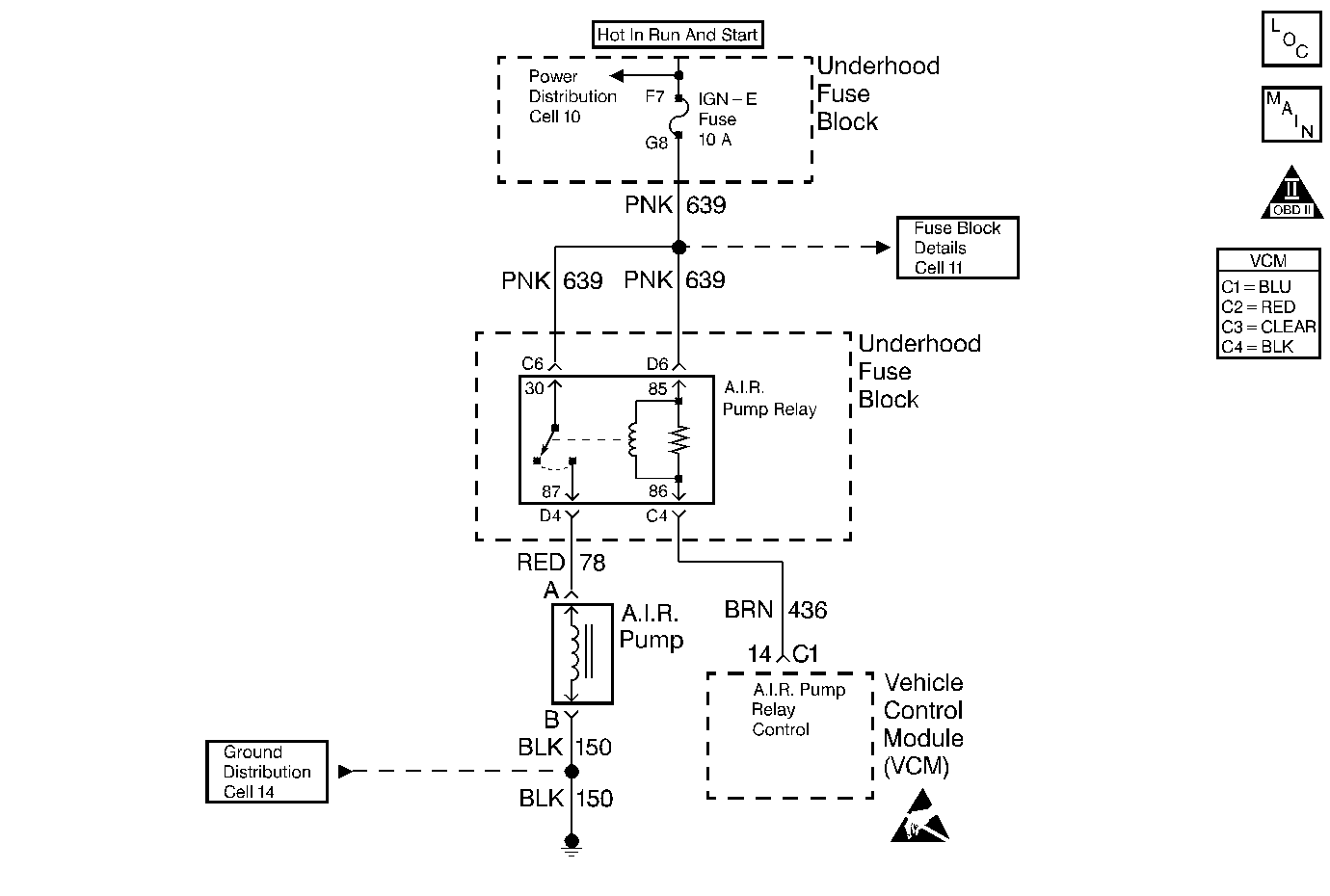
Circuit Description
A secondary air injection (AIR) pump is used on this vehicle to lower tailpipe emissions on start-up. The VCM supplies a ground to the AIR pump relay control circuit. This energizes the AIR pump relay and supplies voltage to the AIR pump clutch. The VCM uses the HO2S voltages and the short term fuel trim to diagnose the secondary air injection system.
The VCM monitors the HO2S voltages and the short term fuel trim value when the AIR pump is energized. This additional air causes the HO2S voltages to shift low, reflecting the leaner mixture. The short term fuel trim should increase above 128 confirming that the VCM is supplying additional fuel. The low HO2S voltages and higher short term fuel trim value provide confirmation that the secondary air injection system is operating properly. When the AIR pump is de-energized, the HO2S voltages should increase and begin switching normally.
This DTC is set when the VCM determines that the HO2S voltages for both banks did not respond as expected during this test. If only one HO2S responded as expected, the VCM sets either a DTC P1415 or P1416 depending on which engine bank the AIR system is inoperative.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active secondary AIR DTCs |
| • | No active CMP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active ECT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active EGR DTCs |
| • | No active fuel trim DTCs |
| • | No active IAC DTCs |
| • | No active IAT sensor DTCs |
| • | No active MAF sensor DTCs |
| • | No active MAP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active HO2S DTCs |
| • | No active transmission DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP system DTCs |
| • | No active TP sensor DTCs |
| • | No active VS sensor DTCs |
| • | No active misfire DTCs |
| • | The commanded air/fuel ratio is 14.7:1 |
| • | The system voltage is greater than 10 volts |
| • | The engine speed is greater than 550 RPM |
| • | The engine load is less than 50% |
| • | The MAF is less than 100 g/s |
| • | The system has been in closed loop operation for more than 15 seconds |
| • | The IAT is greater than 0°C (32°F) |
| • | The ECT is between 75°C and 105°C (167° to 221°F) |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The HO2S voltage remains above 299 mV or the change in the short term fuel trim value is less than a calibrated value.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Low AIR System volume may cause a DTC P1415, P1416 or an intermittent complaint. Also check for the following conditions:
| • | Pinched, kinked or restricted AIR pipes, hoses or fittings |
| • | Leaks, holes, loose fittings or hoses |
| • | Restricted or obstructed AIR pump inlet |
| • | Leaks or restrictions in the vacuum hoses for the AIR Shut Off Valve. |
An AIR supply hose that is melted before the check valve could indicate exhaust gas back-flow past the check valve.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step will determine if the AIR System is functioning correctly.
-
This step will determine if the VCM is capable of controlling the AIR Pump Relay.
-
This step is to check for a short to voltage on the control circuit.
-
The engine must be running for this test to ensure a vacuum supply to the system.
-
This step will determine if the AIR Pump is capable of producing airflow.
-
An open fuse for the battery feed circuit could be caused by a short to ground in the components operated by the relay. Also check the wiring in the circuits on the switched side of the relay. Refer to Diagnostic Aids.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||||
Does the Short Term Fuel Trim indicate a change of more than the specified value within 30 seconds? | 16% | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||||||
3 | The DTC is intermittent. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
4 |
Is the AIR Pump running? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||||
5 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||||
6 |
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||||||
7 | Probe the terminal for the AIR Pump ground circuit on the engine harness side of the AIR Pump harness connector with a test lamp connected to B+. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 38 | Go to Step 28 | ||||||||||||
8 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||||
9 | Check for an open in the AIR Pump battery positive voltage circuit between the AIR Relay and the AIR Pump. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||||
10 | Probe the terminal for the battery positive voltage circuit at the AIR Pump Relay connector with a test lamp connected to a ground. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 29 | ||||||||||||
11 |
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 30 | ||||||||||||
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 35 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||||||
13 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||||
14 | Check for an open in the AIR Pump Relay Control circuit between the relay and the VCM. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||||||
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 31 | Go to Step 39 | |||||||||||||
Does air flow from the AIR Shut Off Valve? | -- | Go to Step 24 | Go to Step 17 | |||||||||||||
Does air flow from the hose? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 25 | |||||||||||||
18 |
Is the vacuum above the specified value while the AIR Pump is running? | 10 in Hg | Go to Step 36 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||||
19 | Check for a leak or restriction in the vacuum hose between the AIR Solenoid and the AIR Shut Off Valve. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||||
20 |
Is the vacuum above the specified value? | 10 in Hg | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 26 | ||||||||||||
21 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 22 | ||||||||||||
22 |
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 33 | ||||||||||||
23 |
Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 37 | Go to Step 32 | ||||||||||||
24 | Check for leaks or restrictions on the following components:
Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||
25 | Check for a restriction or an obstruction in the inlet hose of the AIR Pump. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Step 38 | ||||||||||||
26 | Repair the leak or restriction in the vacuum source hose to the AIR Solenoid. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
27 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
28 | Repair the open in the AIR Pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
Repair the open or short to ground in the battery positive voltage circuit for the AIR Pump Relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | |||||||||||||
30 | Repair the open or short to ground in the ignition positive voltage circuit to the AIR Pump Relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
31 | Repair the short to voltage on the AIR Pump Relay Control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
32 | Repair the open in the AIR Solenoid ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
33 | Repair the open in the AIR Solenoid battery positive voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
34 | Repair as necessary. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Check Valve Pipe Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
35 | Replace the AIR Pump Relay. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
36 | Replace the AIR Shut Off Valve. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Check Valve Pipe Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
37 | Replace the AIR Solenoid. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Check Valve Pipe Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
38 | Replace the AIR Pump. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
39 |
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 40 | -- | ||||||||||||
40 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | Go to Step 41 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||||
41 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
