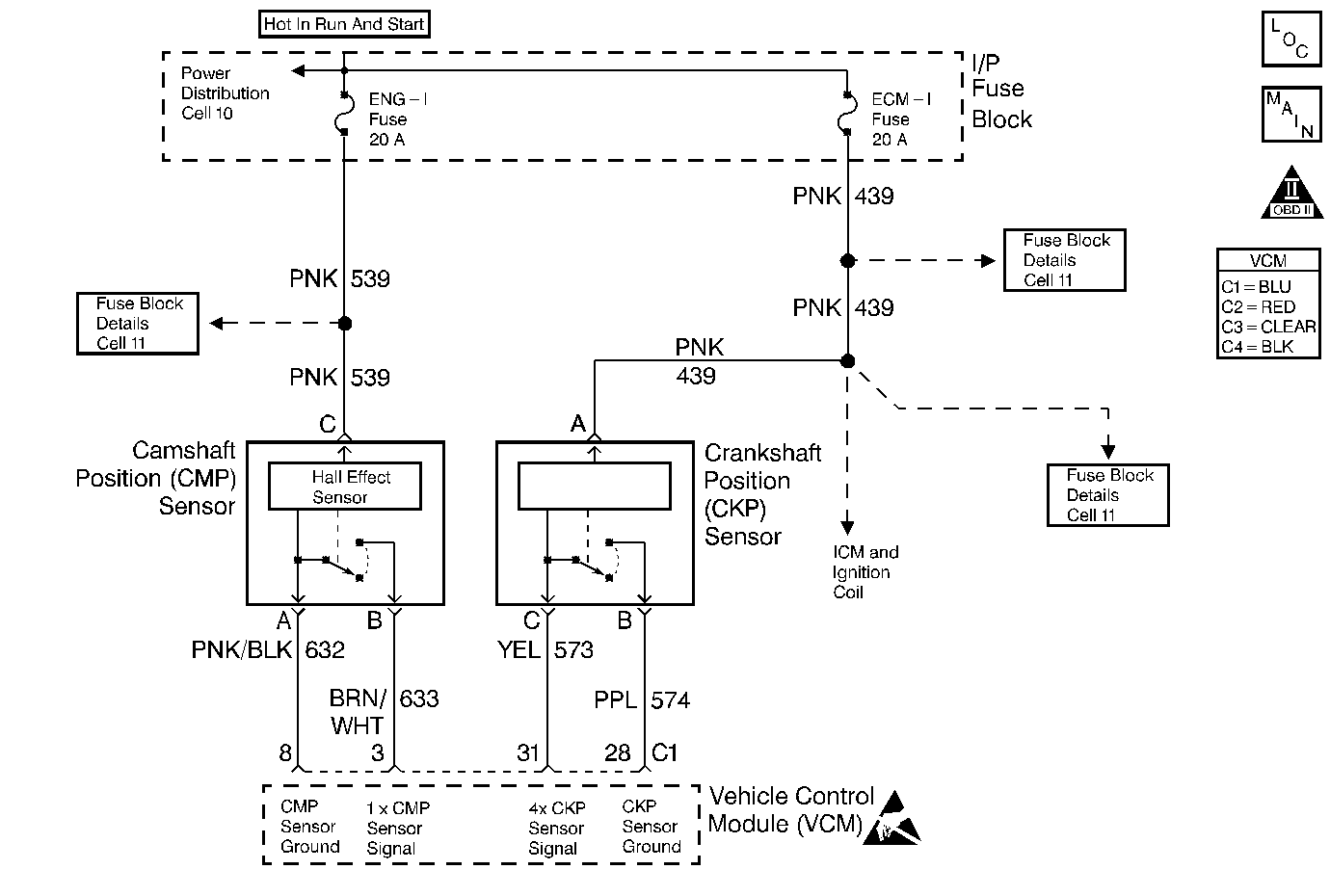
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is a sensor designed to detect changes in a magnetic field. The control module supplies the CMP sensor with signal and ground circuits. Ignition voltage is supplied to the CMP sensor by an independent circuit. The CMP sensor produces a magnetic field whenever the ignition is ON. The CMP sensor is mounted near a reluctor wheel that is attached to the distributor shaft. When the distributor shaft rotates, or when the engine is cranking or running, the reluctor wheel changes the magnetic field. The CMP sensor converts each change in the magnetic field into a PULSE. The number of teeth on the reluctor wheel determines how many pulses the CMP sensor detects per camshaft rotation. The control module uses the CMP sensor signal in order to calculate the correct timing for sequential fuel injection.
If the VCM detects the CMP signal is not synchronized with the CKP sensor signal, this DTC will be set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The CMP sensor reference pulse is not detected at the correct time interval once every crankshaft revolution.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM will turn ON the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) after 2 consecutive test failures.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
A poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation may cause an intermittent.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wire connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Refer to Symptoms .
Test Description
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. This data will be lost when the Clear DTC Information function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 | Check for an intermittent short to the voltage or EMI (electromagnetic interference) such as the wires which run along side the spark plug wires or the high power transmitters (like the mobile radios operating in the vicinity) on the Camshaft Position sensor wires. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
3 | Repair short to voltage or EMI as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Repair Instructions. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
4 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
5 | Use the scan tool in order to display the Capture Info and the Review Capture Info functions. Are there any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to The Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
