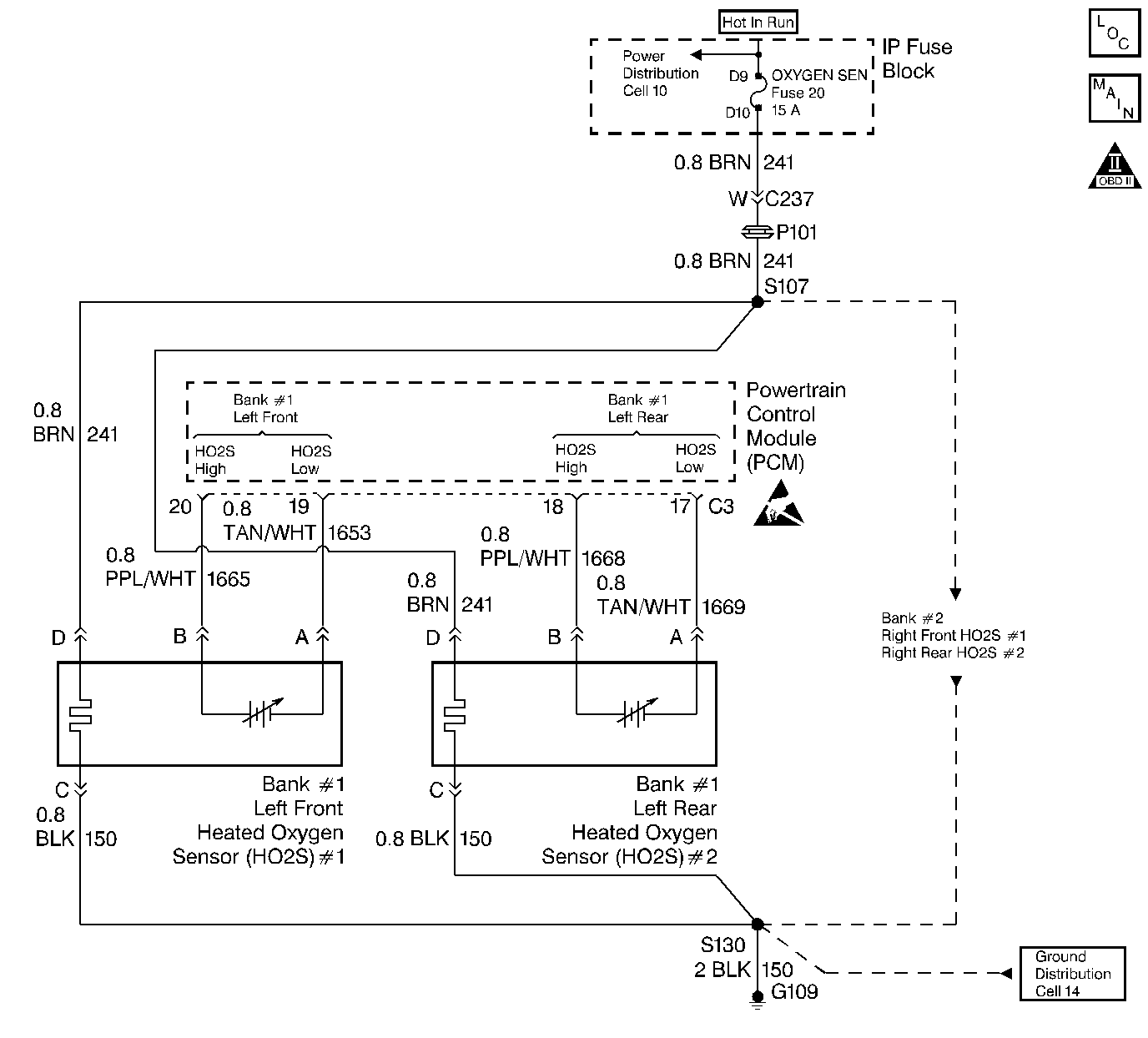
Circuit Description
The PCM supplies a voltage of about 450 mV between the HO2S high
and low signal circuits. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage over a range
from about 1000 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through about 10
mV when exhaust is lean.
The PCM monitors and stores the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) voltage
information. The PCM evaluates the HO2S voltage samples to determine the amount
of time the HO2S voltage was out of range. The PCM will compare the stored
HO2S voltage samples taken within each sample period and determine if majority
of the samples are out of the operating range.
The PCM monitors the HO2S voltage and detects if the voltage goes out
of the bias range. If the PCM does not detect the voltage went out of the
bias range, a DTC will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTCs P0100, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0125, P0200, P0372, P1371 not set. |
| • | Engine operating longer than 68 seconds. |
| • | Engine coolant temperature greater than 48°C (118°F). |
| • | HO2S signal voltage steady between 352 mV and 552 mV for 45 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) when
the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic
fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure
Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips
that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed (Current DTC) will clear when the ignition
is cycled and the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up
cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related
diagnostic. |
| • | PCM battery voltage is interrupted. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation.
This supply of oxygen is provided through the HO2S wires. All HO2S wires and
connections should be inspected for breaks or contamination. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis (8A Cell 5).
|
| • | For intermittents, refer to
Symptoms
. |

