No Communication with Electronic Brake Control Module/Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module Domestic
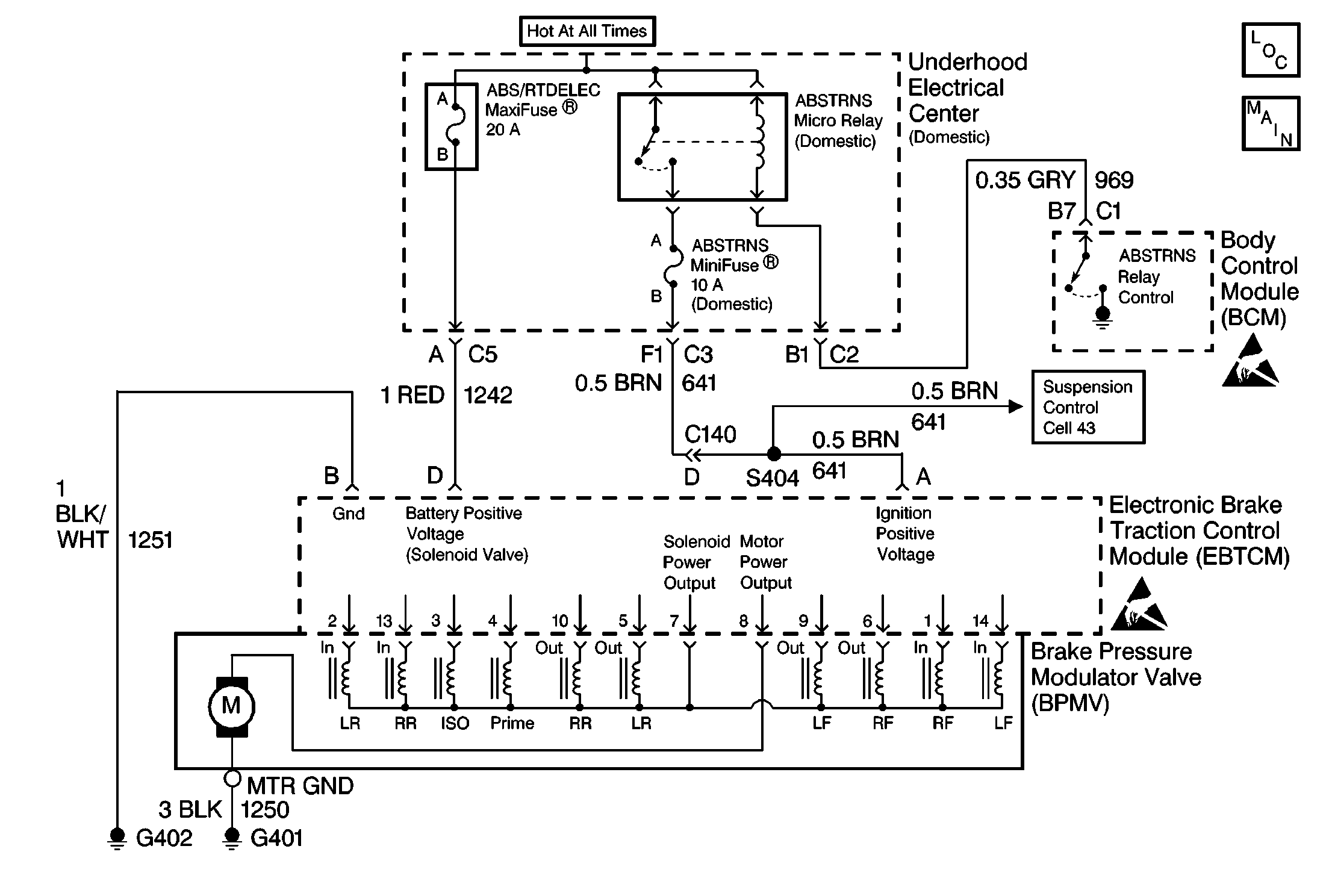
Circuit Description
The Class 2 serial data line allows all the modules on the line to transmit information to each other as needed. Each module is assigned an ID and all the information sent out on the line is assigned a priority by which it is received. When the ignition switch is turned to the ON position each module begins to send and receive information. Each module on the Class 2 serial data line knows what information it needs to send out and what information it should be receiving. What the modules do not know is which module is supposed to send them the information. This information is only learned after the module has received the information it needs along with the ID of the module that sent the information. This information is then remembered until the ignition switch is turned off.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction is most likely caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists refer to General Electrical Diagnosis . |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
Checks for proper operation of the relay.
-
Checks if CKT 641 is shorted to ground.
-
Checks if the EBTCM has an internal short to ground.
-
Checks if the ESC has an internal short to ground.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
DEFINITION: Scan tool can not communicate with the EBTCM. | ||||
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
2 | Can the scan tool communicate with the BCM? | -- | Go to Data Link Communications System Check in Wiring Systems | |
3 | Can the scan tool communicate with the PCM? | -- | Go to Data Link Communications System Check in Wiring Systems | |
4 | Inspect the 10A ABSTRNS fuse in the Underhood Electrical Center. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
5 | Inspect the 20A ABS/RTD fuse in the Underhood Electrical Center. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | |||
7 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | 75 - 105ohms | ||
8 | Replace the ABSTRNS MicroRelay. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
9 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
10 | Repair CKT 969 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
11 |
Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
12 | Repair CKT 641 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
13 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at the 20A ABS/RTD fuse by probing between the fuse test terminals and a good ground. Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | Go to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems | |
14 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at terminal D of J 39700 . Is the voltage within the range specified in the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
15 | Repair CKT 1242 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
16 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | |||
18 | Repair CKT 641 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
19 | Replace the EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
20 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
21 |
Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
22 | Repair CKT 1242 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
23 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the resistance between J 39700 terminal B and a good ground. Is the resistance within the range specified in the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
24 | Repair CKT 1251 or G402 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | |||
26 | Is the vehicle equipped with RTD? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | ||
28 | Suspect the ESC. Refer to RTD Diagnostic System Check in Suspension. Is the ESC diagnosis complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
29 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | 0 - 2ohms | ||
30 | Repair CKT 1122 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
No Communication with Electronic Brake Control Module/Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module Export
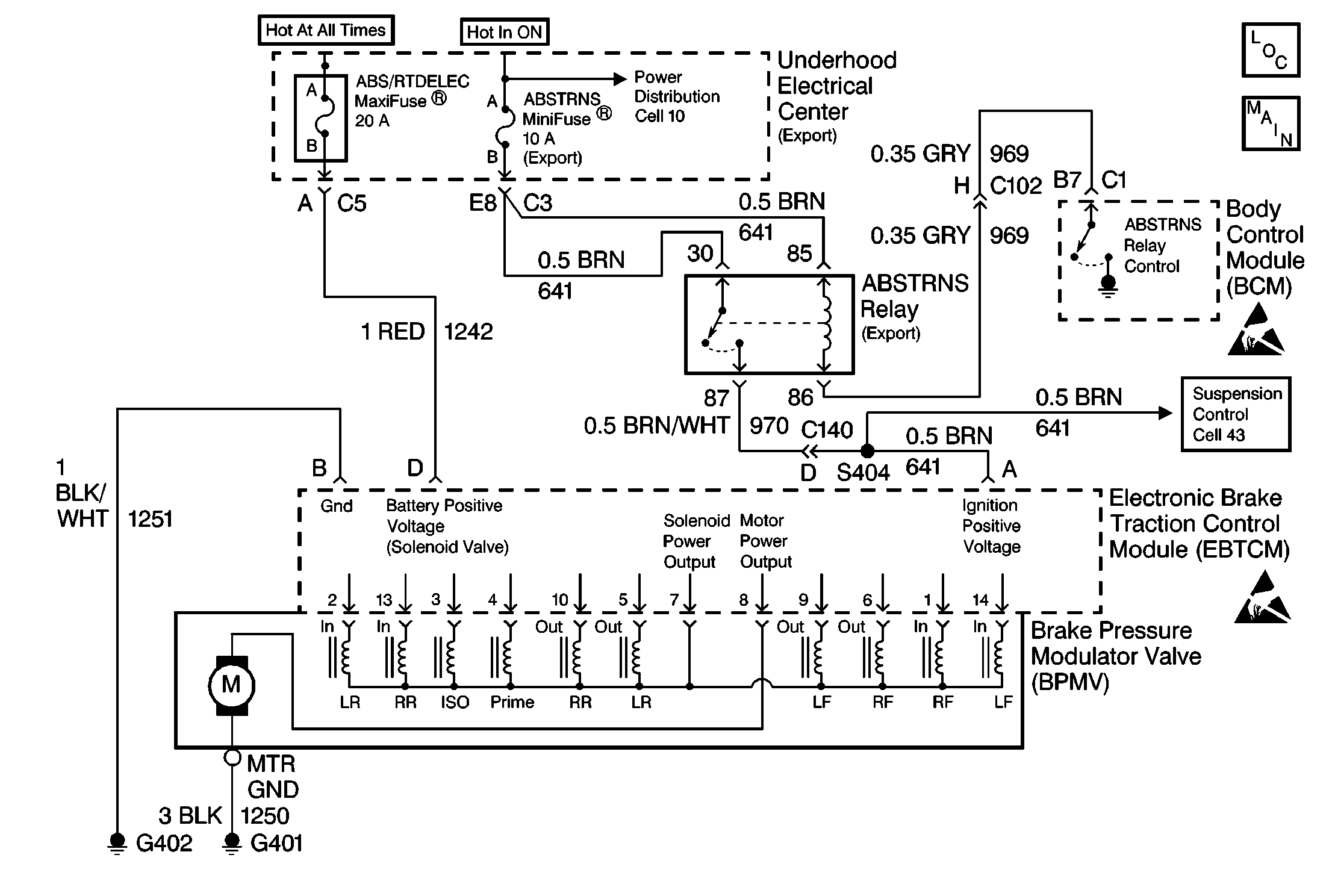
Circuit Description
The Class 2 serial data line allows all the modules on the line to transmit information to each other as needed. Each module is assigned an ID and all the information sent out on the line is assigned a priority by which it is received. When the ignition switch is turned to the ON position each module begins to send and receive information. Each module on the Class 2 serial data line knows what information it needs to send out and what information it should be receiving. What the modules do not know is which module is supposed to send them the information. This information is only learned after the module has received the information it needs along with the ID of the module that sent the information. This information is then remembered until the ignition switch is turned off.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | It is very important that a thorough inspection of the wiring and connectors be performed. Failure to carefully and fully inspect wiring and connectors may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction. |
| • | An intermittent malfunction is most likely caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | If an intermittent malfunction exists refer to General Electrical Diagnosis . |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
Checks for proper operation of the ABSTRNS relay.
-
Checks if the EBTCM has an internal short to ground.
-
Checks if the ESC has an internal short to ground.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
2 | Can the scan tool communicate with the BCM? | -- | Go to Data Link Communications System Check in Wiring Systems | |
3 | Can the scan tool communicate with the PCM? | -- | Go to Data Link Communications System Check in Wiring Systems | |
4 | Inspect the 10A ABSTRNS fuse in the Underhood Electrical Center. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
5 | Inspect the 20A ABS/RTD fuse in the Underhood Electrical Center. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
6 |
Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | Go to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems | |
7 |
Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
8 | Repair CKT 641 between the Underhood Electrical Center connector C3 terminal E8 and the ABSTRNS relay connector terminal 30 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
9 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at terminal 85 of the ABSTRNS relay connector. Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
10 | Repair CKT 641 between the Underhood Electrical Center connector C3 terminal E8 and the ABSTRNS relay connector terminal 85 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
11 |
Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
12 | Repair CKT(s) 970 or 641 between the ABSTRNS relay connector and the EBTCM for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
13 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
14 | Repair CKT 969 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | |||
16 | Replace the ABSTRNS relay. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
17 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at terminal D of the J 39700 . Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | ||
18 | Using J 39200 DMM, measure the voltage at the 20A ABS/RTD fuse by probing between the fuse test terminals and ground. Is the voltage within the range specified within the value(s) column? | Battery Volts | Go to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems | |
19 | Repair CKT 1242 for an open. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
20 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | 0 - 5ohms | ||
21 | Replace the EBTCM. Refer to Electronic Brake and Traction Control Module . Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
22 | Repair open or high resistance in CKT 1251 or G402. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
23 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
24 | Repair CKT(s) 641 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
25 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
26 | Repair CKT 970 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
27 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
28 | Repair CKT 641 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | |||
30 | Is the vehicle equipped with RTD? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | ||
32 | Suspect the ESC. Refer to RTD Diagnostic System Check in Suspension. Is the ESC diagnosis complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
33 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |
34 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | OL (infinite) | ||
35 | Repair CKT 641 for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
36 |
Is the resistance within the range specified within the value(s) column? | 0 - 2ohms | ||
37 | Repair CKT 1122 for an open or high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
