Battery Electrical Drain Diagnosis
If the vehicle exhibits a low or dead battery after an overnight period, or
discharges over a period of 2 or 3 days, the electrical system should be checked
for an excessive electrical drain. This is referred to as Parasitic Load Drain.
If a battery needs recharging and no cause is evident, check the vehicle for
excessive parasitic load drain.
One or more on-board solid state control modules, such as the powertrain
control module (PCM), may at some time, exhibit a failure mode that causes a high
parasitic drain on the vehicle's battery. When the battery is disconnected to install
an ammeter, etc., the excessive current drain may not occur once the circuit
continuity is restored. Even though cycling the ignition key to the ON and then
to the OFF position may cause such a drain to reoccur, there may be drains that
will not reoccur unless the vehicle systems are reactivated in a road test. Since
the ignition switch must not be rotated to the ACCESSORY, ON or START position
with an ammeter installed between the battery terminal and the battery cable, a
current drain test tool must be used as described in the following procedures.
Before starting this procedure, ensure that the ignition switch is in the LOCK
position, all electrical accessories are turned OFF and the doors are closed.
Parasitic Load Diagnosis
Tools Required
| • | J 38758 Parasitic
Draw Test Switch |
Caution: Unless directed otherwise, the ignition and start switch must be in the OFF or LOCK position, and all electrical loads must be OFF before servicing
any electrical component. Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent an electrical spark should a tool or equipment come in contact with an exposed electrical terminal. Failure to follow these precautions may result in personal injury and/or damage to
the vehicle or its components.
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
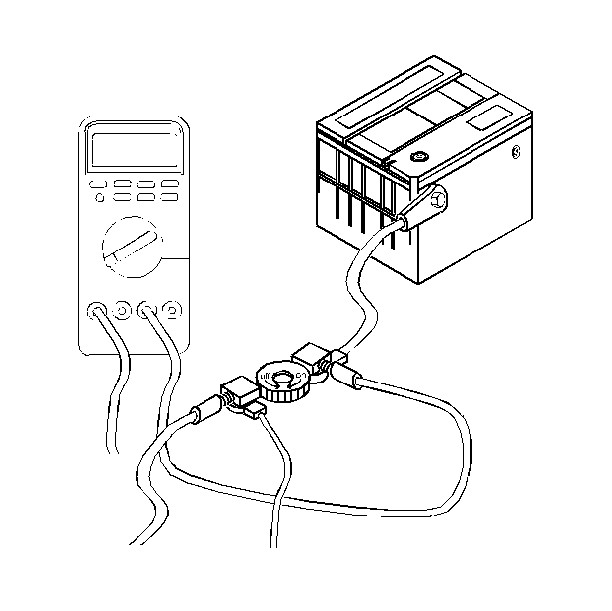
- Install the male end of the J 38758
to the negative battery terminal.
- Turn OFF the test switch.
- Install the negative battery cable to the female end of the test switch.
- Turn ON the test switch.
- Road test the vehicle while activating all accessories, including the
radio and the air conditioning.
- Turn OFF the ignition switch. Remove the key.
Important: From this point on, electrical continuity must be maintained in the ground
circuit of the battery.
- Components such as the PCM have a timer that draws several amps of current
while they cycle down. This can give a false parasitic drain reading. Wait 15 minutes
for these components to power down before continuing this test.
Important: If an ammeter other than the J 39200
is used, ensure that the vehicle does not have a high current drain that would
damage the ammeter when connected to the circuit.
- Connect a jumper wire with a 10 A fuse J 36169-A
to the terminals of the Test switch.
- Turn the test switch to the OFF position.
- Wait ten seconds.
If the fuse does not blow, the current is less than 10 A.
The ammeter can be used safely.
- Before the fused jumper wire is removed, turn the test switch to the
ON position.
- Install J 39200
.
Set the J 39200
to the 10 A
scale.
- Connect the ammeter to the test switch terminals.
- Turn OFF the test switch. This allows the current to flow through the
ammeter.
- Wait one minute, then check the current reading.
| • | When there is a current reading of 2 A or less, turn ON the test
switch, this maintains continuity in the electrical system. |
| • | Then, switch the meter down to the 2 A scale, for a more accurate
reading, when the test switch is reopened. |
- Take the reading in milliamps.
- Note the battery reserve capacity.
| • | Divide this number by 4. |
| • | Compare this to the ammeter reading. |
| • | The current drain should not exceed this number. |
| • | Example: if a battery has a reserve capacity of 100 minutes, the
current drain should not exceed 28 mA. |
- When the current draw is too high, remove the electrical system fuses
one at a time until the draw returns to a value less than or equal to specifications.
| • | Start with the fuses that are hot all the time. |
| • | To remove the fuse, you must first open the door, which may cause a high
enough current flow to damage the ammeter. |
| • | Protect the ammeter, without disturbing the electrical continuity, by
turning ON the test tool before opening the door. |
| • | Remove the courtesy lamp fuse. |
| • | Note the ammeter reading. |
| • | If the parasitic load is still excessive start removing the remaining
fuses one at a time. |
| • | Keep the courtesy lamp fuse out during diagnosis, so the door can remain
open. |
| • | Perform steps 11 through 13 each time a fuse is removed. |
- Removing the PCM fuse should cause a drop of less than 10 mA.
A drop greater than 10 mA indicates a possible short to ground.
- Check PCM output components. Use the PCM connector end views.
No drop in the milliampere reading indicates the PCM is not drawing current.
- Repeat the parasitic load drain test procedure after any repair has been
completed.
- When the cause of the excessive current draw has been located
and repaired, remove the ammeter and the parasitic draw test switch.
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners
must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring
replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant
are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or
corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified.
These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage
the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when
installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
- Connect the negative cable to the negative battery terminal.
Tighten
Tighten the battery cable attaching bolt to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
- Program the Transmitters. Refer to Transmitter Programming/Synchronization
in Keyless Entry.

