Special Tools
| • | J 8089 Carbon Removing Brush |
| • | J 9666 Valve Spring Tester |
For equivalent regional tools, refer to
Special Tools.
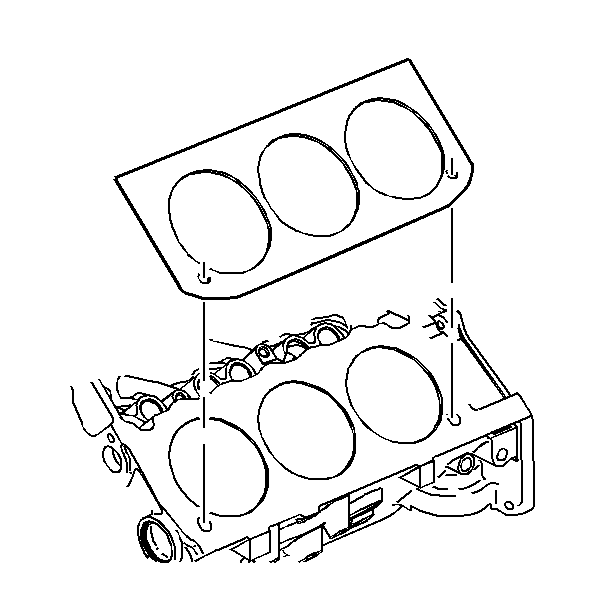
- Inspect the cylinder head gasket and the mating surfaces. Inspect for leaks, corrosion, and blowby.
- If the gasket failed, determine the cause. The following conditions may cause gasket failure:
| • | A loose or warped cylinder head |
| • | Missing, off location, or not fully seated dowel pins |
| • | Low torque on the cylinder head bolts |
| • | Cylinder head bolts with the incorrect length |
| • | A warped engine block surface |
| • | Excessive intake manifold torque |
| • | Cracked engine block threaded holes |
Warning: Refer to Safety Glasses Warning in the Preface section.
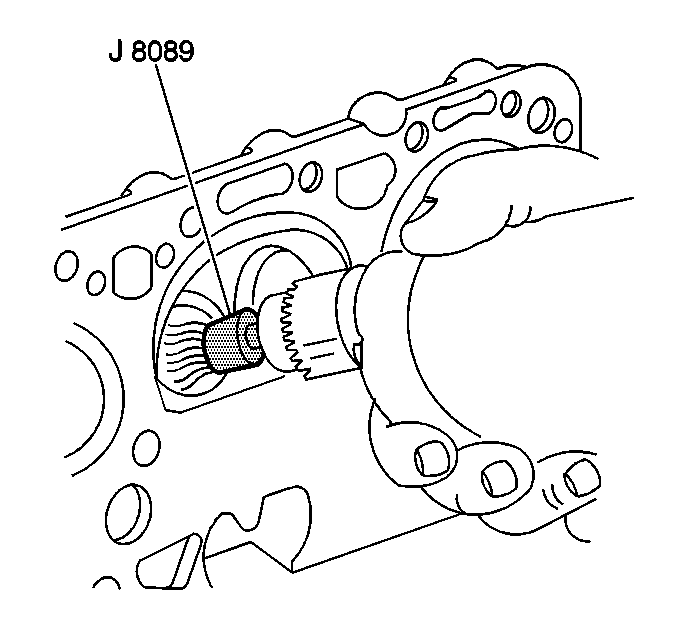
Note: Do not scuff the chamber.
- Use the
J 8089 brush
in order to remove the carbon from the combustion chambers.
- Clean the following components:
| | Do not use a motorized brush on any gasket sealing surface. |
| • | Valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel |
| | Remove all dirt, debris, or threadlocking material from the bolt holes. |
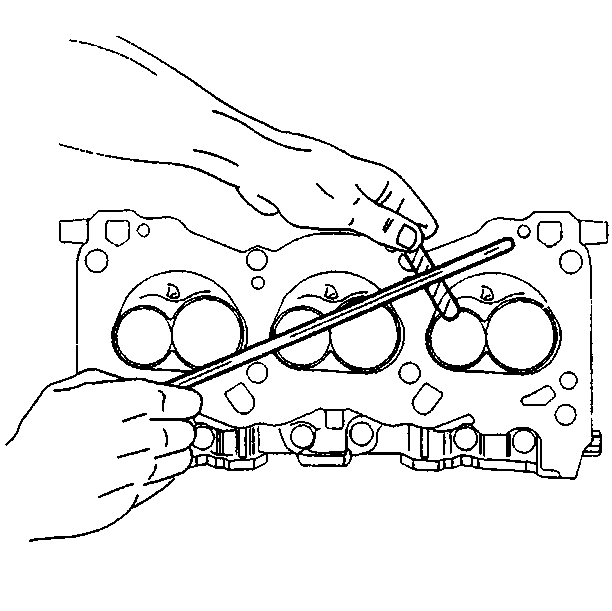
- Inspect the cylinder head mating surfaces for flatness. Recondition the cylinder head mating surface, if necessary, by milling. Replace
the cylinder head if you must remove more than 0.25 mm (0.010 in).
- Inspect the cylinder head for cracks.
- Inspect the cylinder head deck for corrosion. Do not attempt to weld the cylinder head. If the cylinder head is damaged, replace the cylinder head.
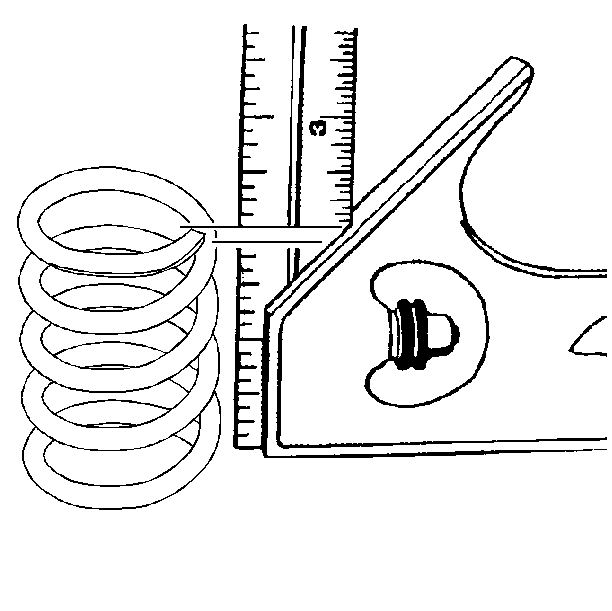
- Inspect the valve springs for squareness.
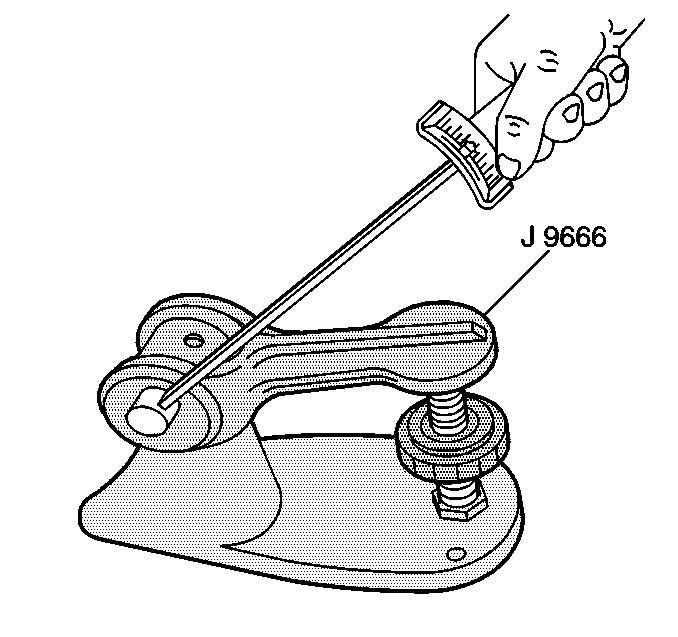
- Use the
J 9666 tester
in order to measure the valve spring tension.
Replace the spring if the spring tension is not within specification.





