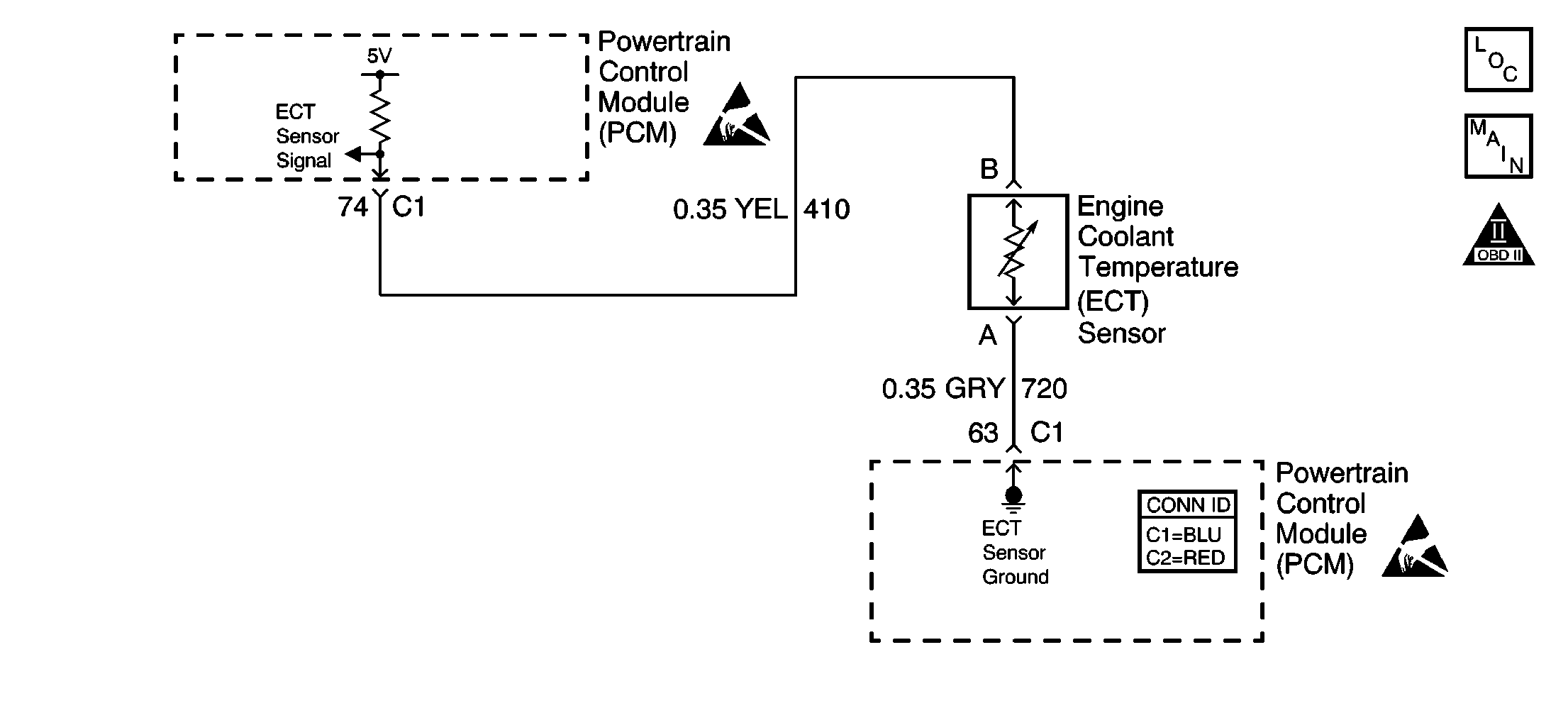
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor in order to determine how long it takes the engine to reach the coolant temperature required for Closed Loop operation. DTC P0125 sets if the PCM determines that the engine does not reach Closed Loop temperature in a specified amount of time. This test will not run if either the intake air or engine coolant temperature is too low at start-up. The PCM only runs this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) on a cold start and only once per cold start.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active ECT DTCs |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) DTCs |
| • | The engine is operating. |
| • | The ECT is between -36°C (-33°F) and +40°C (+104°F) at engine start-up. |
| • | The IAT is -7°C (+19°F) or more. |
| • | The vehicle speed (VS) is 1 km/h (1 mph) or more. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The Closed Loop coolant temperature of 34°C (93°F) is not reached within a predetermined time. The maximum allowable time depends on the start-up coolant temperature and the amount of airflow into the engine. The range for the time is from 2 minutes and 20 seconds to 22 minutes and 30 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent water intrusion into the PCM.
| • | Using the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions such as RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc. that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed. For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms . |
| • | If the engine has sat overnight, the engine coolant temperature and IAT values should display within a few degrees of each other. If the temperatures are not within 3°C (5°F), refer to Temperature Versus Resistance . |
| • | If you determine that the DTC occurs intermittently, performing the P1114 or P1115 diagnostic tables may isolate the cause of the fault. |
| • | An engine coolant temperature exceeding 34°C (93°F), indicates that the engine is capable of reaching the proper temperature, but not necessarily in the correct amount of time. Repeat this diagnostic table on a cold engine, and measure the time required to reach the temperature threshold. Refer to Engine Fails To Reach Normal Operating Temperature in Engine Cooling. When starting a cold engine, measure the amount of time it takes the engine to reach the specified temperature. The engine should reach the specified temperature within 5 minutes or less. If the engine does not reach the specified temperature within 5 minutes, check the following: |
| - | Coolant level |
| - | Thermostat operation |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
An ECT sensor failure could cause a DTC P0125 to set, so correct any ECT DTCs that are set.
-
If it is obvious that the engine is not reaching full operating temperature, for example the radiator hoses never get very warm, or there is a concern of little or no heat from the heater, you can skip this step.
-
This DTC will not report a pass. The scan tool status for this DTC will never report a pass. The scan tool will only display when the diagnostic fails. The repair is not complete if the scan tool indicates that the diagnostic ran and failed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
Are any engine coolant temperature DTCs set? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | ||||||||||
3 |
Does scan tool indicate the ECT sensor is less than the specified value? | -35°C (-31°F) | Go to DTC P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage | |||||||||
4 | Jumper the terminals of the ECT sensor harness connector together using a jumper wire. Does the scan tool indicate the ECT is more than the specified value? | 139°C (282°F) | Go to DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage | |||||||||
5 |
Important: Allow the engine to warm up if it has not already reached the specified temperature. Five minutes is the maximum amount of time it should take to reach this temperature from a cold start. Less time is required if the engine is already warm. Does the scan tool indicate the engine coolant temperature reached the specified value? | 34°C (93°F) | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
Measure the resistance of the ECT sensor using the DMM. Refer to Temperature Versus Resistance . Is the ECT resistance close to the value indicated in the Temperature vs Resistance table? | -- | |||||||||||
7 | Check the following for an engine cooling system problem:
Refer to Engine Fails To Reach Normal Operating Temperature in Engine Cooling. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
8 | Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that this test failed? | -- | |||||||||||
10 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
