For 1990-2009 cars only
- Verify that the correct spark plug is installed. An incorrect spark plug causes driveability conditions. Refer to Ignition System Specifications for the correct spark plug.
- Ensure that the spark plug has the correct heat range. An incorrect heat range causes the following conditions:
- Inspect the terminal post (1) for damage.
- Inspect the insulator (2) for flashover, carbon tracking, or soot. This is caused by the electrical charge traveling across the insulator (2) between the terminal post (1) and ground. Inspect for the following conditions:
- Inspect the insulator (2) for cracks. All or part of the electrical charge may arc through the crack instead of the electrodes (3, 4).
- Inspect for evidence of improper arcing.
- Inspect the spark plug recess area of the cylinder head for debris. Dirty or damaged threads can cause the spark plug not to seat correctly during installation.
| • | Spark plug fouling--Colder plug |
| • | Pre-ignition causing spark plug and/or engine damage--Hotter plug |
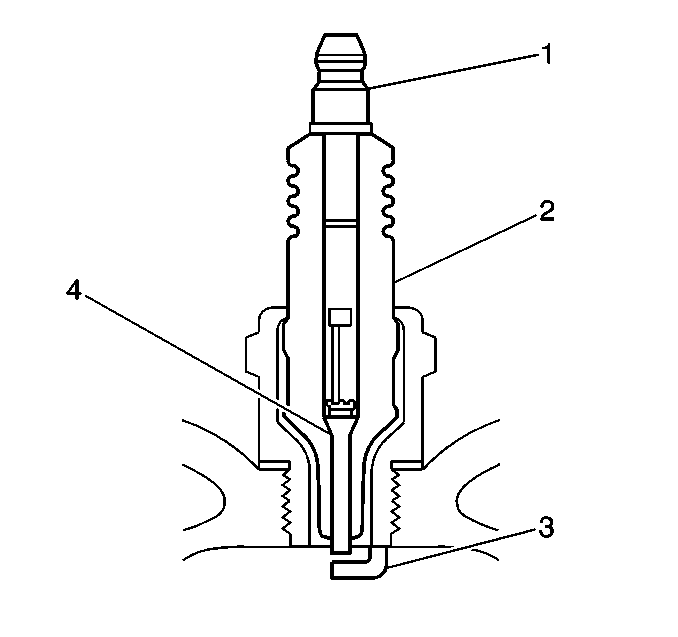
| • | Inspect for a bent or broken terminal post (1). |
| • | Test for a loose terminal post (1) by twisting and pulling the post. The terminal post (1) should not move. |
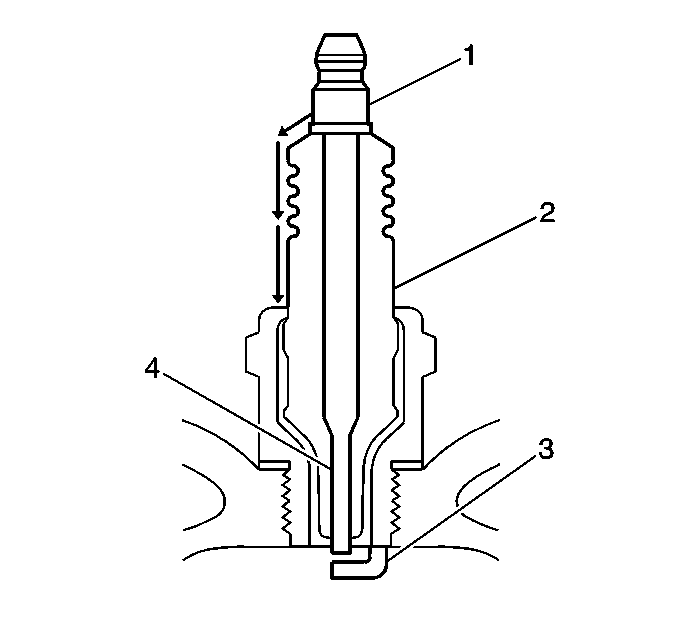
| • | Inspect the spark plug boot for damage. |
| • | Inspect the spark plug recess area of the cylinder head for moisture, such as oil, coolant, or water. A spark plug boot that is saturated causes arcing to ground. |
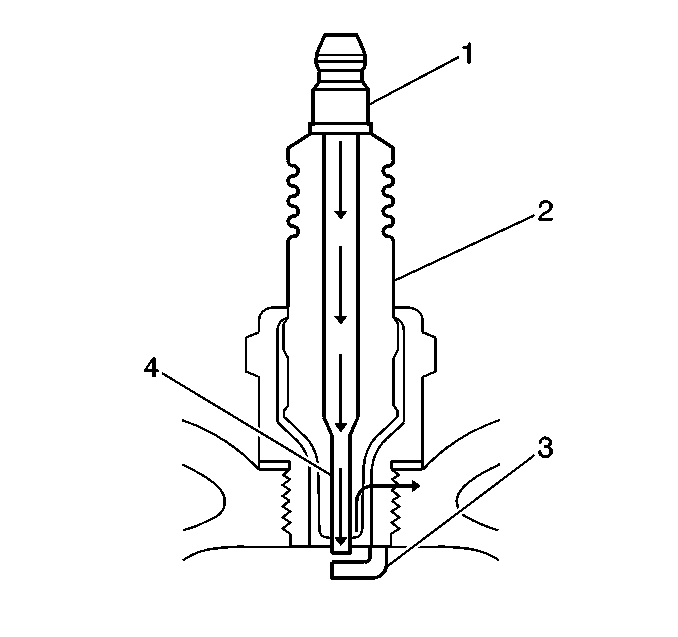
| • | Measure the gap between the center electrode (4) and the side electrode (3) terminals. Refer to Ignition System Specifications . An excessively wide electrode gap can prevent correct spark plug operation. |
| • | Inspect for the correct spark plug torque. Refer to Ignition System Specifications . Insufficient torque can prevent correct spark plug operation. An over torqued spark plug, causes the insulator (2) to crack. |
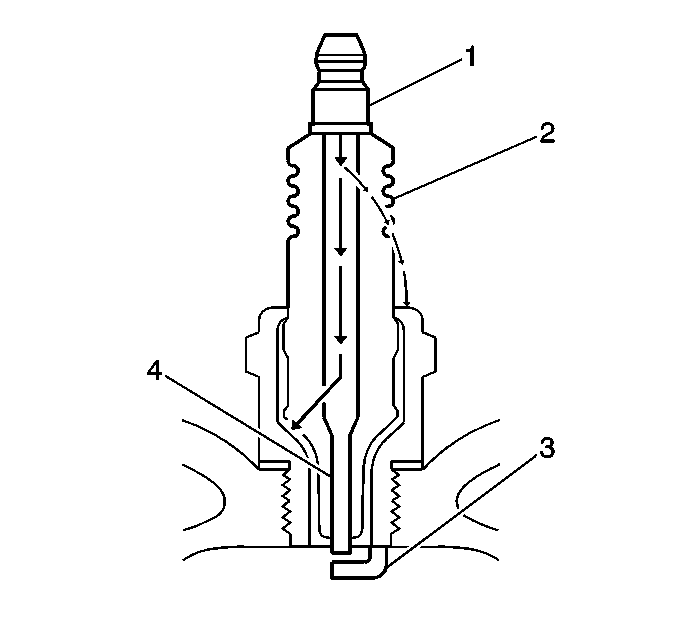
| • | Inspect for signs of tracking that occurred near the insulator tip instead of the center electrode (4). |
| • | Inspect for a broken or worn side electrode (3). |
| • | Inspect for a broken, worn, or loose center electrode (4) by shaking the spark plug. |
| - | A rattling sound indicates internal damage. |
| - | A loose center electrode (4) reduces the spark intensity. |
| • | Inspect for bridged electrodes (3, 4). Deposits on the electrodes (3, 4) reduce or eliminates the gap. |
| • | Inspect for worn or missing platinum pads on the electrodes (3, 4), if equipped. |
| • | Inspect for excessive fouling. |
Visual Inspection
- Normal operation--Brown to grayish tan with small amounts of white powdery deposits are normal combustion by-products from fuels with additives.
- Carbon fouled--Dry, fluffy black carbon, or soot caused by the following conditions:
- Deposit fouling--Oil, coolant, or additives that include substances such as silicone, very white coating, reduces the spark intensity. Most powdery deposits will not affect spark intensity unless they form into a glazing over the electrode.
| • | Rich fuel mixtures |
| - | Leaking fuel injectors |
| - | Excessive fuel pressure |
| - | Restricted air filter element |
| - | Incorrect combustion |
| • | Reduced ignition system voltage output |
| - | Weak ignition coils |
| - | Worn ignition wires |
| - | Incorrect spark plug gap |
| • | Excessive idling or slow speeds under light loads can keep spark plug temperatures so low that normal combustion deposits may not burn off. |
