Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
PCM ,CMP Sensor, CKP Sensor, KS, IPC
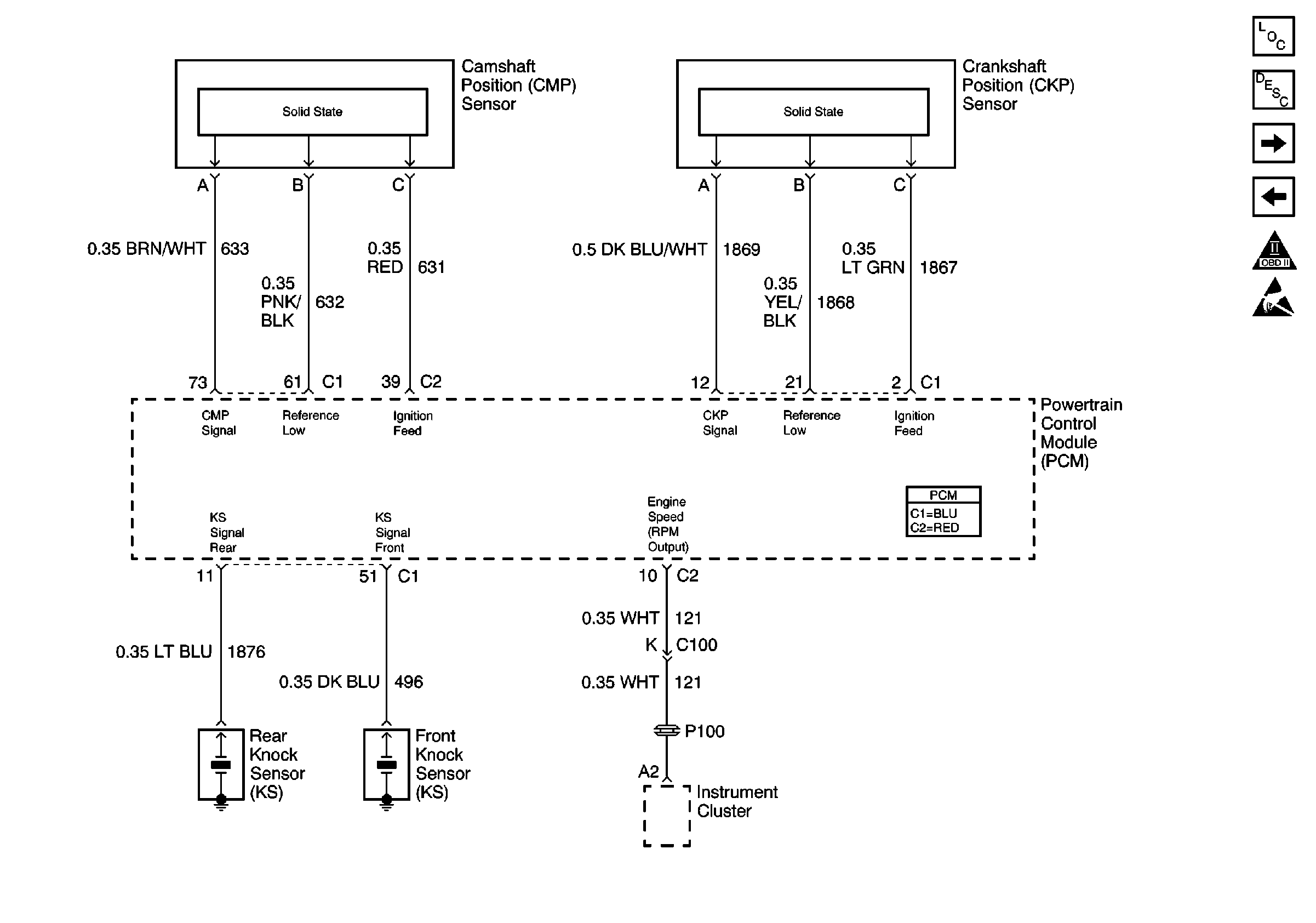
.
Circuit Description
In order to maintain a reasonably low emissions of hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the engine controls
system uses a three-way catalytic converter. The catalyst within
the converter promotes a chemical reaction which oxidizes the
HC and CO present in the exhaust gas. This reaction converts
them into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The catalyst
also reduces NOx, converting it to nitrogen. The PCM monitors
this process using bank 2 heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2.
bank 2 HO2S 2, located in the exhaust stream past the three-way
catalytic converter, produces an output signal which indicates
the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst. This determines
the catalysts ability to convert exhaust emissions effectively.
If the catalyst is functioning correctly, the bank 2 HO2S
2 signal will be far less active than that produced by bank
2 HO2S 1. This indicates that the three-way catalytic
converters oxygen storage capacity is operating at a threshold considered
acceptable.
When the conditions for running this DTC are met, the following occurs:
- The powertrain control module (PCM) captures the current rear
HO2S rich or lean status.
- The air or fuel ratio transitions from rich to lean or lean to
rich depending on the capture rear HO2S rich or lean status.
- The air fuel ratio transitions a second time opposite the first
air fuel ratio transition.
- The PCM captures the response time, the time the HO2S goes from
below 300 mV to above 600 mV and from 600 mV to below
300 mV, of the front and rear HO2S when the air fuel ratio
transitions occurred.
- The PCM measures the time it takes the rear HO2S voltage to cross
a reference rich or lean threshold minus the time it takes the front HO2S
voltage to cross the same rich or lean threshold. The time difference
from the front and rear HO2S is the oxygen storage capacity of the
catalyst. This DTC sets if the time exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active mass air flow (MAF) DTCs |
| • | No active manifold absolute pressure (MAP) DTCs |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) DTCs |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) DTCs |
| • | No active throttle position (TP) DTCs |
| • | No active exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) DTCs |
| • | No active evaporative emission (EVAP) DTCs |
| • | No active vehicle speed sensor (VSS) DTCs |
| • | No active secondary air injection (AIR) DTCs |
| • | No active crankshaft position (CKP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active camshaft position (CMP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active ignition control (IC) DTCs |
| • | No active idle air control (IAC) DTCs |
| • | No active exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) DTCs |
| • | No active evaporative emission (EVAP) DTCs |
| • | No active heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) DTCs |
| • | No active fuel trim DTCs |
| • | No active injector DTCs |
| • | No active transmission DTCs |
| • | Engine operating longer than 400 seconds. |
| • | The ECT is between 80°C (176°F) and 120°C (248°F). |
| • | The IAT is between -15°C (+5°F) and 75°C (167°F) |
| • | Engine speed is more than 800 RPM for a minimum of 30 seconds
(4.8L, 5.3L) or 40 seconds (6.0L) since the end of the last idle
test. |
| • | The BARO is more than 74 kPa. |
| • | The fuel system is operating in Closed Loop. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM determines the oxygen storage capability of the catalytic converter
has degraded below a calibrated threshold.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) when
the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic
fails. The PCM stores this information in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure
Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after
3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not
fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles,
if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
-
Before replacing
the three-way catalytic converter, make sure that any conditions which may
have caused the catalyst to be damaged have been corrected.
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
|
2
| Are any other DTCs
set?
| --
| Go to the applicable DTC table
|
Go to Step 3
|
3
|
- Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | Verify that the three-way catalytic converter is an original equipment
part. |
| • | Inspect the three-way catalytic converter for damage such as dents,
severe discoloration caused by excessive temperature, holes, etc. Refer to
Exhaust System Inspection
in Engine Exhaust. |
| • | Insure that internal three-way catalytic converter rattle caused
by damaged catalyst is not present. |
| • | Inspect exhaust system for leaks, damage, or loose or missing
hardware in the area from the converter to the HO2S 2 primarily. Refer to
Exhaust System Inspection
in Engine Exhaust. |
| • | Insure that the HO2S 1 and the HO2S 2 are secure and that their
pigtails and wiring are not damaged or contacting the exhaust. Refer to
Exhaust System Inspection
in Engine Exhaust. |
- Repair conditions, as necessary.
Did you find and correct a condition?
| --
|
Go to Step 5
|
Go to Step
4
|
4
| Replace the converter.
Refer to
Catalytic Converter Replacement
in Engine Exhaust.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 5
| --
|
5
|
- Select the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) option and the Clear
DTC Information option using the scan tool.
- Idle the engine at the normal operating temperature.
- Select the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) option and the Specific
DTC option, then enter the DTC number using the scan tool.
- Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC
as specified in the supporting text, if applicable.
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed?
| --
|
Go to Step 6
|
Go to Step 2
|
6
| Select the Capture
Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool.
Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed?
| --
| Go to the applicable DTC table
| System OK
|

