DTC P0161 HO2S Heater Performance Bank 2 Sensor 2 w/o RPO OSG
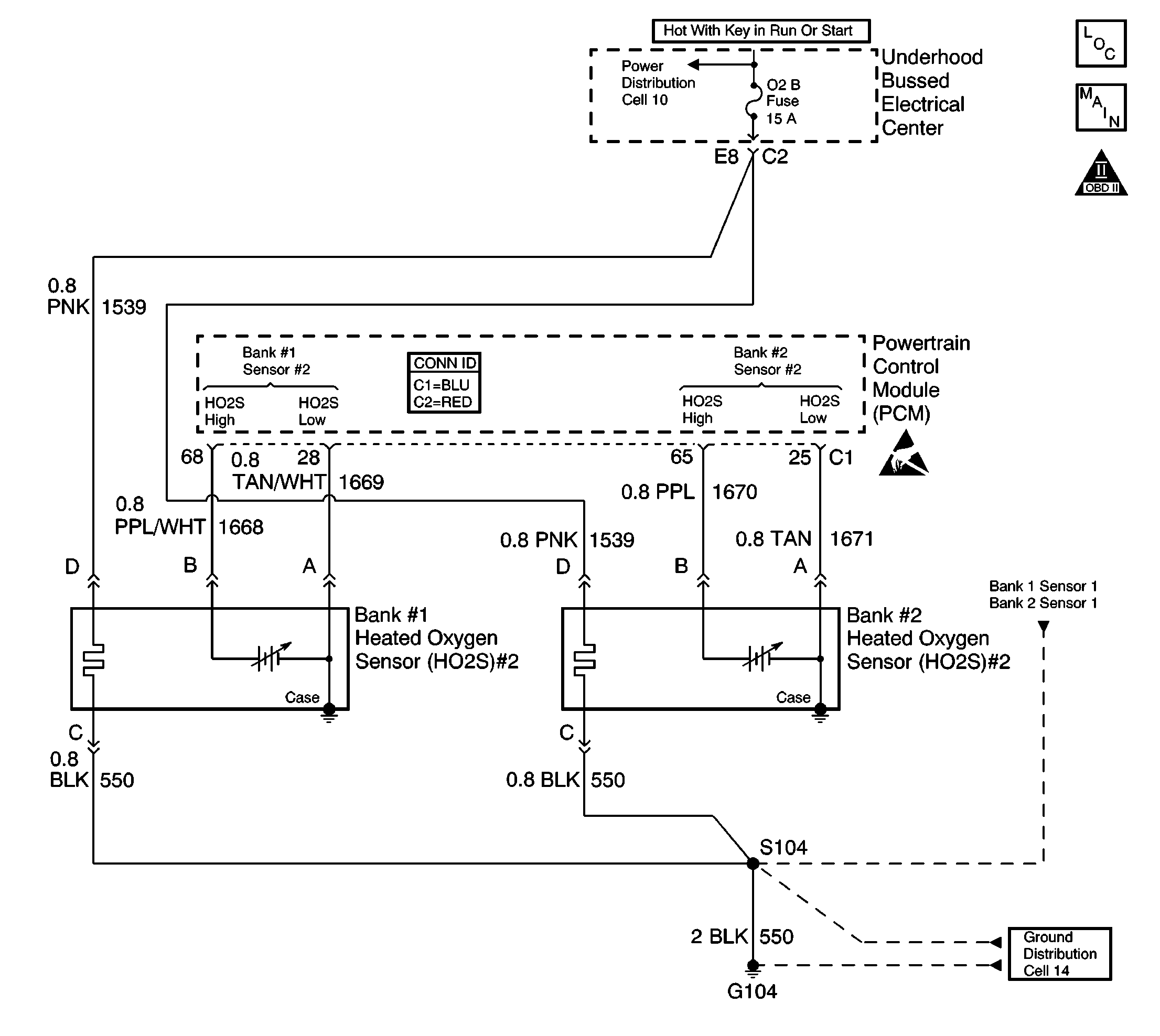
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a bias voltage approximately 450 mV on the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) signal high and low circuits. When you turn the ignition to the ON position, battery voltage is supplied to the HO2S heater. As the heater reaches the operating temperature, the HO2S voltage responds by changing from a bias voltage range to the normal operation. Typically, as the HO2S reaches the operating temperature, the HO2S voltage goes from a bias voltage to a voltage below 300 mV. Depending on the exhaust gas content, it is possible for the HO2S voltage to go above 450 mV.
The PCM runs the heater test only on a cold start depending on the cumulative air flow and only once an ignition cycle. When you start the engine, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. When the HO2S voltage goes above or below the bias range threshold, the PCM determines how much time it took. If the PCM detects that the process took too much time for the HO2S to enter into normal operating range, a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) sets. The time the process takes the HO2S to reach operating temperature is based on the amount of air that flows into the engine.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active mass air flow (MAF) DTCs |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) DTCs |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) DTCs |
| • | No active throttle position (TP) DTCs |
| • | No active injector DTCs |
| • | No active crank sensor DTCs |
| • | No active ignition control DTCs |
| • | The IAT and the ECT are less than 50°C (122°F) and are within 8°C (14.5°F) of each other at engine start-up. |
| • | The ignition voltage is between 10 volts and 18 volts. |
| • | The secondary air injection (AIR), exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), and the catalyst diagnostics are not active. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The HO2S voltage remains between 300 mV and 700 mV for a predetermined amount of time depending on ECT and air flow.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent water intrusion into the PCM.
| • | Using the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data can help determine how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also help determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions such as RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc. that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed. For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms . |
| • | The heater diagnostic will only run on a cold start and run once per ignition cycle. |
| • | An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation. The HO2S wires provides the supply of oxygen. Inspect the HO2S wires and connections for breaks or contamination. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | For an intermittent condition, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The engine must be allowed to cool, as the HO2S may be at operating temperature and no drop or rise in HO2S voltage would occur. If the HO2S voltage stays between 300-700 mV, indicates the HO2S heater is inoperative,
-
If more than one HO2S heater DTC is set, this is a good indication that the HO2S fuse is open. Test all the related circuits going to all of the heated oxygen sensors for a short to ground. If you cannot locate a shorted circuit, it may be necessary to disconnect each HO2S one at a time to locate a shorted sensor.
-
This step tests whether the ignition positive voltage supply is available at the sensor.
-
This step tests whether a ground is available at the sensor.
-
This step tests whether the HO2S heater element is internally open.
-
Inspect the ignition positive voltage circuits at the Underhood Electrical Center for poor connections.
-
Test the ground circuits for an open if more than one heater DTC sets.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
|
Important: If you have been operating the engine, allow the engine to cool for about one-half hour before proceeding.
Does the HO2S voltage go from a bias voltage to above or below the specified values? | 300-700 mV | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Inspect the fuse for the HO2S ignition positive voltage. Is the HO2S fuse open? | -- | |||
Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | |||
Connect the J 35616-200 test lamp between the HO2S ignition positive voltage and the HO2S heater ground. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | |||
Measure the resistance between the HO2S ignition positive voltage and the HO2S heater ground at the HO2S pigtail using the DMM. Is the HO2S resistance within the specified values? | 3.5-14.0 ohms | |||
Repair the open in the HO2S ignition positive voltage circuit to the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
Repair the open in the HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
9 |
Did you find and repair the condition? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
13 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
DTC P0161 HO2S Heater Performance Bank 2 Sensor 2 w/ RPO OSG
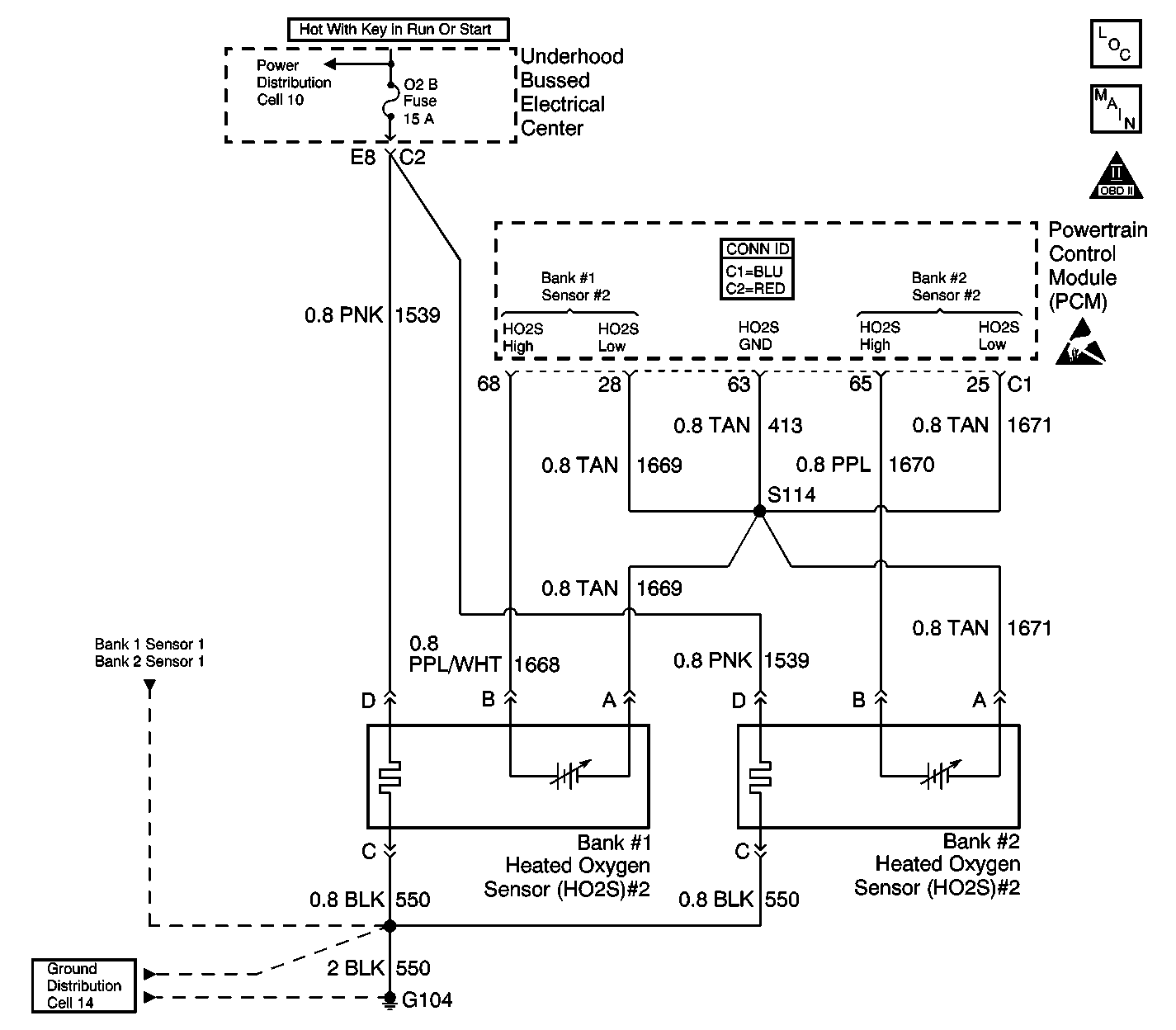
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a sensor designed to create a voltage relative to the oxygen content in the engine exhaust stream. The control module supplies the HO2S with signal high and low circuits. Ignition voltage and ground are supplied to the HO2S heater by independent circuits. The oxygen content of the exhaust indicates when the engine is operating lean or rich. When the HO2S detects that the engine is operating rich, the signal voltage is high, and decreases the signal voltage as the engine runs leaner. This oscillation above and below the bias voltage, sometimes referred to as activity or switching, can be monitored with the HO2S signal voltage.
The HO2S contains a heater that is necessary in order to quickly warm the sensor to operating temperature and to maintain the operating temperature during extended idle conditions. The HO2S needs to be at a high temperature in order to produce a voltage. Once the HO2S has reached operating temperature, the control module monitors the HO2S bias or reference voltage as well as the HO2S signal voltage for Closed Loop fuel control. During normal Closed Loop fuel control operation, the control module will add fuel or enrich the mixture when the HO2S detects a lean exhaust content and subtract fuel, or lean-out the mixture when the HO2S detects a rich exhaust condition.
Certain vehicle models utilize an oxygen sensor after the catalytic converter in order to monitor catalyst efficiency.
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) determines if the HO2S is functioning properly by checking for an adequate number of HO2S voltage transitions above and below the bias range of 300-600 mV. This DTC sets when the powertrain control module (PCM) fails to detect a minimum number of voltage transitions above and below the bias range during the test period. Possible causes of this DTC are listed below:
| • | An open or a short to voltage on either the HO2S signal or HO2S low circuits |
| • | A malfunctioning HO2S |
| • | A problem in the HO2S heater or its circuit |
| • | A poor HO2S ground |
| • | An open HO2S low reference circuit |
This DTC determines if the post-convertor HO2S heater circuit is functioning properly by monitoring the amount of time required for the HO2S to reach operating temperature. This DTC sets when the PCM fails to detect HO2S voltage transitions above and below the bias range within a specified amount of time. Possible cause of this DTC are listed below:
| • | An open circuit in either the HO2S ignition positive voltage or the HO2S heater ground circuits |
| • | An HO2S heater element problem |
Conditions for Running the DTC
Important: This test is void for this cold start if the system voltage remains outside the specified range for more than 4 seconds.
| • | The system voltage is between 11.7-17 volts. |
| • | The mass air flow (MAF) is less than 21 g/s. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 2 seconds. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than 33°C (91°F). |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 33°C (91°F). |
| • | The difference between the ECT and IAT is 5°C (9°F) or less. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage remains within 150 mV of its startup voltage for 270 seconds after cold start.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connection repairs, refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, then refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
As the heater warms the oxygen sensor to operating temperature, the HO2S will output a voltage in relation to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the exhaust usually contains a high oxygen content. With the engine OFF the HO2S voltage will usually decrease from the initial voltage due to the high oxygen content.
-
This step checks for proper HO2S heater ignition positive voltage and ground supply.
-
This step checks for proper PCM and signal circuit operation.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ? | -- | ||||||||||
|
Important: The HO2S must be cool before proceeding with the diagnosis. The Ignition must remain OFF for at least one-half hour before proceeding with the diagnosis.
Does the HO2S voltage increase or decrease from the initial voltage by at least the value specified? | 150 mV | |||||||||||
3 | The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above conditions as necessary. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | |||||||||||
Is the HO2S voltage less than the specified value? | 20 mV | |||||||||||
6 |
Ensure the ignition is ON while the engine is OFF. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | ||||||||||
7 |
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 | Repair the open HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
10 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 | Repair the circuit that measured high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
12 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||||||||||
13 |
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
14 |
Important: The HO2S must be cool before proceeding with the diagnosis. The ignition must remain OFF for at least one-half hour before proceeding with the diagnosis.
Does the HO2S voltage increase or decrease from the initial voltage by at least the value specified? | 150 mV | ||||||||||
15 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
