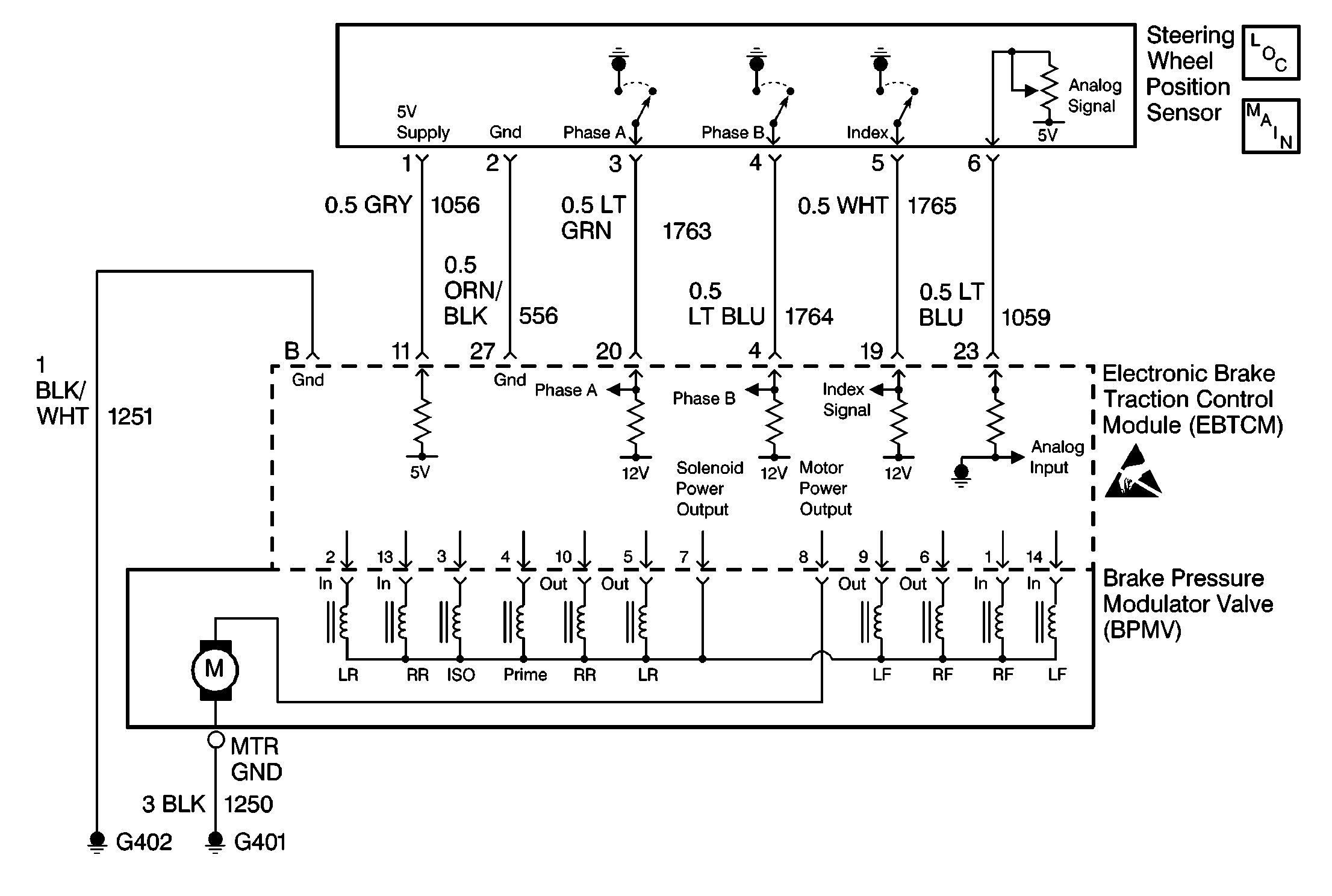
Circuit Description
The EBTCM uses four inputs from the Steering Wheel Position sensor:
| • | Phase A digital input |
| • | Phase B digital input |
| • | Index pulse |
| • | Analog input |
This information is used to calculate three things:
- The front wheels position when centered.
- The front wheels position when turning.
- The rate at which the steering wheel is turning.
The EBTCM runs a centering routine when the vehicle speed goes above 30 Km/h (18 mph). When the vehicle reaches 30 Km/h (18 mph), the EBTCM monitors the Steering Wheel Position Sensor inputs (Phase A, Phase B and Analog voltage) to see if the steering wheel is moving. If the steering wheel is not moving for a set period of time then the EBTCM assumes the vehicle is going in a straight line. At this point, the EBTCM looks at the analog voltage signal and reads the voltage. This voltage normally around 2.5V, is then considered the center position and the digital degrees also become zero at the same time. This centering routine is necessary to compensate for wear in the steering and suspension. Wear in the steering and suspension can result in a change in the relationship between the steering wheel and the front tires when driving in a straight line. By running the centering routine the EBTCM can compensate for these changes by changing the digital and analog center position.
The EBTCM uses the digital input (Phase A and Phase B) from the Steering Wheel Position Sensor to calculate the direction the driver of the vehicle is trying to steer during an ABS event. This information is also used to calculate the rate at which the steering wheel is turning to control the amount of effort required from the driver to turn the steering wheel using Magna Steer®.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTC C1281 will set when the digitally derived centered angle differs from the analog derived angle by 27° or more for a period of 5 seconds. |
| • | DTC C1281 will set if the index pulse is not seen between ± 37° or is seen between -185° and -37° or 37° and 185° of steering wheel travel. |
| • | DTC C1281 will set if phase A and or phase B are shorted. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Magna Steer® is disabled, ABS/TCS remains active. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Condition for DTC is no longer present and scan tool clear DTC function is used. |
| • | Fifty ignition cycles have passed with no DTC(s) detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the analog Steering Wheel Position Sensor input is missing then DTC C1288 will set. |
| • | If the Steering Wheel Position Sensor 5 volt supply or the Steering Wheel Position ground is missing DTC C1288 will set. |
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction can be caused by poor connections, broken insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Checks for the analog voltage to change, if the analog voltage does not change DTC C1281 will set.
-
Checks if the digital Phase A and Phase B are changing state from high to low.
-
checks to see if the analog and digital readings are ± 27° of each other.
-
Checks to see if the EBTCM is supplying the pull up voltage for Phase A.
-
Checks to see if the EBTCM is supplying the pull up voltage for Phase B.
-
Checks to see if the EBTCM is supplying the pull up voltage for the Index pulse.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
2 |
Are any of the following DTC(s) present, C1286 or C1288? | -- | Go to Applicable DTC table | |
3 |
Does the Analog Steer Sensor Voltage change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
4 | Using a scan tool in the Data List monitor the Digital HWPS Input as you rotate the steering wheel from left to right Does the Digital HWPS Input change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
5 |
Does the Analog Steer Sensor Voltage read within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 2.7 - 3.3V | ||
6 |
Does the voltage change as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
7 | Rotate the steering wheel in either direction while monitoring the Digital HWPS Index Pulse with a scan in Data List. Does the Digital HWPS Index Pulse go HIGH within ± 37° of steering center while rotating the steering wheel? | -- | ||
8 | Replace the Steering Wheel Position Sensor. Refer to Steering Wheel Position Sensor Replacement in Steering Wheel and Column. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
9 | Replace the EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
10 |
Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
11 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at terminal 4 of J 39700 as an assistant rotates the steering wheel. Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts as the steering wheel is rotated? | -- | ||
12 |
Does the voltage toggle between 0 and Battery volts one time as the steering wheel is rotated to the right? | -- | ||
13 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
14 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
15 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1V | ||
16 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
17 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
18 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1765. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
19 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
20 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
21 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1V | ||
22 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
23 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
24 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1763. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
25 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
26 | Repair short to ground in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
27 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Above 1V | ||
28 | Repair short to voltage in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
29 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
30 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1764. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
31 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts | ||
32 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts | ||
33 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery volts |
