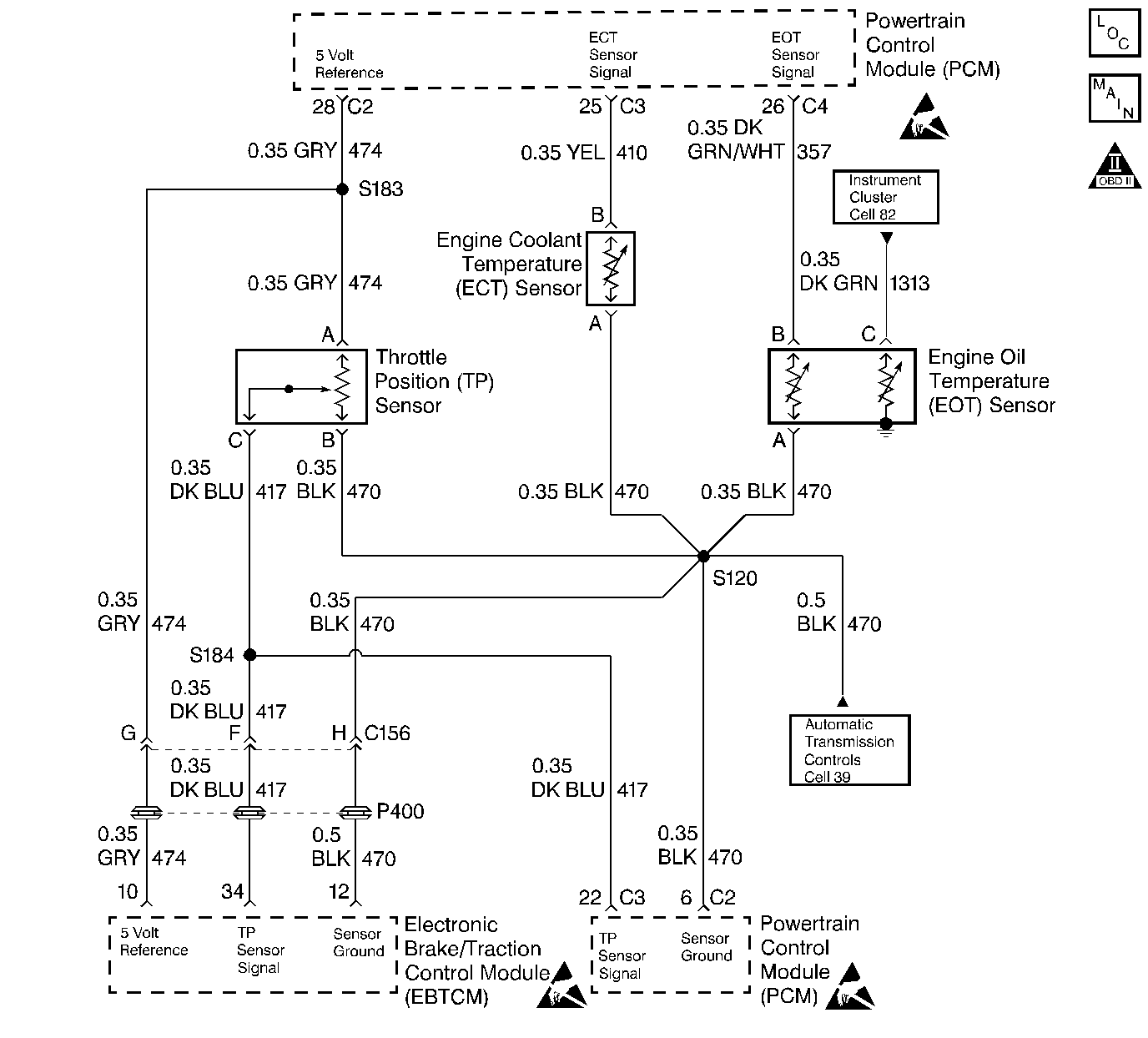
Circuit Description
The Engine Oil Temperature sensor is a thermistor which monitors engine oil temperature. The engine oil temperature sensor is mounted in the engines oiling system The PCM applies a voltage (about 5.0 volts) on the signal circuit to the sensor. When the engine oil is cold, the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the PCM signal voltage will be high. As the engine oil warms, the sensor resistance becomes less, and the PCM voltage drops.
The PCM uses the oil temperature information to control A/C clutch and the engine cooling fans. This sensors information is also sent across serial data (UART), to the Central Control Module (CCM) to determine when to change the engine oil. For more information on the oil life monitor system, refer to Section 8D, Central Control Module.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Time since engine start is 30 minutes. |
| • | Engine oil temperature is greater than 152°C (306°F) for 4.5 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | A last test failed (Current DTC) will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | PCM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | Using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | An intermittent may be caused by the following: |
| - | Mis-routed harness |
| - | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| - | Broken wire inside the insulation. |
For intermittents, refer to Symptoms .
| • | If other DTCs are set that share the same ground and/or 5.0 volt reference circuit, check for faulty connections and for faulty wiring. |
| • | If the engine has been allowed to sit overnight, the engine oil temperature and engine coolant temperature values should display within a few degrees of each other. If the temperatures are not within 3°C (5°F), refer to Temperature vs Resistance . |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Determines if the malfunction is present.
-
Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can be useful in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that were noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
-
If the engine oil temperature goes below -30°C (-22°F), indicates the PCM and wiring are OK.
-
Disconnecting the PCM will allow using the DVM (J 39200) to check continuity of the circuits. This will aid in locating an open or shorted circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Is Engine Oil Temp. at or above the specified value? | 152°C (306°F) | |||
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the Engine Oil Temp. below the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | |||
Was the Engine Oil Temperature. signal circuit grounded? | -- | |||
6 | Replace the Engine Oil Temperature sensor. Refer to EOT Sensor . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 |
Important:: Replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
9 | Using the scan tool, select Capture Info, Review Info. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
