Completely inspect the turbocharger and all other engine components that may cause similar conditions before replacing the turbocharger.
Use the following information to diagnose problems caused by the turbocharger.
The turbocharger is serviced as a complete unit.
- Remove the turbocharger oil return pipe bolts.
- Remove the turbocharger oil return pipe and gasket.
- Clean mating surfaces.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, compared to a normal compressor wheel
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a soft object.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a hard object.
- Inspect compressor blades for heavy rubbing.
- Check the housing for signs of rubbing.
- Check the compressor wheel for a build-up of dirt.
- If the turbocharger does not pass any of these inspections, replace the turbocharger.
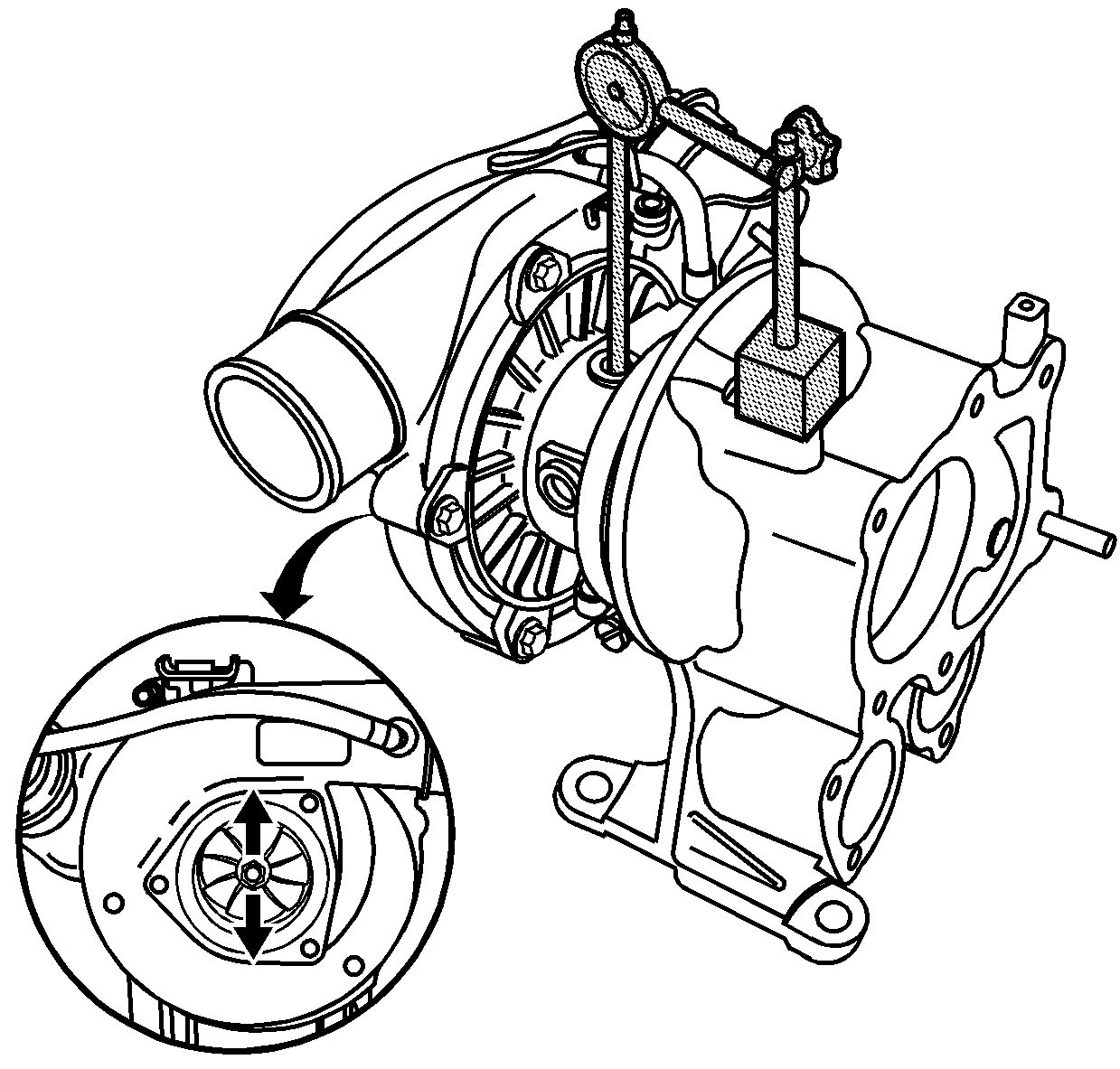
- Measure the radial play. If the radial play exceeds 0.20 mm (0.0079 in) of movement, replace the turbocharger.
- Measure the axial play. If the axial play exceeds 0.11 mm (0.0043 in) of movement, replace the turbocharger.
- Install the turbocharger oil return pipe and new gasket.
- Install the turbocharger oil return pipe bolts.
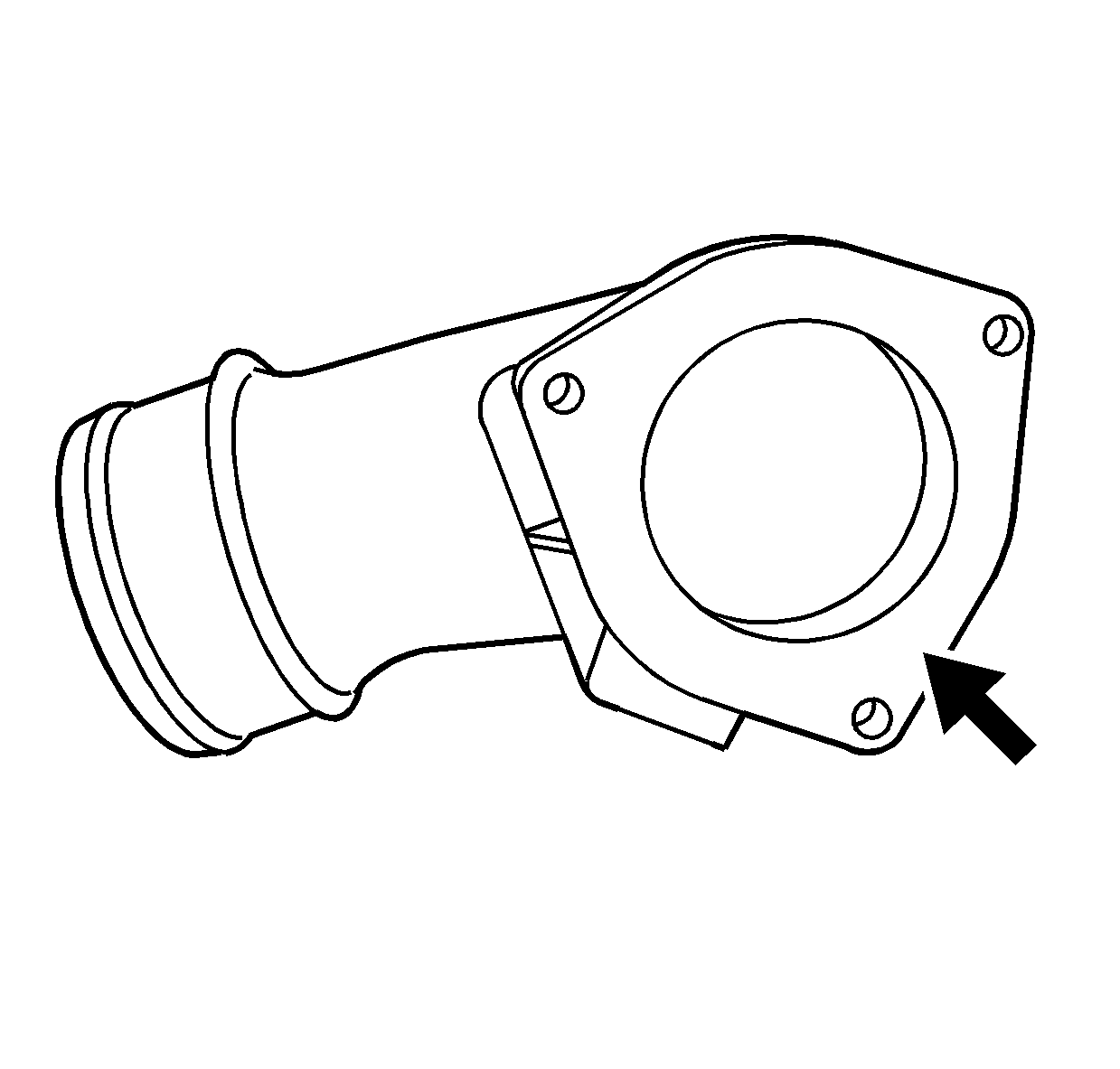
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct.
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct for cracks.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces for damage.
- Replace the turbocharger inlet duct if any damage is found.
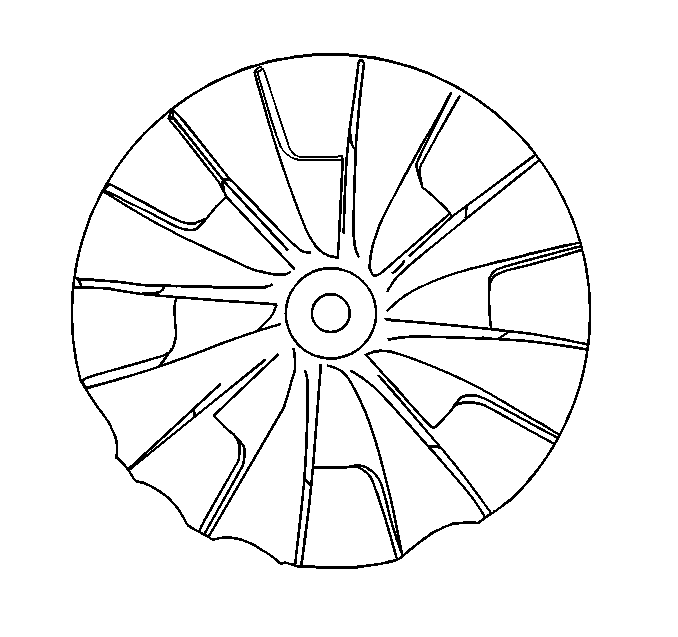
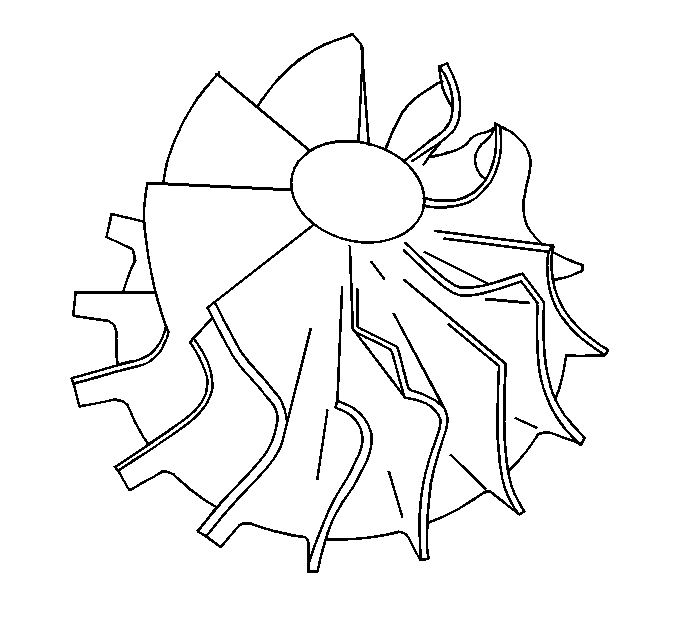
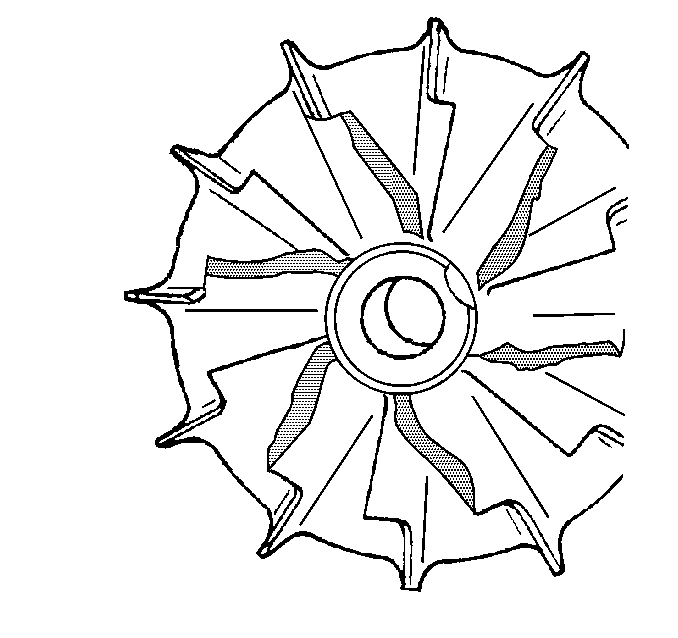
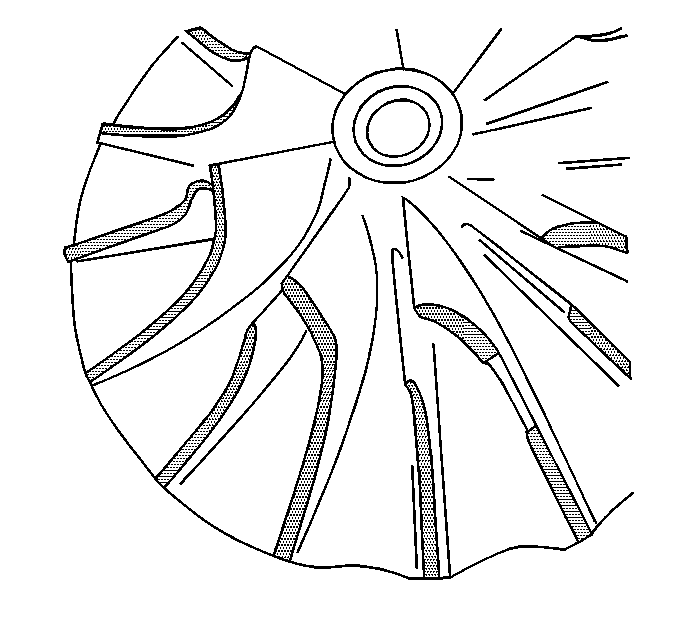
Ensure that the following conditions do not exist on the compressor wheel blades:
| • | Cracks |
| • | Bends |
| • | Erosion of the blades |
| • | Broken blades |
Important:
• Carefully grasp the compressor wheel nut with your fingers and rotate
the wheel in a clockwise direction. The wheel should turn freely with no
signs of binding or scraping caused by housing contact. • Rotate the turbocharger while pushing in and pulling out on the compressor
wheel; the wheel should rotate freely with no contact with the housing. • Carefully grasp the compressor wheel nut with your fingers and rotate
the wheel while moving the wheel up and down. There should be no compressor
wheel to the housing contact. AXIAL AND RADIAL PLAY IS NORMAL EVEN ON A NEW TURBOCHARGER. If the compressor wheel comes in contact with the housing, it will be
very evident when rotating the wheel. The wheel will drag or scrape on the
housing surface and visual damage will be evident on the wheel blades and
the housing surface.
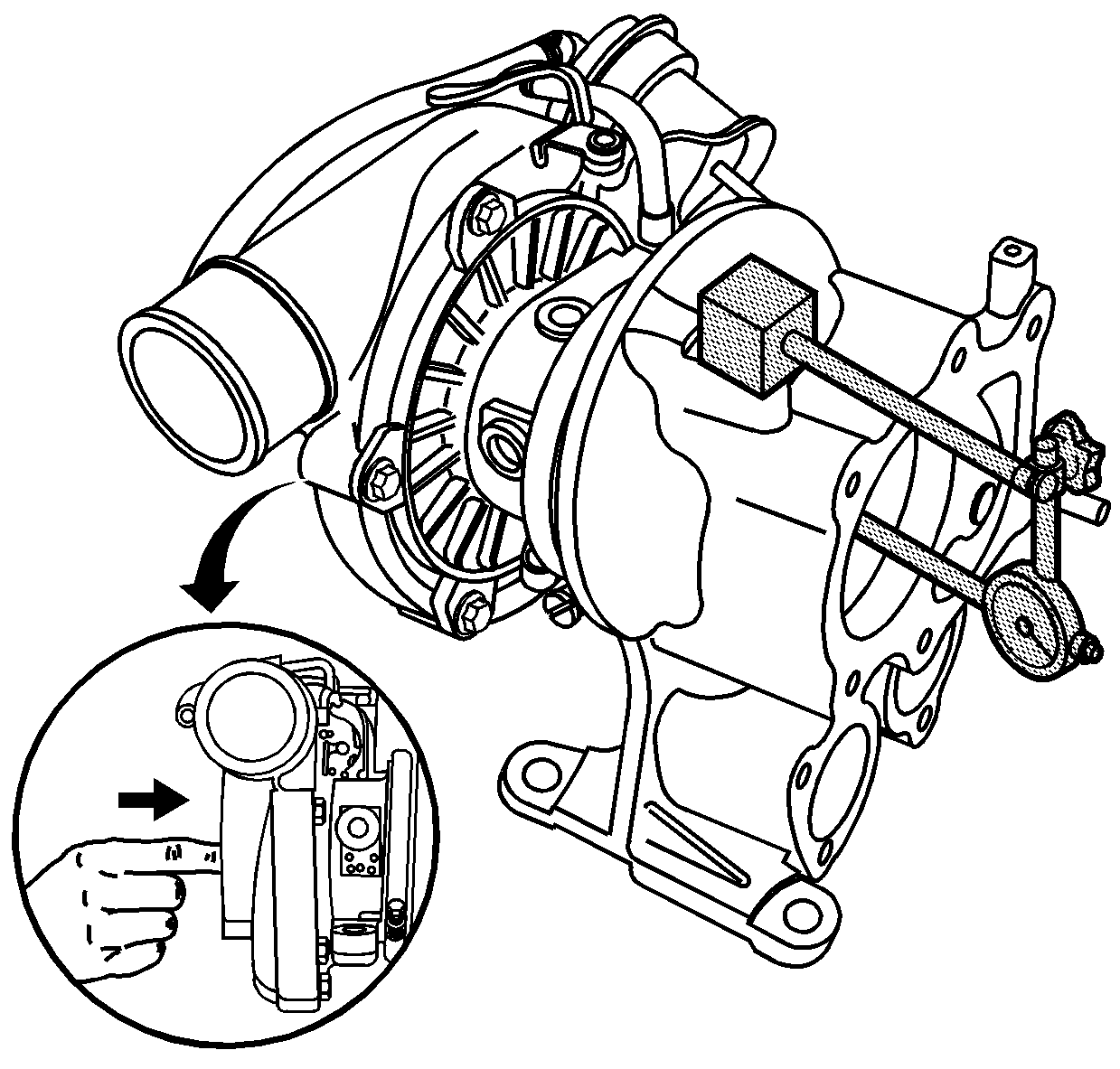

Tighten
Tighten the turbocharger oil return pipe bolts to 21 N·m
(15 lb ft).