle features a multiple coil configuration and is known as coil
near plug. There are two styles of ignition coil assemblies (1,2).
The engine could have either style. The ignition coil mounting bracket
is attached to the rocker cover (3).
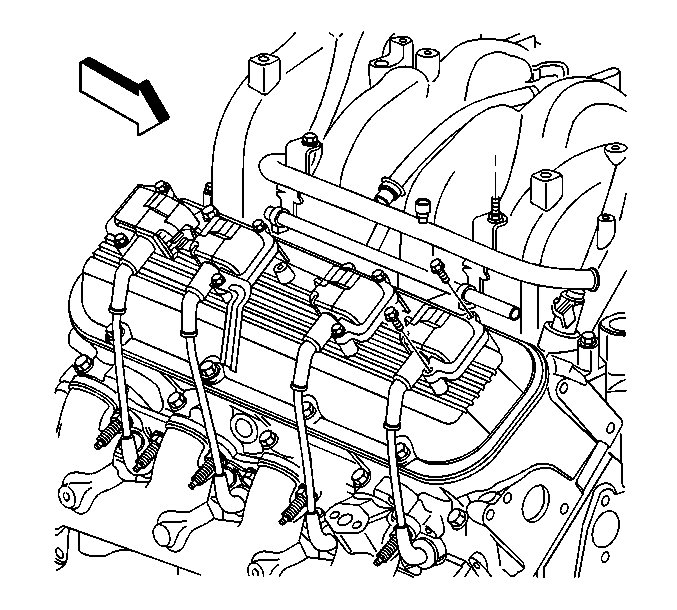
The 8 ignition coils are individually mounted above each cylinder
on the rocker covers, the coils are fired sequentially. There is
an ignition control (IC) circuit for each ignition coil . The
8 ignition control circuits are connected to the PCM, the PCM triggers
each ignition coil individually and makes all timing decisions.
The ignition coils are supplied with the following circuits:
| • | The ignition 1 voltage circuit |
| • | The ignition control circuit |
| • | The reference low circuit |
The ignition 1 voltage circuits are fused separately for each bank of
the engine. The 2 fuses also supply the power for the injectors for that bank
of the engine. Each coil is serviced separately.
This system puts out very high ignition energy for plug firing. Less
energy is lost to ignition wire resistance because the ignition wires are
much shorter than in a conventional ignition system.
Circuits Affecting Ignition Control
To properly control ignition timing, the PCM relies on the following
information:
| • | The engine load, manifold pressure or vacuum |
| • | The atmospheric, barometric, pressure |
| • | The intake air temperature |
| • | The crankshaft position |
The ignition control (IC) system consists of the following components:
| • | The 24X crankshaft position sensor |
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) |
The ignition control utilizes the following to control spark timing
functions:
| • | The 24X signal--The 24X crankshaft position sensor sends
a signal to the PCM. The PCM uses this signal to determine crankshaft position.
The PCM also utilizes this signal to trigger the fuel injectors. |
| • | The ignition control (IC) circuits--The PCM uses these circuits
to trigger the ignition coils. |
Noteworthy Ignition Information
There are important considerations to point out when servicing the ignition
system. The following noteworthy information will list some of these to help
the technician in servicing the ignition system.
| • | The ignition coils secondary voltage output capabilities are very
high--more than 40,000 volts. Avoid body contact with ignition
high voltage secondary components when the engine is running
or personal injury may result. |
| • | The 24X crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is the most critical
part of the ignition system. If the sensor is damaged so that pulses are not
generated, the engine does not start. |
| • | The CKP sensor clearance is very important. If the interrupter
ring is bent or damaged in any way, the CKP sensor may be destroyed. Extreme
care must be exercised during removal and installation procedures. |
| • | The ignition timing is not adjustable. There are no timing marks
on the crankshaft balancer or the timing chain cover. |
| • | Be careful not to damage the secondary ignition wires or boots
when servicing the ignition system. Rotate each boot in order to dislodge
the boot from the plug or coil tower before pulling the boot from the
spark plug or the ignition coil. |
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The PCM is responsible for maintaining proper spark and fuel injection
timing for all driving conditions. To provide optimum driveability and emissions,
the PCM monitors input signals from the additional following
components in calculating ignition control (IC) spark timing:
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | The mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| • | The trans range inputs from the transmission range switch (PRND) |
| • | The throttle position (TP) sensor |
| • | The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) |




