- Boil the cylinder block in caustic solution.
- Flush the cylinder block with clean water or steam.
- Clean the following areas:
| | Remove excessive cylinder ring ridge, as required. |
| | Remove all sludge or restrictions. |
| • | Scale deposits from the coolant passages |
| • | All dirt or debris from threaded bolt holes |
Warning: Refer to Safety Glasses Warning in the Preface section.
- Dry the block with compressed air.
- Lubricate the cylinder bores with clean engine oil to prevent rusting.
- Inspect the engine block for the following conditions:
| • | Gasket surfaces for deep gouges or other damage |
| • | Crankshaft bearing bores for wear |
| - | The surfaces where the crankshaft bearings contact the crankshaft bearing bore must be smooth. |
| - | All crankshaft bearing bores must be round and uniform in inside diameter (ID) at all the bearing supports. |
| • | Camshaft bearing bores for wear or damage |
| • | Valve lifter bores for scuffing or wear |
| • | Engine block for cracks or other damage |
| • | Cylinder walls for scoring or gouges |
| • | Coolant jackets for cracks |
| • | Crankshaft bearing webs for cracks |
| • | Engine mount bosses for damage |
| • | The oil passages for restrictions |
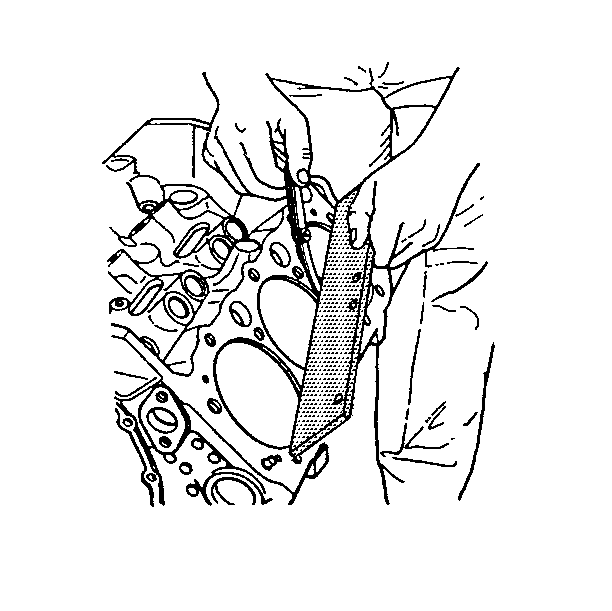
- Using a straight edge and a feeler gage, inspect the engine block cylinder head deck for flatness.
The surface must be
flat within 0.100 mm (0.004 in).
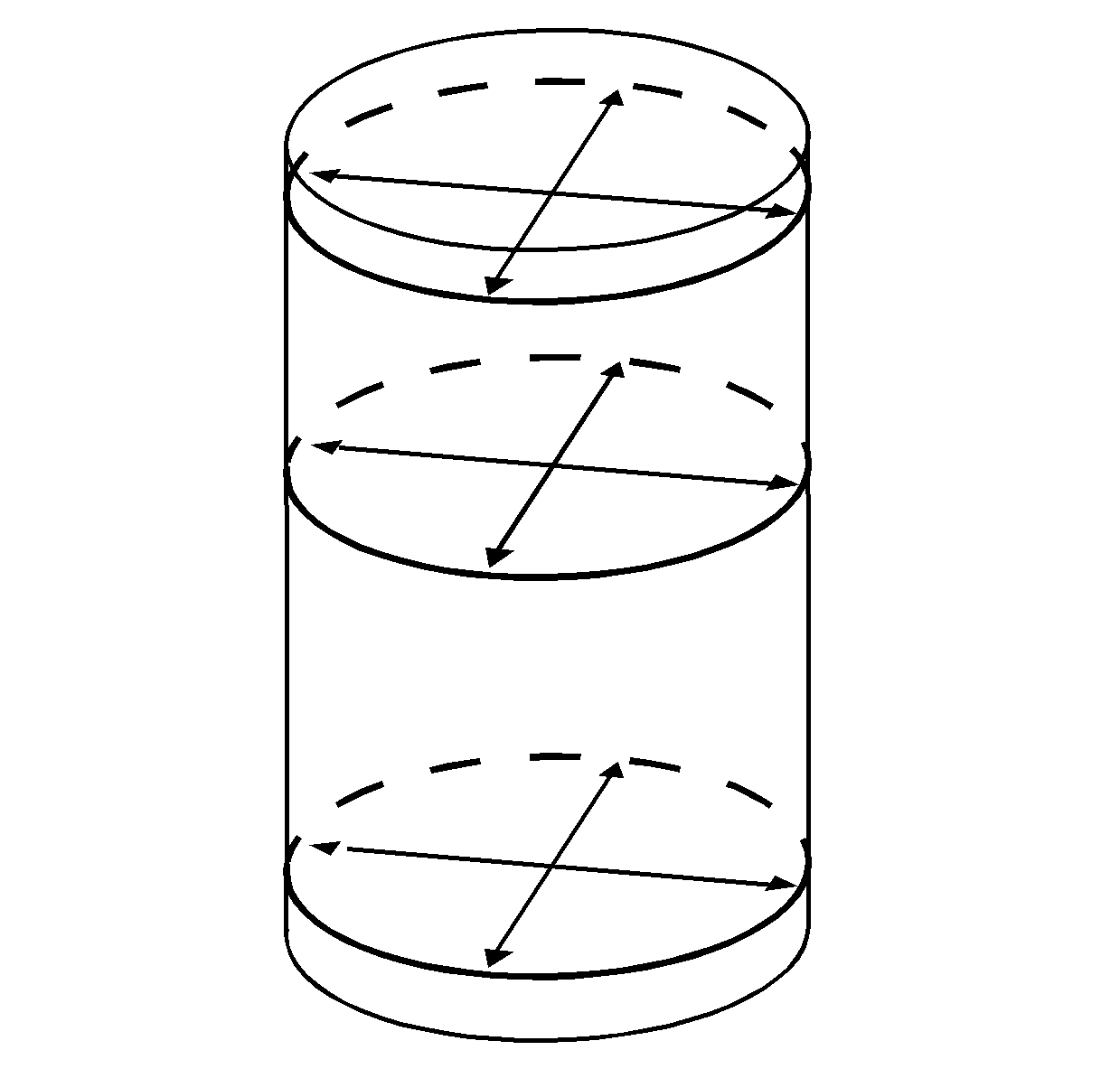
- Use a bore gage and measure the cylinder bore for taper, out-of-round and oversize. Slide the bore gage up and down throughout the
length of the cylinder bore. Check the bore both parallel and perpendicular to the centerline of the crankshaft at the top, center and bottom of the bore. A cylinder bore that measures 107.940-107.990 mm (4.249-4.251 in) may be serviced
with a standard size piston/connecting rod assembly. A cylinder bore that exceeds the maximum diameter must be serviced with an oversized piston/connecting rod assembly.



