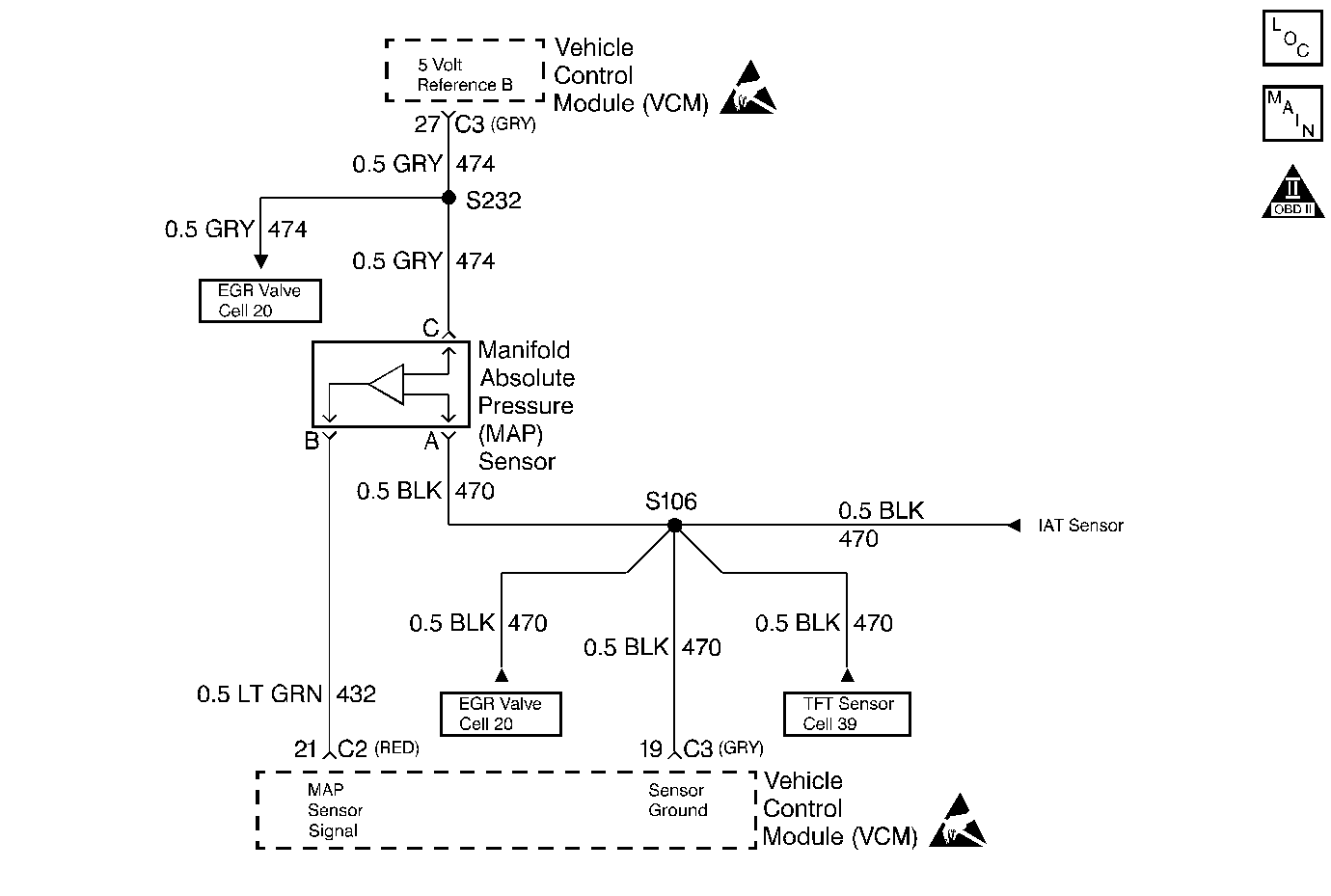
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds to changes in the intake manifold pressure (vacuum). A 5 volt reference is applied to the sensor. A variable resistor moves in relation to the manifold pressure and a voltage signal is sent back to the VCM on the 5 volt reference circuit. This voltage signal varies from 1.0-1.5 volts at closed throttle to 4.0-4.5 volts at wide open throttle (low vacuum).
A substantial change in the throttle position and the engine speed must precede any substantial change in the MAP.
The VCM utilizes the MAP signal and the throttle position in order to determine the correct amount of fuel delivered to the engine. This DTC is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No IAC sensor DTCs |
| • | No EGR DTCs |
| • | Engine running |
| • | Engine speed changes less than 100 RPM |
| • | Throttle position changes less than 1.95 % |
| • | EGR flow changes less than 5 % |
| • | Idle air changes less than 5 counts |
| • | No change in brake switch status |
| • | No change in the clutch status (manual transmission) |
| • | No change in A/C status |
| • | No change in power steering switch status |
| • | The above conditions have stabilized for a period of 2.0 seconds |
| • | The above conditions are met for 24 consecutive tests in a 100 test sample |
| • | Change in MAP is greater than 0.18 volts |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM turns ON the MIL when 2 failures are reported after 2 consecutive trips. The VCM substitutes a calculated value for the MAP sensor value so an acceptable driving condition is maintained.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
After 3 trips without a failure, the MIL turns OFF. After 40 ignition cycles, if no failure was reported, the DTC will clear.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the MAP sensor vacuum source for leaks, restrictions or poor connections.
Important: The electrical connector must remain securely fastened.
Important: After removing the MAP Sensor from the intake manifold, replace the MAP Sensor to intake manifold seal.
Disconnect the MAP Sensor from the intake manifold and gently twist the sensor in order to check for intermittent connections. Output changes greater than 0.1 volt indicate a bad connector or connection.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Check the MAP sensor output voltage to the VCM. Without the engine running, this voltage represents a barometric reading to the VCM.
Important: When comparing the scan tool readings to a known good vehicle, compare vehicles which use a MAP sensor having the same color insert or the same Hot Stamped number.
Important: The electrical connector must remain securely fastened.
Important: After removing the MAP sensor from the intake manifold, replace the MAP Sensor to intake manifold seal.
-
Applying 34 kPa (10 Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change. The voltage value obtained by subtracting the second reading from the first should be greater than 1.5 volts. When applying vacuum to the sensor, the change should be instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a faulty sensor.
-
Disconnect the sensor from the bracket and gently twist the sensor in order to check for intermittent connections. Output changes greater than 0.1 volt indicate a bad connector or connection. If OK, replace the sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record freeze frame and the failure records for reference because the Clear Info function will lose the data. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Is the MAP sensor voltage within the typical scan tool data, plus or minus the specified value? | 0.4 V | ||
Is the difference greater than the specified value? | 1.5 V | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Check the MAP sensor connections. Was a problem found? | -- | |||
5 | Repair the connections as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Engine Electrical. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
6 | Replace the MAP sensor. Refer to MAP Sensor Replacement for the 4.3L. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
8 | Using the scan tool, select the Capture Info and the Review Info. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to The Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
