Circuit Description
The Class II Serial Data Circuit is used to communicate between systems. Each system connected to the Class II Serial Data line is assigned its own recognition code (ID / address). This code is used to identify which module or systems are communicating. The Node Alive or State of Health (SOH) messages are broadcast on the bus every two seconds. If a module is monitoring Node Alive messages for that module, it will reset its 5 second time for that particular module. Any system that cannot communicate properly will also store the appropriate communication DTCs that are assigned to the system(s) it could not communicate with.
The VTD sends a Vehicle Security Password when its ignition 1 input becomes active and includes its source ID. The Vehicle Security Password includes either a Fuel Continue Password or a Fuel Disable Password. The Vehicle Control Module (VCM)/Powertrain Control Module (PCM) learns the source ID, Monitors for the Node Alive messages, and responds with a Vehicle Security Status message including its VCM/PCM ID. The VTD learns the VCM ID, monitors for Node Alive messages from the VCM/PCM ID, and responds with a Vehicle Security Status acknowledge message. This tells the VCM, I heard you so you can stop sending the message.
Lost Communications DTCs (U-Codes) are equal to U1000 plus the ID. This is U1016 and U1192 for VTD.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The VCM/PCM has established communications and received the Vehicle Security Password during this ignition cycle from the VTD (Passlock) Control Module. |
| • | The VCM/PCM communications, no Node Alive/SOH messages received, from the VTD (Passlock) Control Module for 5 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
When a failure occurs after the VCM/PCM enables fuel due to receipt of a Vehicle Security Password containing the Fuel Continue Password:
| • | The vehicle starts |
| • | The VCM/PCM continues to enable fuel delivery (Fuel Enabled after Security Fault mode), until the fault is corrected and a valid password is received from the VTD (Passlock) Control Module. If the fault is corrected and a valid password is received, fuel delivery is enabled. The difference is that the Fail Enable Active bit in the Vehicle Security Status message will now be false while the Fuel Continue State bit will be true. |
| • | A DTC U1192 is stored in the VCM/PCM memory |
| • | The VCM/PCM will not illuminate the MIL |
When the failure occurs with the ignition OFF, or before the VCM/PCM received a valid Passlock password during engine cranking:
| • | The vehicle does not start or it starts and stalls |
| • | The VCM/PCM disables fuel delivery until the fault is corrected and a valid password is received from the VTD (Passlock) Control Module. Fuel delivery is disabled for the current ignition cycle. |
| • | A DTC U1192 is stored in the VCM/PCM memory |
| • | The VCM/PCM will not illuminate the MIL |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | This DTC requires an ignition cycle in order to change from Current to History |
| • | The VCM establishes communication with the VTD (Passlock) Control Module |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive ignition cycles if the condition for the malfunction is no longer present |
| • | The DTCs can be cleared using a scan tool |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Do not clear the DTCs unless directed by a diagnostic procedure. Clearing the DTCs will also clear valuable Freeze Frame and Failure Records information.
| • | Check for published service bulletins relating to the exhibited symptoms or component operation. |
| • | Inspect all related wiring and connections, including the connections at the VCM and the VTD (Passlock) Control Module. These connections may cause an intermittent malfunction. |
| • | Thoroughly check any circuit that can cause an intermittent complaint for the listed items: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating of connectors |
| - | Broken connector locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| - | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| - | Corroded terminals or connections |
| • | If the Class II Serial Data line is shorted to ground or shorted to voltage, all the modules or systems connected to the Class II Serial Data line will not be able to communicate properly. These systems or modules are capable of storing loss of communications DTC's (DTC's with the letter U as a prefix) in their memory. After repairing the cause of a DTC U1192, clear all DTCs from all systems capable of storing this DTC. |
| • | The scan tools Diagnostic Circuit Check can be used to: |
| - | Monitor the Class II Serial Data circuit for modules which have been or are communicating |
| - | Monitor for the presence of loss of communications DTCs (U1001-U1199) |
| - | Clear the loss of communication DTCs. When a Clear Codes command is issued, all codes, Freeze Frame, and Failure Records information is cleared. |
| • | The scan tools Diagnostic Circuit Check status of Active indicates that the module is communicating with the scan tool. An Inactive status indicates that the module previously communicated with the scan tool, but is not communicating currently. If a module is not listed at all, the module never successfully established communications with the scan tool. Refer to Electrical Diagnosis for the complete Class II data link to determine if there are any unlisted modules. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
If the scan tool indicates No Data Communication with Vehicle, inspect the Diagnostic Link Connector. Inspect Ignition (On/Off?), then no communication with any control module is possible. This problem will be diagnosed properly by following the Diagnostic Table Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with any Class II Modules, found in this section.
-
If the engine cranks but does not start, or the engine starts and immediately stalls, a problem with the EVO/Passlock Module's power and/or ground circuits could be the problem. Refer to Diagnostic System Check - Theft Deterrent .
-
This step verifies that a problem communicating with the EVO/Passlock Module exists.
-
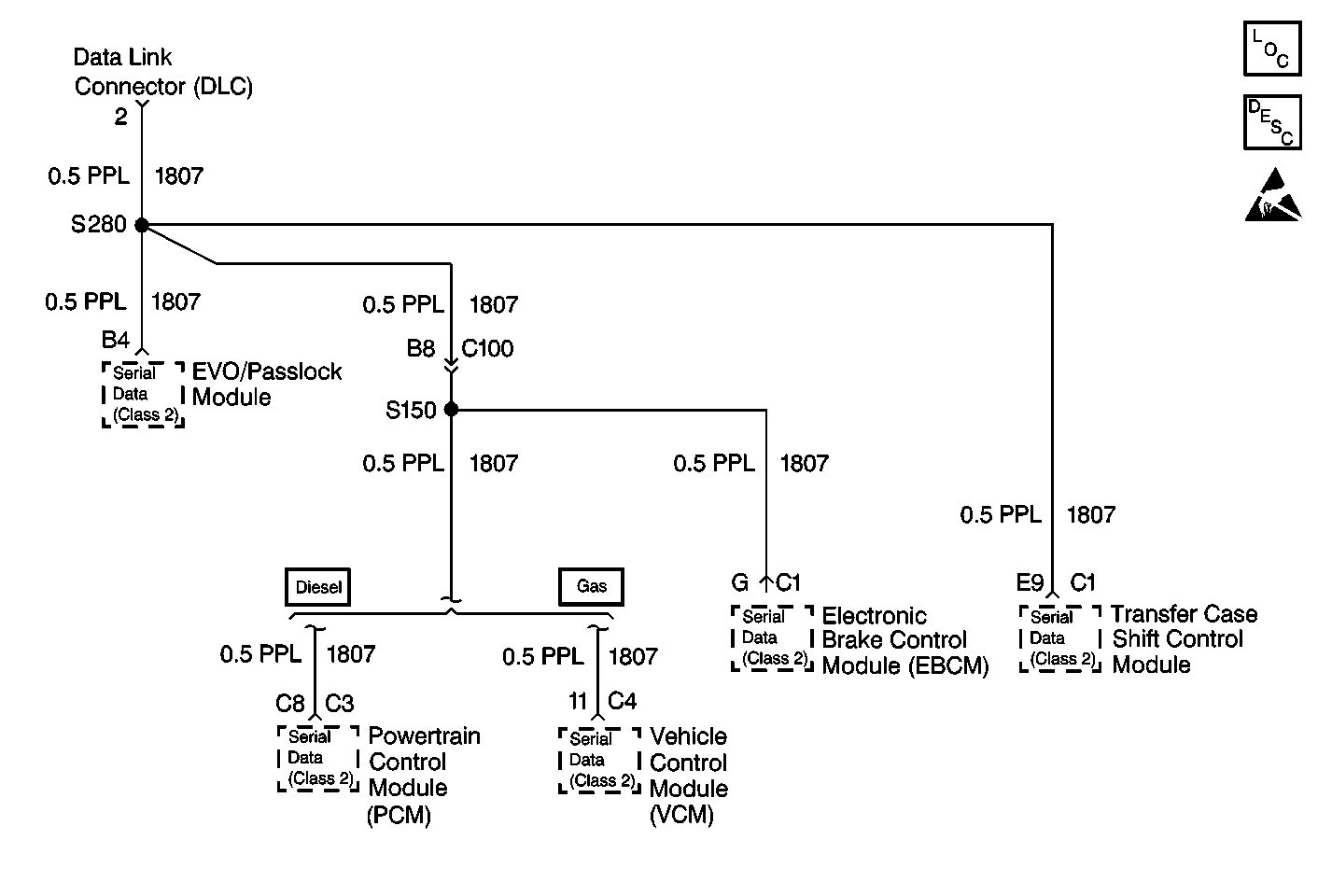
If communication can be established with the VCM/PCM, continuity exists in CKT 1807 from the Data Link Connector terminal 2 through Splice S280.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (5.0L/5.7L), Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (6.5L) or Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (7.4L) in Engine Controls |
2 | With the scan tool connected to the Data Link Connector (DLC).
Can communications be established with the VCM/PCM? | -- | Go to Step 3 | |
3 |
Is the resistance below the specified value? | 0-5ohms | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 |
4 | Replace the EVO/Passlock™ Module. Refer to Theft Deterrent Module Replacement in Theft Deterrent. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
5 | Locate and repair the open or cause of resistance in CKT 1807 (PPL) between the Passlock™ Module and splice S280. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- |
