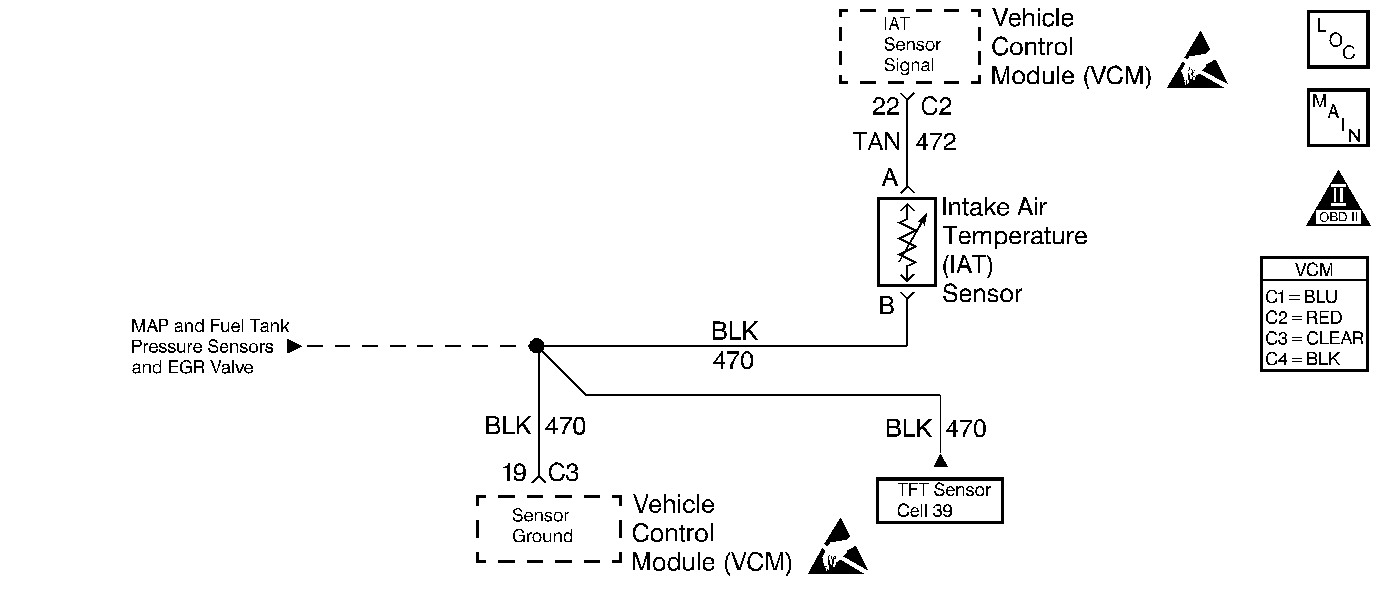
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor. The control module supplies the IAT sensor a reference voltage on the IAT sensor signal circuit and a ground circuit. When the IAT sensor resistance is high, indicating a cold sensor, the IAT sensor signal voltage remains near the supplied voltage and decreases the signal voltage as the sensor warms. The control module monitors the IAT sensor signal circuit in order to calculate the temperature of the air entering the engine.
This DTC is designed to detect intermittent low voltage signals on the IAT sensor signal circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active VS sensor DTCs |
| • | The vehicle speed is greater than 2 mph (3 km/h). |
| • | The engine has been running for more than 100 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The IAT voltage is less than a calibrated voltage for more than 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM stores the DTC in History if the VCM detects an intermittent problem.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
A scan tool indicates the temperature of the ambient air entering the throttle body. The air temperature should read very close to the temperature of the outside air and should rise gradually as the engine warms up and the underhood temperature increases. If DTC P1112 is set, the problem is intermittent. Check for a short to ground in the IAT sensor signal circuit. Accomplish this by moving the VCM harness at various locations and monitoring the IAT temperature or the IAT voltage on the scan tool. If the voltage varies, look for a short to ground in the area of the harness that caused the waiver. Also, a sensor may become skewed or mis-scaled. The Temperature vs. Resistance Value Table will help to detect a skewed sensor. Refer to Temperature vs Resistance .
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the insulation.
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wire connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | Corrosion |
| • | Moisture in the connector |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Important: Be sure to use the same diagnostic test equipment for all measurements.
-
If the IAT sensor voltage is less than 0.25 volts, then the conditions for the DTC are still present.
-
If any other non-intermittent DTCs are set go there first.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save the Freeze Frame and Failure records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Is the IAT sensor voltage less than the specified value? | 0.25V | |||
Are any non-intermittent DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | ||
4 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
5 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
6 |
Did the voltage fluctuate? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
7 | Repair the circuit as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
9 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
