For 1990-2009 cars only
A crankcase ventilation system is used to consume crankcase vapors created during the combustion process instead of venting them to the atmosphere.
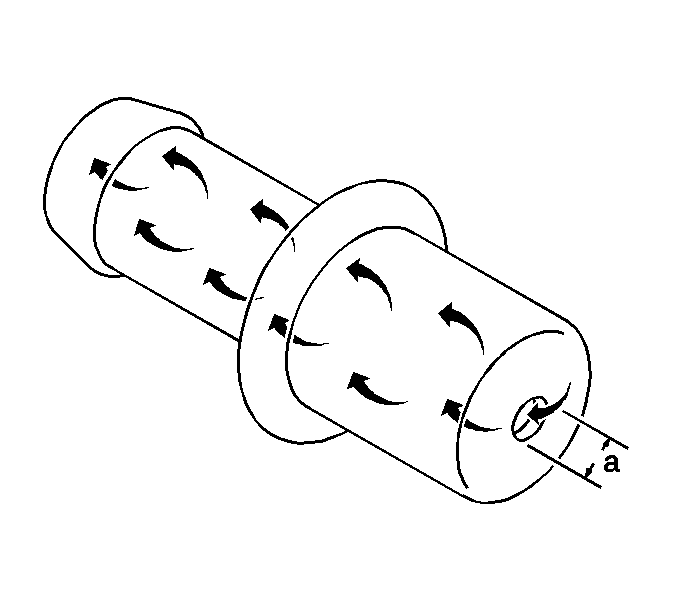
Fresh air is supplied through a filter to the crankcase, the crankcase mixes the fresh air with the blow-by gases and then passed through a positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) orificed tube into the intake manifold.
The PCV orificed tube restricts the flow rate of the blow-by gases using a 3 mm (0.118 in) (a) orifice located at the end of the tube. If abnormal operating conditions arise, the system is designed to allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to back flow through the crankcase vent tube into the throttle body in order to be consumed by normal combustion.
