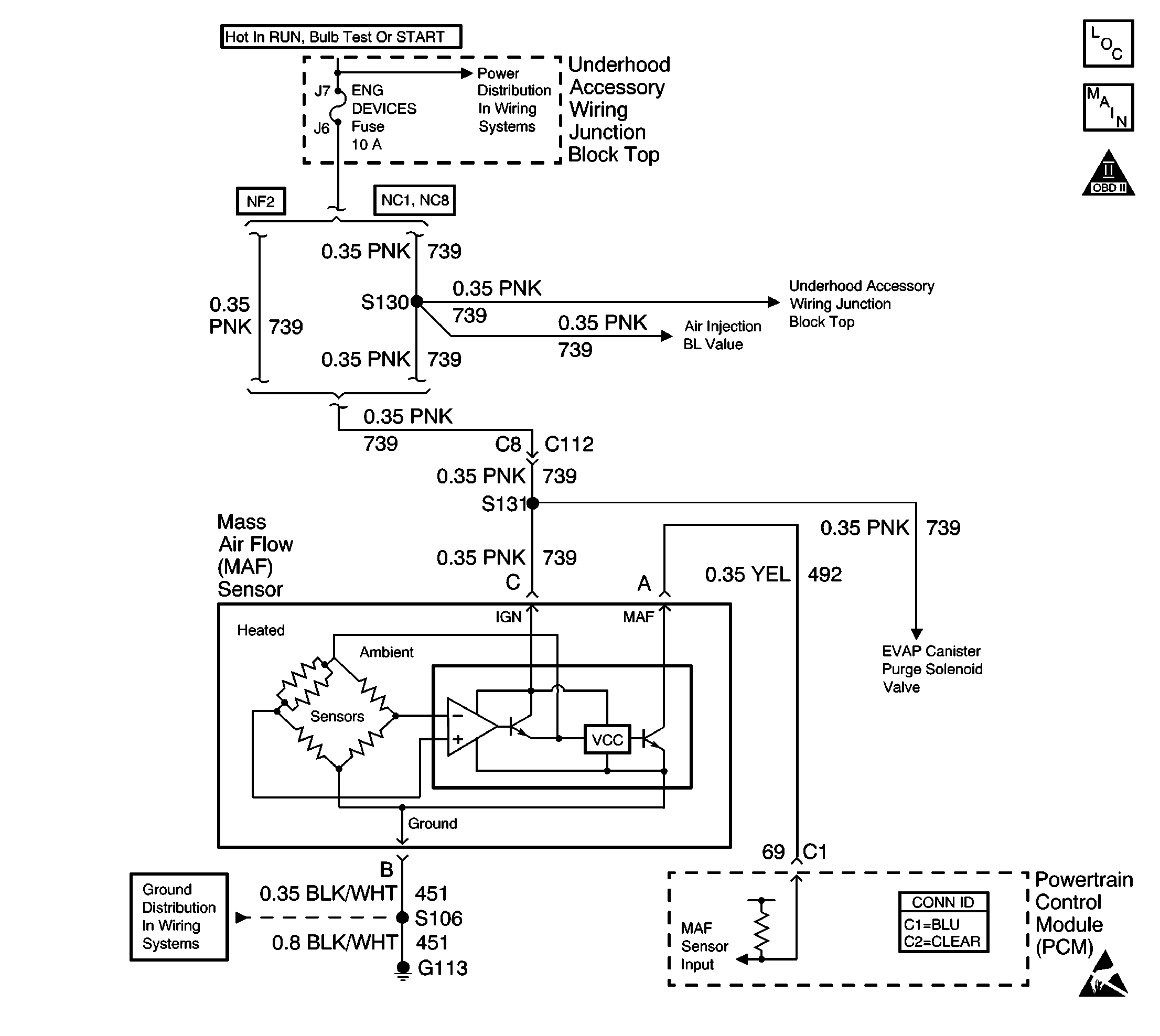
Circuit Description
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it into the engine during a given time. The PCM uses the mass air flow information to monitor engine operating conditions for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity of air entering the engine indicates an acceleration or high load situation, while a small quantity of air indicates deceleration or idle. The MAF sensor produces a frequency signal which can be monitored using a scan tool. The frequency will vary within a range of around 2,000 Hertz at idle to about 10,000 Hertz at maximum engine load. If the signal frequency from the MAF sensor is lower than the possible range of a normally operating MAF sensor DTC P0102 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The TP angle is less than 50 percent. |
| • | The system voltage is between 9 and 18 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | MAF signal frequency is less than 1,200 Hertz. |
| • | The above conditions present for more than 0.5 seconds + 400 3X reference periods (133 crankshaft revolutions). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
A low minimum air rate can cause DTC P0102 to set during deceleration. Check the minimum air rate as follows:
- Run the engine until fully warm (above 85°C / 185°F).
- Disconnect the IAC.
- Install a J 37027-A IAC system monitor.
- With the engine idling, command the IAC valve to the fully extended position (0 counts).
- With the IAC fully extended, observe the mass air flow reading on the scan tool.
- Check for conditions that can cause a low minimum air rate, including throttle bore and throttle plate coking if the mass air flow reading is less than 2.27 g/sec.
- If the minimum air rate is less than specifications, clean or replace the throttle body as necessary. Refer to Throttle Body Assembly Replacement .
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at the PCM. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Misrouted harness. Inspect the MAF sensor harness to ensure that it is not routed too close to high voltage wires such as spark plug leads. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the MAF sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Plugged intake air duct or filter element. A wide-open throttle acceleration from a stop should cause the mass air flow displayed on a scan tool to increase from about 4-7 gm/s at idle to 100 gm/s or greater at the time of the 1-2 shift. If not, check for a restriction. |
If the DTC cannot be duplicated and is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Fail Records can be useful in determining when the DTC was last set. Also refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This step verifies that the problem is present at idle.
-
A voltage reading of less than 4 or over 6 volts at the MAF sensor signal circuit indicates a malfunction in the wiring or a poor connection.
-
Verifies that ignition feed voltage and a good ground are available at the MAF sensor.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate MAF Frequency less than the specified value? | 1200 Hz (1.2 kHz) | |||||||||||||
3 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P0102 failed this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||
4 | Inspect for the following conditions:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? | 5 V | |||||||||||||
Connect a DMM between the ignition feed circuit of the MAF sensor and a known good ground. Does the voltage measure equal to the specified value? | Battery Positive Voltage | |||||||||||||
7 | Test the ground circuit for the MAF sensor for an open or high resistance and repair if necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
8 | Test the signal circuit of the MAF sensor for an open, short to ground, or a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
9 | Repair the open or high resistance in the ignition feed circuit of the MAF sensor. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
10 | Inspect for a poor connection at the MAF sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
11 | Replace the MAF sensor. Refer to Mass Airflow Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
12 | Inspect for poor connections at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||||
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||
14 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
