System Description
The diagnostic system check is an organized approach to identifying an Antilock Brake System (ABS) malfunction. The diagnostic system check must be the starting point for any ABS complaint diagnosis. The diagnostic system check directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. Refer to the table below.
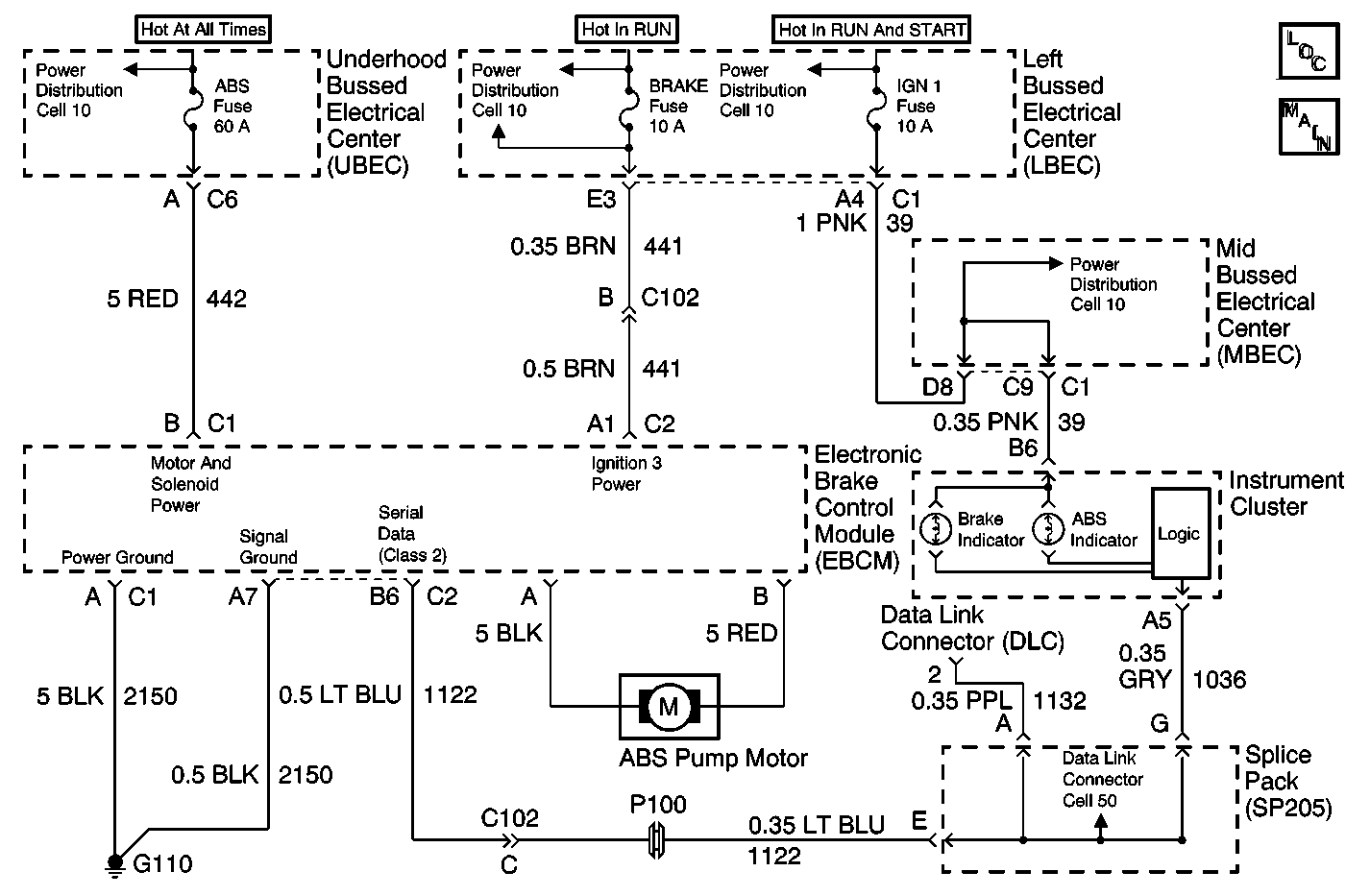
Diagnostic serial data is transmitted/received by the EBCM through connector C2, terminal B6. The EBCM is supplied battery voltage through connector C1, terminal B and switched ignition voltage through connector C2, terminal A1. Grounds are provided through connectors C1, terminal A, and C2 terminal A7.
Diagnostic Aids
Excessive resistance in the ground or power supply circuits will not allow communication with the EBCM. If communication with the EBCM is not possible, ensure that the ABS ground connection is good and that there is no excessive resistance in any of the power supply circuits.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step checks for normal ABS indicator lamp operation.
-
This step checks for ignition voltage at the EBCM.
-
This step checks for high resistance in the ground circuit.
-
This step decides between the LBEC or CKT 441 as the cause of the malfunction.
-
This step checks for a short to ground in the ignition voltage circuit.
-
This step uses the scan tool to monitor the class 2 data line for the proper messaging which turns on the ABS indicator lamp.
-
Using the scan tool, this step attempts to manually turn the ABS indicator Lamp ON.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Is data being received from the EBCM? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 4 |
2 | Using the Scan Tool , check for any DTCs. Are any current or history DTCs displayed? | -- | Go to Symptom and Diagnostic Trouble Code Table | Go to Step 3 |
Did the ABS indicator lamp turn on for two seconds and then turn off? | -- | System is operating normally. Go to Diagnostic Aids. | Go to Step 11 | |
4 | Attempt to communicate with other class 2 modules. Can communications be established with another class 2 module? | -- | Go to Step 5 | |
Is the voltage measured within the specified range? | 10-15V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 9 | |
Using the J 39200 , measure the resistance between terminal A7 in the 16-way EBCM harness connector and ground by probing terminal 7 in the J 39700. Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 12 | |
7 |
Is the terminal contact or the connection poor? | -- | Go to Step 8 | |
8 | Replace the terminals or repair the poor connection. Refer to Repairing Connector Terminals . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
Is the voltage measured within the specified range. | 10-15V | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 13 | |
Using the J 39200 , measure the resistance between the 16-way EBCM connector terminal A1 and ground by probing terminals 1 and 7 in the J 39700. Is the resistance measurement equal to the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 14 | |
Does the ABS Indicator Lamp data list parameter change from ON to OFF? | -- | Go to Step 18 | ||
12 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 2150. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
13 | Repair open or high resistance in LBEC. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
14 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
15 | Check CKT 441 for an open, or inspect the 16-way EBCM harness connector for physical damage which may result in an open with the 16-way EBCM harness connector connected to the EBCM. Is there evidence of damage? | -- | Go to Step 16 | |
16 | Repair the wiring or terminals which are damaged. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Repairing Connector Terminals . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
17 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 1 | -- |
Using the ABS Lamp Test portion of the Special Functions Menu on the scan tool, manually command the ABS Indicator Lamp to ON. Does the ABS Indicator Lamp turn ON? | -- | Go to Step 17 |
