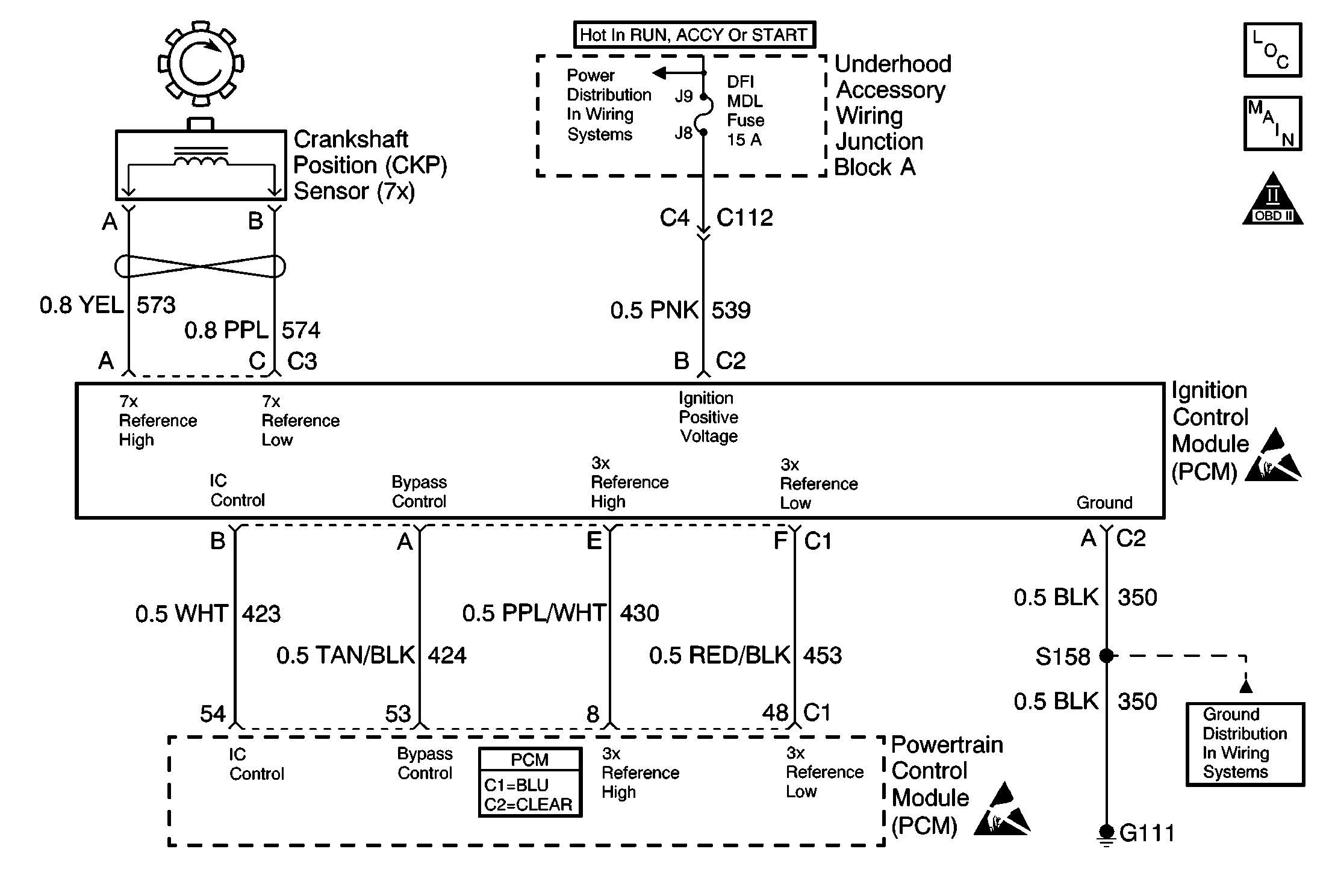
Circuit Description
During cranking, the ignition control module (ICM) monitors the 7X crankcase position (CKP) sensor input for recognition of the sync signal. The sync signal is used only by the ICM for synchronization at start-up to determine the correct cylinder pair to spark. Once the engine speed reaches approximately 600 RPM the powertrain control module (PCM) sends 5.0 volts to the bypass control circuit at the ICM causing the IC control circuit to become ungrounded and allowing the 24X signal to be used for better low engine speed performance. At higher engine speeds (1650+) the PCM uses the 3X reference pulses to control the ignition timing because a higher resolution signal is not needed.
Conventional ignition coils have one end of the secondary winding connected to the engine ground. In this ignition system, neither end of the secondary winding is grounded. Instead, each end of a coil's secondary winding is attached to a spark plug. Each cylinder is paired with the cylinder that is opposite (1-4, 2-5, 3-6). These 2 plugs are on companion cylinders, i.e., on top dead center at the same time. When the coil discharges, both plugs fire at the same time to complete the series circuit. The cylinder on compression is said to be the event cylinder and the one on exhaust is the waste cylinder. The cylinder on the exhaust stroke requires very little of the available energy to fire the spark plug. The remaining energy will be used as required by the cylinder on the compression stroke. The same process is repeated when the cylinders reverse roles. This method of ignition is called a waste spark ignition system.
This table assumes there are no ignition system, fuel injector, cam sensor, or crank sensor DTCs present. The electronic ignition system check tests for faulty ignition coils, spark plugs, plug wires, the 7X crank sensor, and ICM. This table requires the J 26792 spark tester.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions:
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The J 26792 spark tester presents a more difficult load on the secondary ignition than a normal spark plug. If a miss, stumble, or hesitation is being caused by a spark plug not firing, the spark tester should also not fire.
-
Use a 5 percent saltwater solution in a spray bottle to induce voltage arcing to ground through any faulty insulation of the spark plug wires.
-
If the no-spark condition follows the suspected coil, that coil is faulty. Otherwise, the ignition module is the cause of the no-spark condition. This test could also be performed by substituting a known good coil for the one causing the no-spark condition.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||
Does the scan tool indicate a 3X reference signal present? | -- | |||||||
Did you observe any non-sparking cylinders? | -- | |||||||
Inspect and test the affected cylinder spark plug wires, the ignition coils, and the spark plugs for a short to ground or arcing to ground. If carbon tracking or corrosion is present, replace both components affected. Refer to the appropriate procedures:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||
5 | Test the affected spark plug wires for proper resistance. Replace any spark plug wires not meeting the specified resistance value. Refer to Spark Plug Wire Harness Replacement in Engine Electrical. Did you find and correct the condition? | 1,968 ohms/M (600 ohms/ft) | ||||||
Switch the affected cylinder coil with a known good coil. If the fault follows the affected coil, replace the faulty coil. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||
7 | Inspect the spark plug wires for proper routing and for the correct firing order. If any spark plug wires are found to be misrouted, reroute the wires as necessary. Refer to Spark Plug Wire Harness Replacement in Engine Electrical. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
8 | With a DMM, test the spark plugs for an internal short to ground. Replace any grounded spark plugs. Refer to Spark Plug Replacement in Engine Electrical. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
9 |
If any spark plugs are found to be damaged, replace the affected spark plugs. Refer to Spark Plug Replacement in Engine Electrical. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||
10 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
11 | Connect a test lamp between the ICM ignition feed circuit and the ICM ground circuit. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||
12 |
Does the test lamp illuminate when probing either circuit? | -- | ||||||
13 |
Does the test lamp illuminate when probing either circuit? | -- | ||||||
14 |
Does the DMM indicate an AC duty cycle present? | -- | ||||||
15 | Test the 7X crankshaft position sensor circuits for the following conditions:
Repair any damaged wiring. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||
16 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
17 | Repair the short to ground in the 7X reference circuit that illuminated the test lamp. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
18 | Repair the short to voltage in the 7X reference circuit that illuminated the test lamp. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
19 | Repair the open in the ICM ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||
20 | Replace the ignition control module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||
21 | Replace the 7X crankshaft position sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- |
